|
|
| (57 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| {{being_updated}}
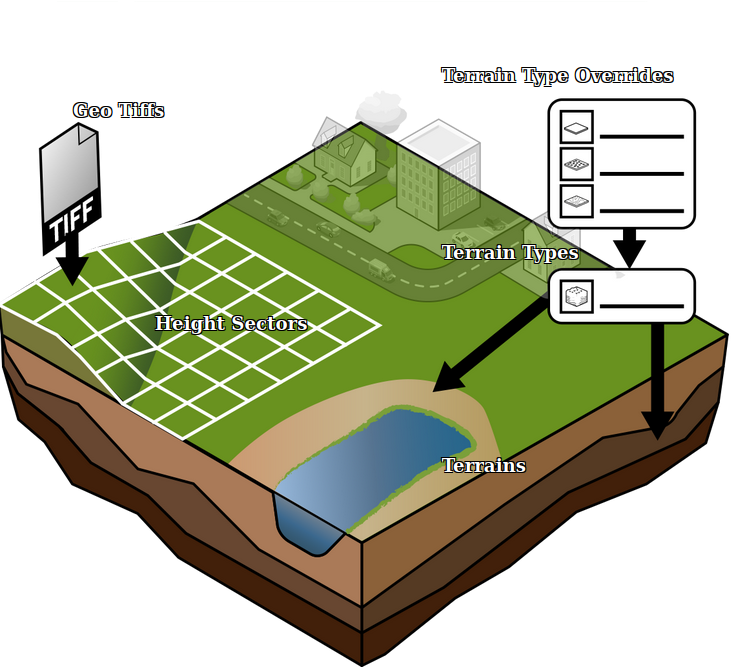
| | [[File:Api_current_situation_geography.png|thumb|right|400px|[[Terrain]]s in relation to [[Terrain Type]]s and [[Height sector]]s.]] |
| | The composition of the surface (above-ground) and sub-surface (underground) in the [[Project]] is defined using Terrains. A Terrain has a polygons indicating its boundaries and a [[Terrain Type]] indicating its type. For every location in the project, two terrains will be present: one [[layer|surface layer]] Terrain and one [[layer|underground]] Terrain. |
|
| |
|
| {{learned|what land is|what the relationship is between land and terrain in the {{software}}|which types of land type are present in the {{software}}|how to edit the land of a selected area}} | | ===Terrain Type=== |
| | {{main|Terrain Type}} |
| | The Terrain polygons each have an associated [[Terrain Type]], which holds the actual data of what the Terrain polygon represents. Only the [[Terrain Type]] holds any [[Attribute]]s to define the Terrain's behavior. |
|
| |
|
| ==What is Terrain?== | | ===Terrain elevation=== |
| Terrain in the {{software}}, describes the surface, subsurface and elevation of your project. Terrain excludes everything which is build-up on the terrain, which is described in buildings. Terrain can be edited via GEO DATA -> Terrain.
| | {{main|Elevation model}} |
| | Although conceptually related, the [[elevation model|height of the Terrain]] is explicitly not part of the Terrain itself or of the [[Terrain Type]]s. Instead, based on the presence or selection of specific [[Terrain Type]]s, modifications to the [[elevation model]] are made. For example, replacing a terrain with a type of [[water (Terrain Attribute)|water]] will cause a change for the [[elevation model]], but that change can be suppressed. |
|
| |
|
| ==Surface==
| | Terrains define what [[Terrain Type]] is present for any given location, and thus how the ground behaves. The [[elevation model]] defines the height of the ground for any given location. |
| In the {{software}} there are different terrain types are available. Each land type has different predefined attributes that affect [[indicators]] and [[Overlay|overlays]] such as [[Green (Indicator)|green]], [[Livability (Indicator)|livability]] and the [[Rainfall_(Overlay)|rainfall flooding]]. All types are described in the table below.
| |
|
| |
|
| {| class="wikitable" | | {{article end |
| ! EN
| | |notes=* When creating a new project in the Netherlands, the default Terrains and their [[Terrain Type]]s are based on data from the [[Project_Sources#BRO|BRO]]. |
| ! NL
| | * Terrains are never edited directly. Instead, users draw or import geometries for alternative Terrain Types. |
| ! Description
| | |howtos=* [[How to manually change the Terrain]] |
| |-
| | * [[How to import a GeoJSON of waterways]] |
| |Concrete
| | * [[How to import a GeoTIFF of waterway depths]] |
| |Beton
| | |seealso=* [[Terrain Type]] |
| |This land type can mostly be found in urban and industrial areas
| | * [[Terrain Attributes]] |
| |-
| | * [[Elevation model]] |
| |River Water
| | * [[Height map]] |
| |Boezemwater
| | * [[Underground Overlay]] |
| |Larger water bodies, navigable for (small) boats
| | }} |
| |-
| |
| |Dike
| |
| |Dijk
| |
| |Dike is a land type that usually lays between water and constructions, or other areas which need to be protected. Dikes are constructed phenomenon, offering protection from floods and high tides
| |
| |- | |
| |Dunes
| |
| |Duinen
| |
| |Dunes is a land type that usually lays between the beach and the rest of the land mass. Dunes are a natural phenomenon, a row of wind shaped sandy hills, protecting the inland from floods and high tides. Sometimes, due to erosion, dunes also occur inland and can eventually develop into a large arid region - the Sahara sand dunes.
| |
| |- | |
| |Golf brekers
| |
| |Breakwater
| |
| |Breakwater is land type designated to protect the actual coast line from waves, floods and tidal erosion.
| |
| |-
| |
| |Grasland
| |
| |Grassland | |
| |All that is grass
| |
| |-
| |
| |Open land
| |
| |Open land
| |
| |This is the default land type for land in the {{software}}. If an empty world is generated, all land will have this land type
| |
| |-
| |
| |Water
| |
| |Water
| |
| |Small water bodies
| |
| |-
| |
| |Sand
| |
| |Zand
| |
| |All that is sand
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| Each surface terrain-type has the following attributes:
| | {{Template:Editor current situation nav}} |
|
| |
|
| {| class="wikitable"
| | [[Category:Items]][[Category:Terrain]] |
| ! Attribute
| |
| ! Unit
| |
| ! Description
| |
| |-
| |
| |BUILDABLE
| |
| |
| |
| |Indication if a terrain can be built upon or not.
| |
| |-
| |
| |GROUND_INFILTRATION_MD
| |
| |meter per day
| |
| |Limitation in capacity of ground infiltration from the surface into the sub-soil, used in the [[Rainfall_(Overlay)|Rainfall Overlay]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |HEAT_EFFECT
| |
| |degrees celsius
| |
| |Impact of terrain on the [[Heat_(Overlay)|heat stress overlay]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |LIVABILITY_EFFECT
| |
| |
| |
| |Impact of terrain on the [[Livability_(Overlay)|livability overlay]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |POLDER_WATER
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |SAFETY
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |TERRAIN_MIX
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |TEXTURE_TYPE
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |WATER
| |
| |
| |
| |Whether this is a water-type terrain. This means constructions that can only be built on land cannot be built on this terrain. In addition, it also counts as a water terrain for overlay calculations. If 1, cells of this type will average the waterlevel, if 0, surface flow will be computed (see [[Rainfall_(Overlay)|Rainfall Overlay]])
| |
| |-
| |
| |WATER_DEPTH_M
| |
| |m
| |
| |When the [[Wizard|new project wizard]] creates a new project, and this is water-type terrain, this is the maximum depth of that water body.
| |
| |-
| |
| |WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR
| |
| |
| |
| |Factor by which the reference evaporation (see [[Rainfall_(Overlay)|Rainfall Overlay]]) is multiplied
| |
| |-
| |
| |WATER_MANNING
| |
| |s/[m<sup>1/3</sup>]
| |
| |Roughness of the surface, used in the surface flow computation of the [[Rainfall_(Overlay)|Rainfall Overlay]].
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ==Subsurface==
| |
| In the {{software}} there are different subsurface types available. Subsurface terrain data is acquired from [[GEO_Data|FGR]]. Note: as of Tygron Platform version 2019.0.0 this has become [[GEO_Data|BRO]]. The [[Underground_(Overlay)|Subsurface Overlay]] shows the different soil types composing the subsurface, each having distinctive predefined attributes.<!-- that affect the [[Water_Overlays|Water Overlays]].--> The table below shows a division into the different terrain categories, which, in turn, have their own subdivisions into multiple subsurface soil types.
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| ! EN
| |
| ! NL
| |
| ! Description
| |
| |-
| |
| |Gravel
| |
| |Grind
| |
| |Terrain with a gravel underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Clay
| |
| |Klei
| |
| |Terrain with a clay underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Chalk
| |
| |Krijt
| |
| |Terrain with a chalk underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Loam
| |
| |Leem
| |
| |Terrain with a loam underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Loess
| |
| |Löss
| |
| |Terrain with a loess underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Unknown
| |
| |Onbekend
| |
| |Default underground if no data is available for your project
| |
| |-
| |
| |Silt
| |
| |Silt
| |
| |Terrain with a silt underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Peat
| |
| |Veen
| |
| |Terrain with a peat underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Sand
| |
| |Zand
| |
| |Terrain with a sand underground layer
| |
| |-
| |
| |Marine clay
| |
| |Zeeklei
| |
| |Terrain with a marine clay underground layer
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| | |
| Each underground terrain type has the following attributes:
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| ! Attribute
| |
| ! Unit
| |
| ! Description
| |
| |-
| |
| |ANGLE_OF_REPOSE
| |
| |Degrees
| |
| |When the [[Wizard|new project wizard]] creates a new project, and this is water-type terrain, this is the maximum steepness of the sloop at the edges of the water (taludhoek).
| |
| |-
| |
| |BUILDABLE
| |
| |
| |
| |Attribute that determines if a Construction can be built there (0=no, 1=yes)
| |
| |-
| |
| |GROUND_INFILTRATION_MD
| |
| |meter per day
| |
| |Limitation in capacity of ground infiltration from the surface into the sub-soil, used in the [[Rainfall_(Overlay)|Rainfall Overlay]]
| |
| |-
| |
| |PEAT_FRACTION
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |TOPLAYER_THICKNESS
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |-
| |
| |WATER_STORAGE_PERCENTAGE
| |
| |
| |
| |Volume of water that can be stored per volume of soil, usually expressed as the saturated minus residual water content properties of soil
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ==Elevation==
| |
| In the terrain menu, the user can change the elevation-model in the project or import/select an elevation model Geotiff. More info on elevation can be found on the [[Terrain_height|terrain height page]]
| |