Geo Data Wizard: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* [[Area|Areas]] - Importing areas to create a 2D [[Overlay]] | * [[Area|Areas]] - Importing areas to create a 2D [[Overlay]] | ||
* [[Measures]] - Importing a group of 3D-objects as a [[Measures|measure]] to perform as an action | * [[Measures]] - Importing a group of 3D-objects as a [[Measures|measure]] to perform as an action | ||
* [[Measuring_tool#Import.2C_export_and_saving_measurements|Point Measurements]] - Importing measurements to visualize in the [[ | * [[Measuring_tool#Import.2C_export_and_saving_measurements|Point Measurements]] - Importing measurements to visualize in the [[Measuring tool]] | ||
Each of these wizards contain comparable steps which are described below. | Each of these wizards contain comparable steps which are described below. | ||
The wizard can be found by following these steps: | The wizard can be found by following these steps: | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 14 January 2021
The Geo Data Wizard
The Geo Data Wizard or in short Data Wizard is a series of steps to guide you through the process of importing Geo data in the Tygron Platform. It is designed to minimalise the use of a GIS for preparing the data.
Import type
There are several different Data Wizards which each guide you through different processes for importing Geo data in the Tygron Platform.
The different wizards are for importing data as:
- Buildings - Importing Constructions (3D-objects) into the model and for updating attributes of Constructions based on the attributes in the data
- Terrain - Importing shapes to define the terrain
- Neighborhoods - Importing shapes to define the neighborhoods
- Zoning - Importing Zones in the Zoning plan (Bestemmingsplan)
- Areas - Importing areas to create a 2D Overlay
- Measures - Importing a group of 3D-objects as a measure to perform as an action
- Point Measurements - Importing measurements to visualize in the Measuring tool
Each of these wizards contain comparable steps which are described below.
The wizard can be found by following these steps:
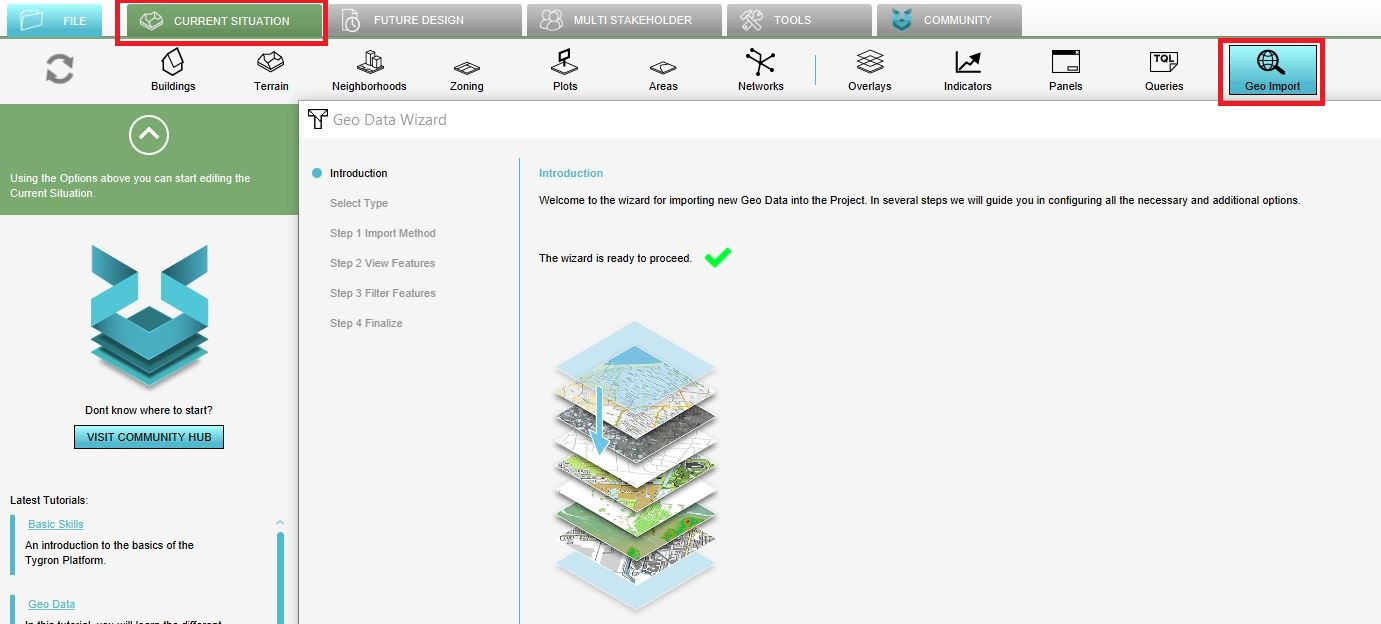
File:QA verschil terrains buildings measures wiki.jpg
(In Dutch)
Steps in the Geo Data Wizard
In the data wizards there are several steps to guide you in transforming your dataset in order to only import the relevant features in the data into the Tygron Platform.
Import method
There are four methods for importing Geo Data in the data wizard. These methods can be divided into two: uploading data from a file to the Tygron Platform and the other is downloading data through an URL to the Tygron Platform. The method to choose is based on how you have your data available:
- Through a GeoJSON file: If you have a file with 2D data, choose the first option. Make sure you create the GeoJSON file first, if your data is in another format.
- Through a I3S Scene Layer Package file (SLPK): If you have a 3D model and want to import this as a 3D model in the Tygron Platform, choose the second option. Make sure you create the SLPK file first, if your data is in another file format.
- Through a Web Feature Service (WFS): If you have an URL on where dats is published according to the WFS standard, choose the third option: WFS.
- Through a Catalogue Service for the Web (CSW): If you do not have data available but want to browse through an online catalogue in search for datasets or you have a Catalogue service URL, choose the fourth option: CSW.
View
In step 2, the data that is currently in your project in the Tygron Platform is visible. The amount of points, lines or polygons in the dataset are visible. Since only polygons are allowed in the Tygron Platform, the points and lines need to be buffered. By buffering these features, the points and lines become polygons. The buffer size is adjustable. Based on the data, choose a realistic buffer size. If your dataset contains of lines which represent roads, choose a buffer size that is realistic for the width of these roads. if your dataset consists of only polygons, the buffer size is not used.
Filter
In the next step you can filter the features. For example, if you have a dataset containing all sorts of roads, you can filter only the highways in this dataset. The filtering is based on Attribute name ( attribute textual value) or on Attribute value(a numerical condition). For example, if the roads have an attribute max. speed in km/h. You can filter the roads that have a max. speed of 80 or more km/h to get only the highways.
Add or update
In this step you are asked whether you want to add new data or update the data already present in your project. If you want to import the roads dataset as functions while there are already roads present in the project, updating would be the way to go. For data from a SLPK file, choose if you want to Update or Replace the shapes already existing. If you choose Replace you get some additional steps which must be setup. You will have new options for Naming, Assigning Functions and assigning stakeholders to the newly imported models. Updating means that you are adding new models to existing Functions. Replace means that you delete the existing function(s) and completely replace the previous function with a new one including the imported model.
Select attributes
As mentioned in the requirements for importing geo data in the Tygron Platform, only numerical attributes can be imported. In this screen all the attributes in the dataset are listed. The attributes that are numerical, are already checked. In the TQL Name column, you are given the option to rename your attribute.
Name the features
If you choose to add new features, the Naming step will be visible. This step is necessary to keep track of the data you imported in the Tygron Platform. With a clever chosen name, it is easy to distinguish features from each other. There are three options for naming your features:
- By their file name
- Based on an attribute
- A word with a number
Assign functions
If you choose the Geo Data wizard for:
you will be asked to choose a function for the features in your dataset. You can choose one function or choose multiple, based on an attribute name or an attribute value. The latter option is necessary when you have multiple different functions in your file, such as trees and roads.
Assign stakeholders
Choose the owner of the features you want to import. Also, multiple owners can be chosen, based on a mapping of attribute names or attribute values.
Error messages in the Geo Data Wizard
Errors when importing data most of the time have to do with no CRS (Coordinate Reference System) or the wrong CRS definition.
- No CRS defined
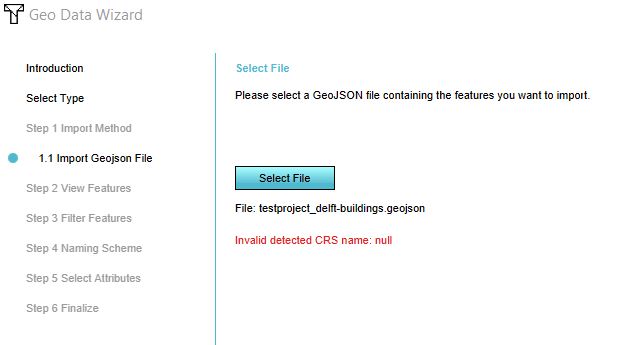
"Invalid detected CRS name: null"
Error: This error message means that the dataset you are trying to import does not have a CRS (Coordinate Reference System) and therefore the Tygron Platform can't place the data on the right location. This error mostly occurs when having a GeoJSON file without a CRS property defined.
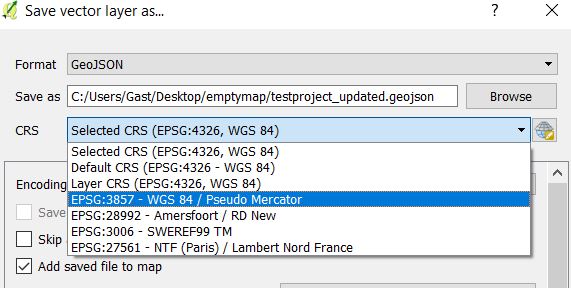
Solution: Open the GeoJSON file in a GIS and save it with the correct CRS, so the property is added to the GeoJSON file. See below for the steps in QGIS.
-
Error message in the Geo data wizard
-
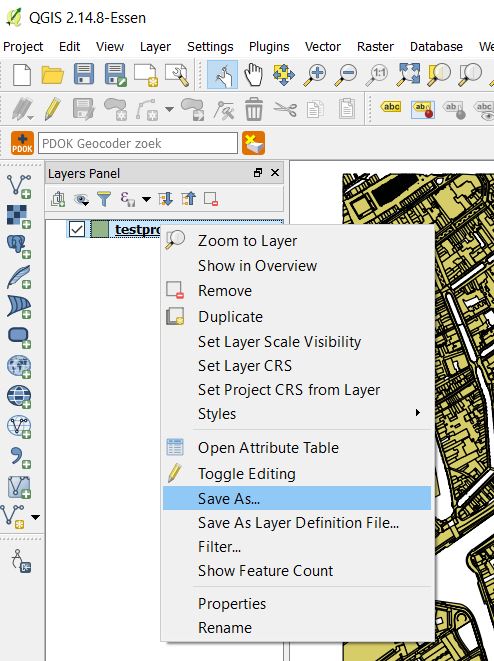
Open the file in QGIS and right click on the layer to choose Save as.
-
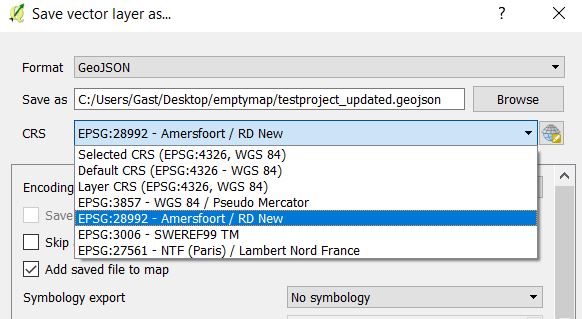
In the Save as menu, choose the right CRS the data is in. In the Netherlands, this is probably EPSG:28992 - Amersfooort/RD New
- The imported data does not have a location anywhere in your project
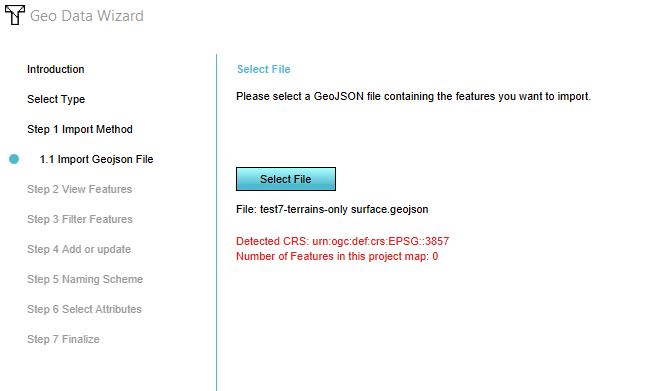
"Detected CRS: urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG:3857 Number of Features in this project map: 0" (or something similar)
Error: Geo data always has a location in the real world. This error message means that the dataset you are trying to import does not have a location in your project. For example if you have a project of an area in Amsterdam and you are trying to import data of neighborhoods in the Hague, you will get this error message. If you are sure that the data you are trying to import is in the same location (for example data of neighborhoods in Amsterdam into a Tygron Platform project in one of these neighborhoods in Amsterdam), the error message could also mean that the defined CRS is not correct for the data.
Solution: Import data that has a location in your project or if you are sure that the data you are trying to import is in the same location, open the GeoJSON file in a GIS and save it with the correct CRS. See below for the steps in QGIS.
-
Error message in the Geo data wizard
-
Open the file in QGIS and right click on the layer to choose Save as.
-
In the Save as menu, choose the right CRS the data is in. In the Netherlands, this is probably EPSG:28992 - Amersfooort/RD New
- Longitude and Latitude error
"Invalid:um:ogc:def:crs:OGC:1.3:CRS84 Coordinates: Latitude 393 44.4'N is too close to a pole" (or something similar)
Error: This can happen when importing a dataset in the WGS84 Coordinate Reference System (EPSG:4326) and means that the data can not be correctly imported by the Tygron Platform.
Solution: Open the GeoJSON file in a GIS and transform the data to a different CRS. See below for the steps in QGIS.
-
Error message in the Geo data wizard
-
Open the file in QGIS and right click on the layer to choose Save as.
-
In the Save as menu, choose a different CRS to transform the data to, for example EPSG:3857 WGS84/Pseudo Mercator