Area: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
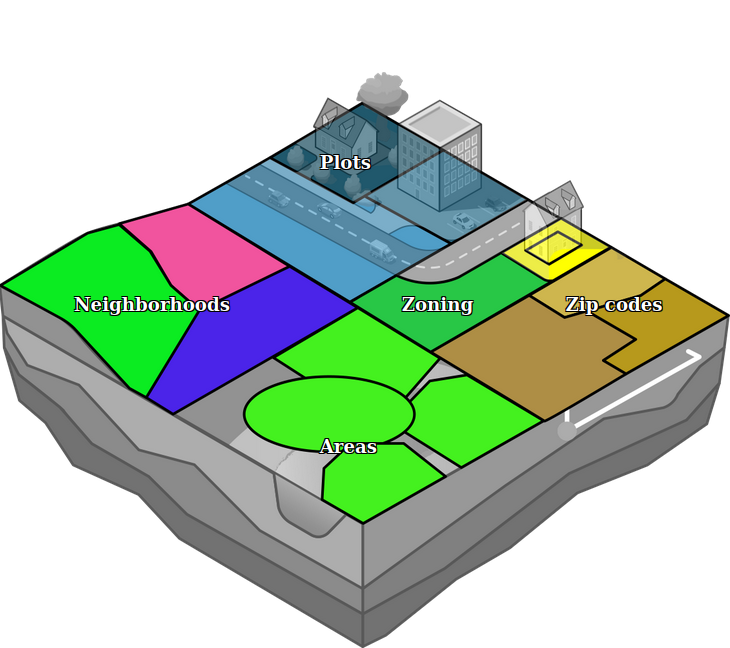
[[File: | [[File:Api_current_situation_urban_subdiv.png|thumb|right|400px|[[Area]] in comparison to [[Neighborhood]]s, [[Zone]]s and [[Plot]]s]] | ||
In the {{software}}, an area is comprised of a polygon, a name and a number of [[attribute]]s, which can be completely user-defined. Areas do not do much on their own, but can be used in conjunction with [[Overlay]]s, [[TQL]] and [[Excel]] to implement powerful and complex calculations for a project. | In the {{software}}, an area is comprised of a polygon, a name and a number of [[attribute]]s, which can be completely user-defined. Areas do not do much on their own, but can be used in conjunction with [[Overlay]]s, [[TQL]] and [[Excel]] to implement powerful and complex calculations for a project. | ||
Revision as of 12:05, 18 October 2022
In the Tygron Platform, an area is comprised of a polygon, a name and a number of attributes, which can be completely user-defined. Areas do not do much on their own, but can be used in conjunction with Overlays, TQL and Excel to implement powerful and complex calculations for a project.
Contrary to buildings, neighborhoods, or terrains, areas are allowed to overlap. They are also not bound to a layer. Because of this, they can be used for multiple purposes at the same time. By using attributes, it's possible to define and identify the purpose of an area.
How to
- How to add an area
- How to duplicate areas
- How to remove areas
- How to remove multiple areas with a filter.
- How to edit area properties
Overlays
Specific areas can be visualized using an Areas (Overlay). This overlay can be used to inform stakeholders about a specific concept or calculation. The overlay can also change during the session if, for example, the area is (de)activate or its color is changed.