Terrain root depth m (Water Overlay)
| Icon | Attribute | Unit | Layer | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
ROOT_DEPTH_M | m | Surface | The depth of the roots of the terrain type. This depth is used to determine whether evaporation will occur from the groundwater. |
Terrains can be configured with plant-related attributes, similar to Buildings configured as crops and foliage, allowing it to draw water from the ground and evaporate it.
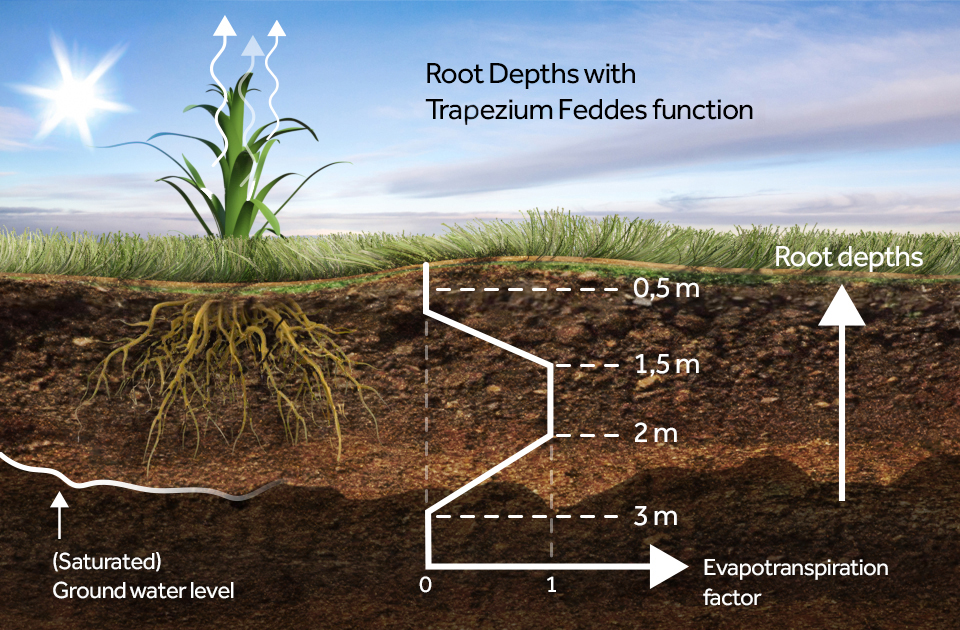
Feddes Trapezium
Plants can experience oxygen stress when the groundwater level is too high. The plant roots become saturated so that the plant can no longer transpire. To simulate the oxygen stress, the ROOT_DEPTH_M can also be configured with four values instead of one, which will be interpreted using Feddes transpiration model. In the model, when the groundwater level rises, the transpiration increases. However, at a certain point, the groundwater is too high and the transpiration decreases. Water on the surface can then still evaporate, but the plant cannot transpire anymore.
The sequence for the four values should be defined in order of largest to smallest depth values and are interpreted as a 0-1-1-0 transpiration factor trapezium.
Notes
- For plants to evaporate water, both the ROOT_DEPTH_M and the WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR must be appropriately configured.
- Trees typically have deeper root than crops.
- When a Building is present in any given location, the values for evaporation in the ground will overrule any values set by terrain in the same location. To model ground evaporation without a Building, set the attributes of the Building on the applicable terrain type instead.
- When there is no Building present on the surface, and the terrain has a ROOT_DEPTH_M of 0, the amount of evaporation which takes place in that location is 0.