Geo Data: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* For creating more overview in your project, for example by highlighting areas | * For creating more overview in your project, for example by highlighting areas | ||
In these situations, it might be useful to overwrite or import data. | In these situations, it might be useful to overwrite or import data. | ||
The next sections describe how to: | |||
* [[Geo_Data#Import_Geo_data|Import Geo data]] | |||
* [[Geo_Data#Export_Geo_data|Export Geo data]] | |||
* [[[[Geo_Data#View_Geo_data|View Geo data in other software]] | |||
==Import Geo data== | ==Import Geo data== | ||
Revision as of 08:25, 26 September 2019
What is Geo data
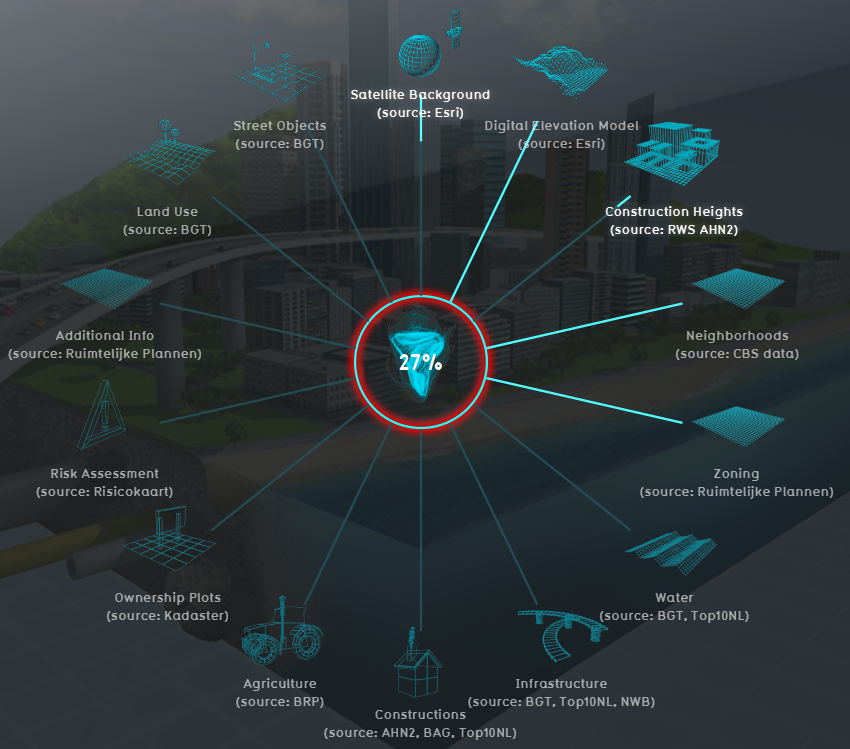
Geographical data or geo data is data which have a location component. Almost all data is linked to a location or a place and are, therefore, geo data. Geo data can be, for example, a paper map, a digital web map or just a simple text file with coordinates. Geo datasets is either vector data (that is, features which are points, lines or polygons) or raster data (that is, data in grid cells). The features in vector data can have multiple attributes with values. Raster data mostly consist of a value and a color.
How do Geo datasets relate to the Tygron Platform
The Tygron Platform uses Geo data (vector and raster data) for creating the 3D-model world. For this, the Tygron Platform automatically connects to (Open) Datasets, based on the availability of the data for the chosen location of the project. For example the Base Registers in the Netherlands and Open Street Maps worldwide.
A principle that generally applies: if your 3D World lacks certain information, then it is not available in the used datasets.
For more information on which data is used for your generating your project, see the project sources page.
To add missing Geo data you can add additional Geo data manually (see below for options).
When to use your own data
- The project takes place in a location for which there are no data sources available to create the project
- The default data sources are not accurate or up-to-date enough
- The default datasets are not detailed enough
- To do a more extended analysis in the Tygron Platform
- To use in combination with an Excel Indicator or Panel
- For creating more overview in your project, for example by highlighting areas
In these situations, it might be useful to overwrite or import data.
The next sections describe how to:
Import Geo data
Almost all data can be imported in the Tygron Platform, as long as the data is about specific locations and contains geometry (and therefore coordinates). Thus basically when the data is Geo data. This also means that digital files of spatial plans can be imported in the Tygron Platform. There are different methods for importing Geo Data. The method to choose is based on how you have your data available, as vector or raster data.
Data preparation
Before importing data, take a look at the data preparation page for some tips on how to prepare (vector) data for easy importing.
Import vector data
Requirements
With the Geo data wizard you can easily import vector data. The wizard also helps you to transform your data to the proper format for importing. The following requirements for vector data apply:
- Geo Data in the Tygron Platform are always polygons. Line and point features are not allowed by the Tygron Platform. The data wizards helps you by buffering the line and point features to polygons.
- All desired attributes must be numerical, so that they can be loaded as valid attribute values. Non-numeric attributes are ignored when attempting to load them as attributes.
- The Geo dataset should have a CRS (Coordinate Reference System) defined, for the Platform to properly translate the coordinates to the right location.
Import methods
There are four different import methods:
- with a GeoJSON file
- through a Web Feature Service (WFS)
- through a Catalogue Service for the Web (CSW)
- through a Scene layer package (SLPK)
Choose a method based on how you have your data available. Read more on the data wizard page about the options.
Errors
If you run into any errors check this section on the most common errors.
Import raster data
Requirements
The following requirements for raster data apply:
- The Geo dataset should have a CRS (Coordinate Reference System) defined, for the Platform to properly translate the coordinates to the right location.
Import methods
There are two different import methods:
- through a Web Map Service (WMS).
- as a Geotiff overlay
Choose a method based on how you have your data available.
Export Geo data
Export vector data
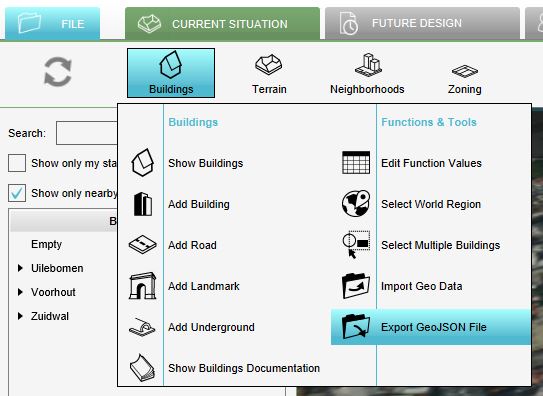
The components that make up the 3D world can be exported as 2D vector data in GeoJSON format. With this data, further/other calculations or analysis can be done in for example GIS software. In the Current Situation tab, each of the following menus has an export GeoJSON option:
- Hover over the desired menu you want to export objects from.
- Select Export GeoJSON file
- Choose additional options to make a selection of the to be exported data or for export all, click on the Export button.
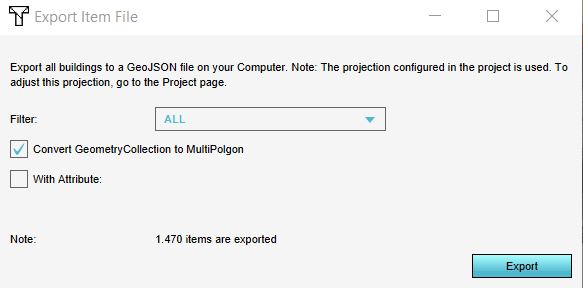
In the Export Item File panel that will show up, different options for exporting are available:
- Objects from a certain category/type (only for the Buildings and Terrains) can be exported by selecting the desired category/type.
- Only objects that have a certain attribute can be exported by checking the With Attribute option and selecting the desired attribute. For example if you only want culverts, you can select the category Underground (since the function culverts belongs to the category Underground) and check the With Attribute option and select the attribute name CULVERT_DIAMETER for example. This will export culverts, since only these objects have this attribute in common.
Export raster data
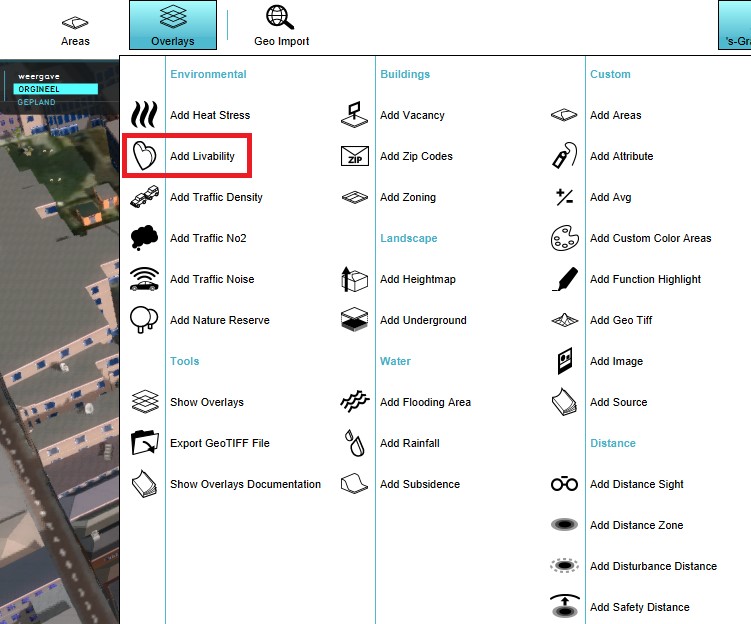
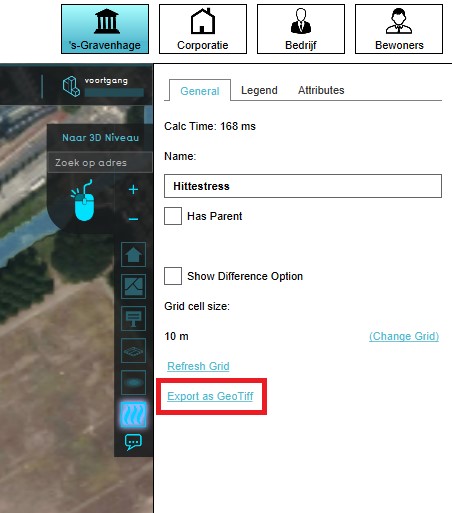
Grid overlays can be exported as a GeoTIFF or ASCII file. With such a file, calculations from for example the Water overlay can be exported to be further processed for analysis in GIS software. For exporting the grid overlays, take also note of the grid size. The smaller the grid size, the more accurate the exported GeoTIFF is.
- Select any grid overlay in the editor.
- On the right panel, select "Export Grid File".
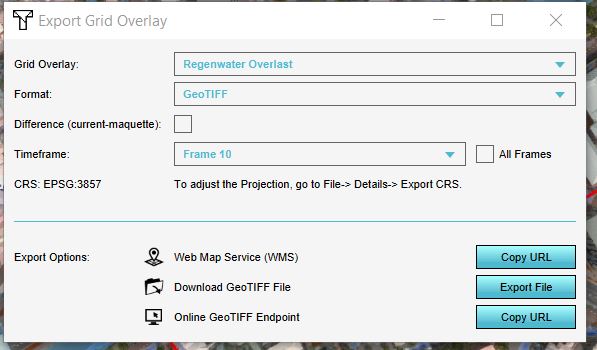
- Choose the overlay, format and click on the Export button.
In the Export Grid File panel that will show up, different options for exporting are available:
- If in a test run the option Export difference (current and maquette) is selected, the difference in results between the maquette state and the current state will be exported. If you checked this option outside of the test run, or did not do any Actions, the exported dataset will consist no difference.
- For the water overlays, it is possible to export a dataset at a certain timeframe, by selecting the ID of the timeframe. Keep in mind that the ID of the timeframe start at 0. Thus if you have 10 timeframes in the overlay, the timeframes IDs range from 0 to 9.