Tutorial Heat Stress Project: Difference between revisions
(→Step 3) |
No edit summary |
||
| (118 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Heat Overlay allows users to visualize a generated Physiological Equivalent Temperature (PET) overlay, along with other intermediate overlay results. The Heat Overlay can be configured using the Wizard. | The Heat Overlay allows users to visualize a generated Physiological Equivalent Temperature (PET) overlay, along with other intermediate overlay results. The Heat Overlay can be configured using the Wizard. | ||
Using this tutorial you can setup a new [[Heat stress (Overlay)|Heat Overlay]] in | Using this tutorial you can setup a new [[Heat stress (Overlay)|Heat Overlay]] in this Heat Stress Tutorial projects by using the Heat Overlay Wizard step by step. We have selected this project so you are able to compare the outcome this project with the Demo Heat Stres project. | ||
==Getting Started== | ==Getting Started== | ||
* Open the {{software}}, | * Open the {{software}}, login with your username and password. | ||
* Choose | * Choose the Tutorial Heat Stress project in edit projects. | ||
<gallery mode="nolines"> | |||
< | File:Edit_project_in_trail.jpg|Edit projects in main menu | ||
File:Tutorial_Heat_Stress_project.jpg|Tutorial Heat Stress project | |||
</gallery> | |||
{{clear|both}} | |||
==Add Heat Overlay== | ==Add Heat Overlay== | ||
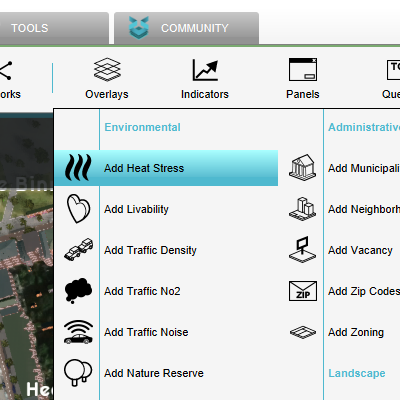
Hover over the button ''Overlays'', in the '' | [[File:Add_heat_overlay.png|thumb|250px|right|Add Overlay]] | ||
Hover over the button [[Overlay|''Overlays'']], in the [[Current_Situation|''Current situation tab'']] and select Add Heat Stress.<br> | |||
The Heat Overlay is added to the Overlays in the left-side-panel, and in the overlay bar on the right side of the map. | |||
{{clear|both}} | |||
==Configure Wizard== | ==Configure Wizard== | ||
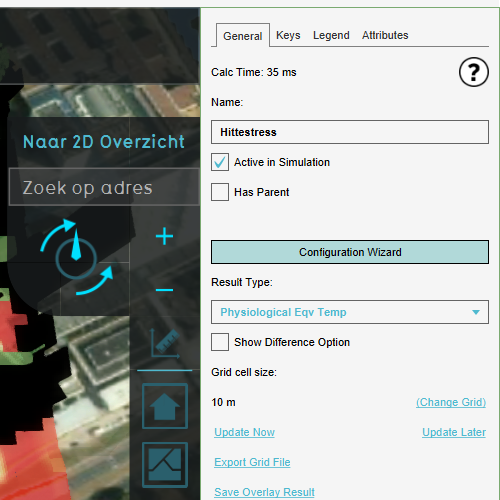
* Open the Wizard by clicking on the "Configuration Wizard" button on the right panel | * Open the Wizard by clicking on the "Configuration Wizard" button on the right panel<br> | ||
[[File:Open_wizard.png|250px|thumb|right|Open Wizard]] | [[File:Open_wizard.png|250px|thumb|right|Open Wizard]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
* Now you can see the steps which you will be setting up. | * Now you can see the steps which you will be setting up. | ||
=== Step 1: | |||
In Step 1 you can choose either the new (more accurate) [[Heat_DPRA_Module|DPRA]] | {{clear|both}} | ||
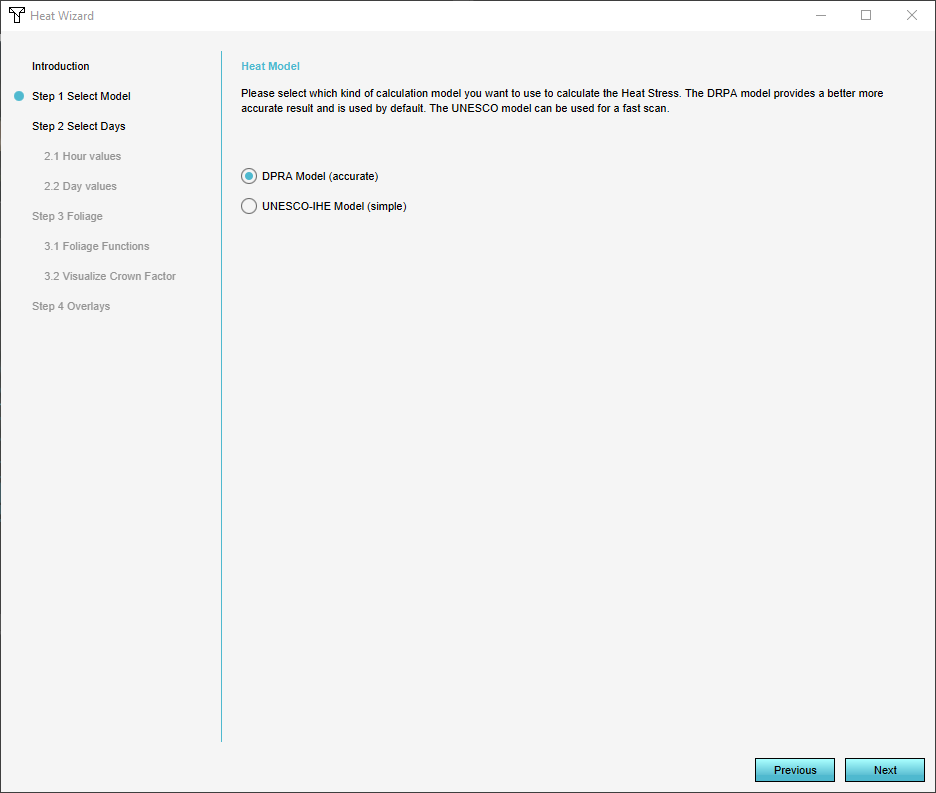
=== Step 1: Select model === | |||
In Step 1 you can choose either the new (more accurate) [[Heat_DPRA_Module|DPRA Model]] or the [[UNESCO Heat Module|UNESCO Heat stress module]] that was used in previous releases of the {{software}}. | |||
*For this tutorial select the [[Heat_DPRA_Module|DPRA]] Model. | |||
<gallery mode="nolines"> | |||
File:Heat-step1.PNG|Step 1 Select model | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== Step 2: Choose date and time of day === | === Step 2: Choose date and time of day === | ||
In Step 2 you can select the start and end date for the PET calculation, also the specific hours. Additional paramaters can also be adjusted for the specific hours and days given. | In Step 2 ''Select Days'' you can select the start and end date for the PET calculation, also the specific hours. Additional paramaters can also be adjusted for the specific hours and days given. | ||
* | * By default August 2nd, 2013 is selected. You can also choose to select multiple consecutive days when using the Heat Overlay Wizard. | ||
* Select Edit and configure the hours you want to generate results for: | * Select Edit and configure the hours you want to generate results for: Select every hour from 12:00 to 18:00 pm. Each day-hour combination will become a result. This result is stored as a time-frame to relate it back to the day and time. For each day, and for each time of day, the following will be automatically generated when using the wizard. It is possible to select a new start date and an end date aswell. If you do so, you need to import your own downloaded data. If you want to make use of your own data, in the [[Tutorial_Heat_Overlay_(Heat_Overlay)#Supply_daily_and_hourly_weather_station_data|Supply daily and hourly weather station data]] part of this page for more information on how to implement this data. For now we make use of the default settings, because of the possibility to compare the results of this tutorial to the Demo Heat Stress project. | ||
* Now you see an overview of the sun angle at each time of day and other relevant factors. To find out more about the attributes and the impact they have on the overall system go to [[Heat_Stress_module_overview|Heat Stress Overview]]. | * Select Next. | ||
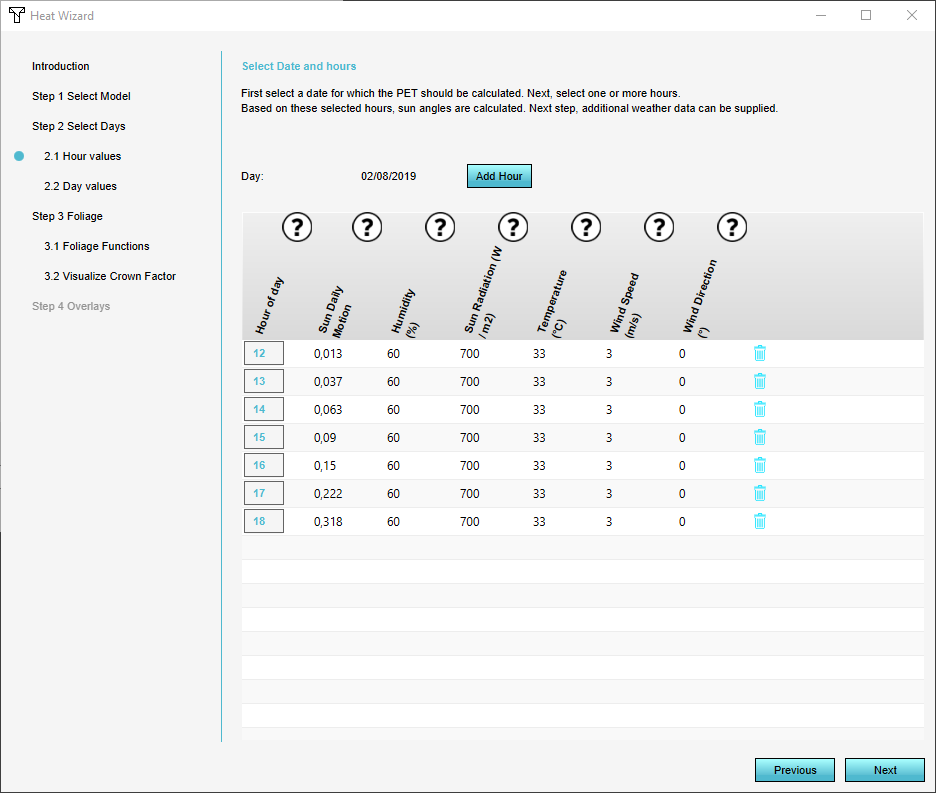
Step 2.1 ''Hour Values'' The day and time pairs, along with the project location, will be used to automatically calculate the [[Sun_altitude_(Heat_Overlay)|sun altitude]] and [[Sun_azimuth_(Heat_Overlay)|sun azimuth angles]] for each day-time pair. If desired you can add a subsequent hour to the list by clicking ''Add Hour''. | |||
* If all hours are correct select Next.<br> | |||
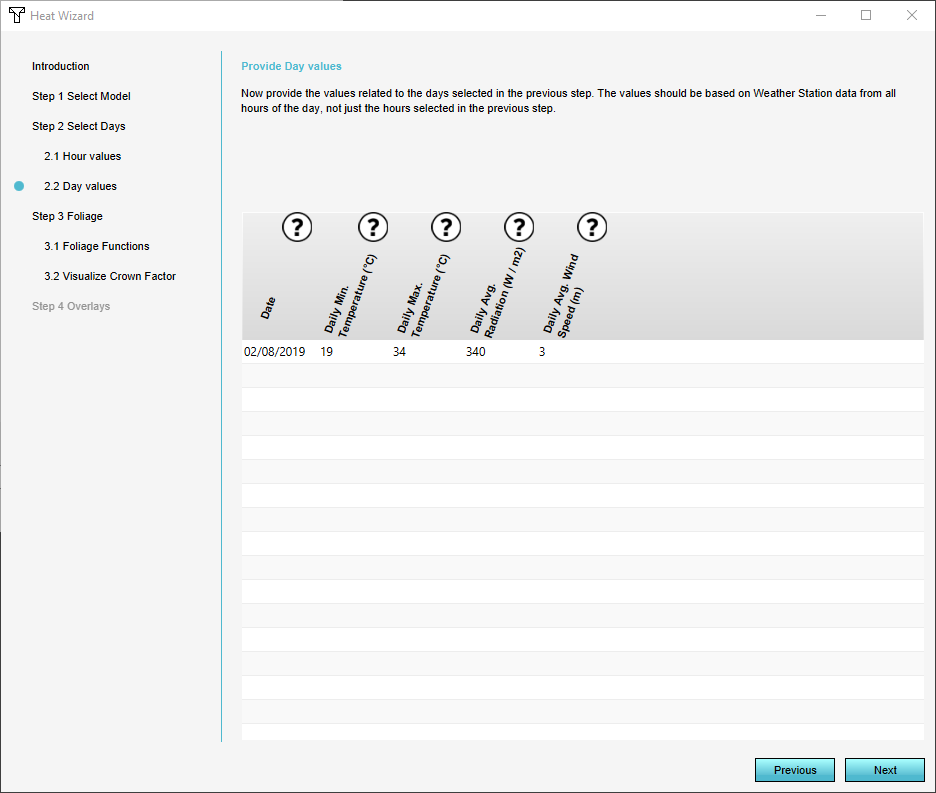
Step 2.2 ''Day Values'' The [[Sun_daily_motion_(Heat_Overlay)|sun daily motion factor]] is a parameter used in the atmospheric temperature formula. It will be automatically selected from the sun motion factor table, based on the date (column) and time of day (row). | |||
* Now you see an overview of the sun angle at each time of day and other relevant factors. To find out more about the attributes and the impact they have on the overall system go to [[Heat_Stress_module_overview|Heat Stress Overview]]. | |||
* Select next. | |||
<gallery mode="nolines"> | |||
File:Heat_step2.PNG|Step 2 Select days and hours | |||
File:Heat_step2.1.PNG|Step 2.1 Configure hours | |||
File:Heat_step2.2.PNG|Step 2.2 Weather Station data | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Supply daily and hourly weather station data=== | |||
By default you see an overview of the weather station data of August 2nd 2013. To learn more about how to upload weather station data go to [[KNMI weather data]] and the [[How to import KNMI weather data into Microsoft Excel]] page. Download the historical hourly weather data for your own, in the Netherlands located, project area and use the data from specific columns as input. In a nutshell, using the weather data, you have to supply both Daily and Hourly Values. Check the links below to learn how you can supply these. Per value and explanation is given so you know what kind of data you need to collect for abroad projects as well. | |||
* [[How to calculate the hourly radiation]] | |||
* [[How to calculate the hourly humidity]] | |||
* [[How to calculate the hourly wind direction]] | |||
* [[How to calculate the hourly wind speed]] | |||
* [[How to calculate the daily average wind speed]] | |||
* [[How to calculate the daily min and max temperature]] | |||
* [[How to calculate the daily average radiation]] | |||
=== Step 3: Foliage === | |||
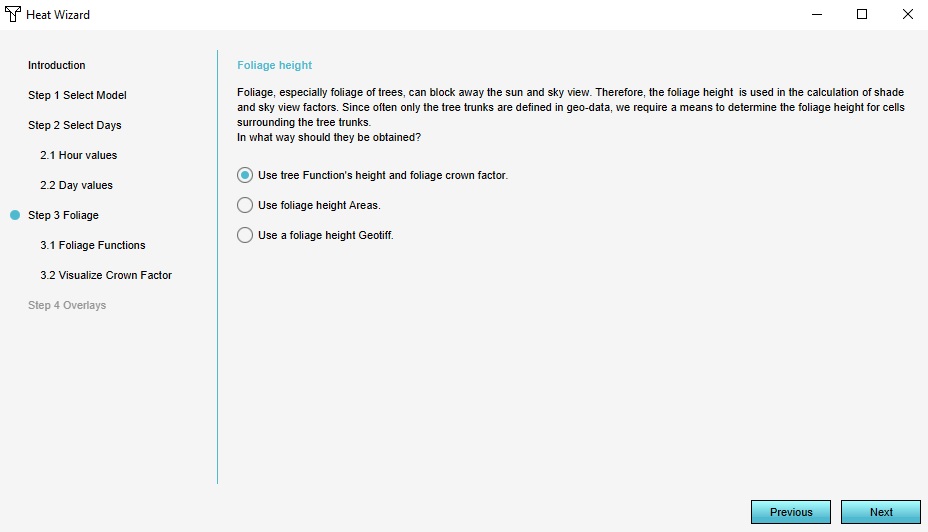
In step 3 ''Foliage height'' you can define how to treat the foliage in your project. You can setup how you want the foliage height and crown factor to behave and wether or not you want to visualize foliage in the Heat Overlay. Select what source will define the foliage height, you have three options: | |||
# Buildings with [[Function|functions]] related to foliage. The [[Foliage_height_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|foliage height calculation model]] will determine the foliage height using the height of the vegetation (as buildings) and the foliage crown factor attribute. This option is the most convenient option if you want to experiment with future design scenario's by using actions, measures and upgrades. For more information on how to adjust this option go to [[How_to_adjust_the_foliage_height_and_crown_factor|How to adjust the foliage height and crown factor]]. | |||
# Areas with a foliage height attribute, defining the foliage height for a whole area; For more information on how to adjust this option go to [[How_to_import_foliage_height_areas|How to import foliage height areas]]. | |||
# [[GeoTIFF]], defining a foliage height value for each cell in its raster. This is the most precise option to apply this data set. For more information on how to adjust this option go to [[How_to_import_a_foliage_height_GeoTIFF|How to import a foliage height GeoTIFF]]. <br> | |||
* For this tutorial, choose ''Use tree Function's height and foliage crown factor'' and click Next. <br> | |||
Step 3.1 Foliage Functions<br> | |||
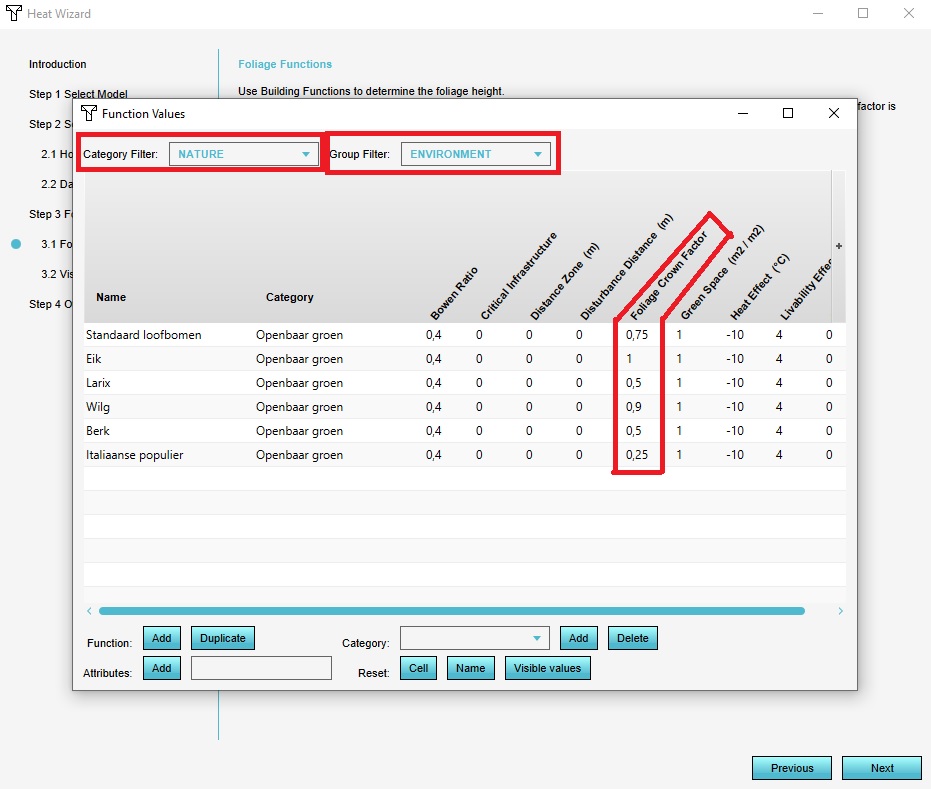
In this step you can edit the Function Values of the different types of trees. By default six types of trees are present in the Platform and each have their own specific Foliage Crown Factor. If you have imported your own foliage data you can edit the Function Values in this step manually, but probably the imported data is already provided with the correct Foliage Crown factor. When you want to adjust the Function Value please select the Nature Category with the Group Filter Environment to get a overview of the different types of trees. | |||
* For this tutorial, do nothing and select Next. <br> | |||
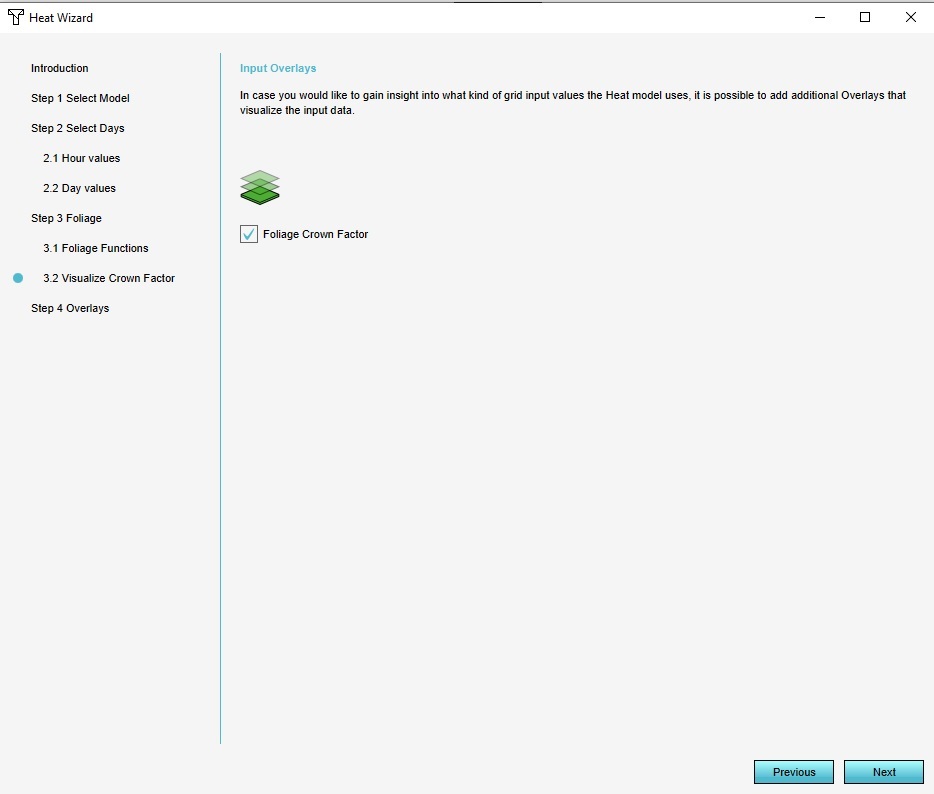
Step 3.2 Visualize Crown Factor<br> | |||
In this step you can select a checkbox that will provide you with insight on what kind of input values the Heat model uses. This is displayed in an Overlay of the the Foliage Crown factor. | |||
*Select the Foliage Crown Factor checkbox and select Next. | |||
<gallery mode="nolines"> | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
File: | File:Step_3_Foliage_height.jpg|Step 3 Foliage height | ||
File: | File:Foliage_Crown_Factor_Function_Values.jpg|Step 3.1 Foliage Functions | ||
File: | File:Input_Overlays_step_3.2.jpg|Step 3.2 Visualize Crown Factor | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
=== Step | === Step 4: Overlays === | ||
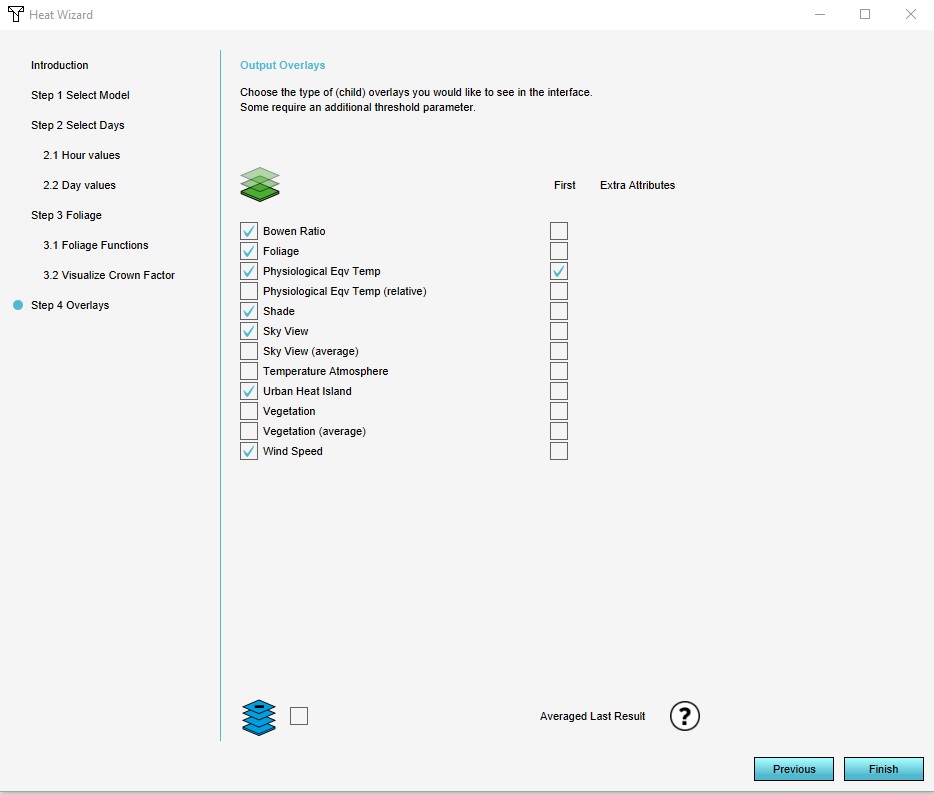
In step | In the final step you can choose which result types you want to display in the Overlay. Most users will be interested in the PET (Physiological Equivalent Temperature) but it varies from project to project. Choose all output overlays to get insight in the different components that configure the PET. For an overview of the different result types and their meanings go to [[Result_types_ (Heat_Overlay)|Result types (Heat_Overlay)]]. | ||
*Choose which of these results will be shown as the parent overlay in the overlay menu bar by checking on the "First" checkbox. All other overlays which are selected by checking the checkbox in the fornt of the overlay name will be shown as a child overlay. In this case we select at least the PET (Physiological Equivalent Temperature) overlay as First. | |||
* [[ | * Select the child overlays, in this case the [[Foliage result type (Heat Overlay)|Foliage]], [[Bowen ratio _result type (Heat Overlay)|Bowen Ratio]], [[Shade result type (Heat Overlay)|Shade]], [[Sky view result type (Heat Overlay)|Sky view]], [[Uhi result type (Heat Overlay)|Urban Heat Island]] and [[Wind speed (Heat Overlay)|Wind Speed]]. | ||
*Select ''Finish'' to close the Wizard. You have succesfully setup your Heat Stress Overlay. | |||
<gallery mode="nolines"> | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
File: | File:Output_Heat_Stress.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
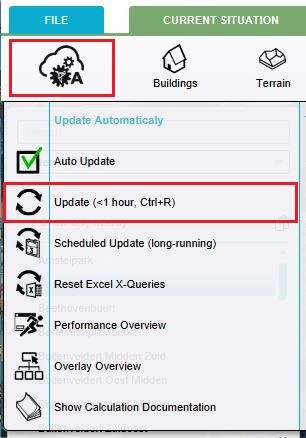
*If no results are show in your overlays, you probably need to recalculate your outcomes in order to display it in the overlays. If that's the case, please click the recalculated button in the upper left corner as you can see in the picture below. All outcomes will be recalculated and displayed now. | |||
* | |||
<gallery mode="nolines"> | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
File: | File:Recalculate.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Explore your results== | |||
[[File:Heat overlaysth.PNG|thumb|right|250px|Heat Overlay]][[File:Shade Wageningenth.PNG|thumb|right|250px|Shade Overlay]] | |||
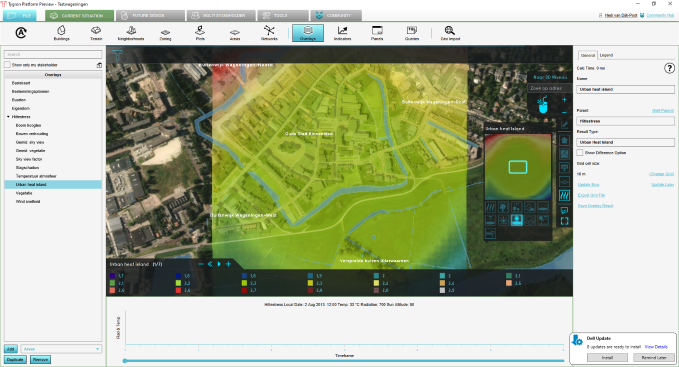
In this part of the tutorial we will give you some suggestions on how to adjust more settings and results. Hover over the Heat Stress Overlay on the right and its different child overlays. | |||
* You can run through the different time frame results by using the arrows in the Left corner of the [[viewer ]]interface. | |||
* Can you improve your result even further by uploading detailed Foliage data? | |||
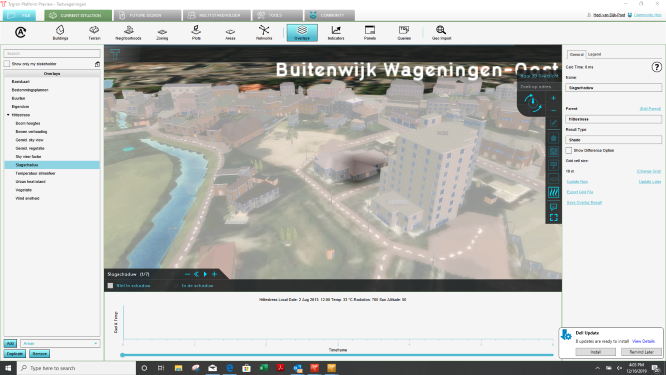
* Check the Shade child overlay. You can for example clearly see the impact of the high building in ''Buitenwijk Wageningen Oost''. | |||
* Note that you can change the grid size of your calculation by choosing (Change Grid) in the middle of the right column in your screen. Change it from 10m to 1 m and inspect the result. As a result the black gridcels of the buildings will become more accurate in your overlay and more simular to the 'HitteWageningen' project. | |||
{{clear|both}} | |||
==Further reading== | |||
To read more documentation about the Heat Overlay explore the [[DPRA Heat Module]] documentation. | |||
<!-- | |||
== Setup == | == Setup == | ||
Generally, the steps required to use and configure the Heat Stress Overlay are as followed: | Generally, the steps required to use and configure the Heat Stress Overlay are as followed: | ||
| Line 111: | Line 158: | ||
* Buildings with [[Function|functions]] related to foliage. The [[Foliage_height_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|foliage height calculation model]] will determine the foliage height using the height of the vegetation (as buildings) and the foliage crown factor attribute; | * Buildings with [[Function|functions]] related to foliage. The [[Foliage_height_calculation_model_(Heat_Overlay)|foliage height calculation model]] will determine the foliage height using the height of the vegetation (as buildings) and the foliage crown factor attribute; | ||
* Areas with as foliage height attribute, defining the foliage height for a whole area; | * Areas with as foliage height attribute, defining the foliage height for a whole area; | ||
* [[ | * [[GeoTIFF]], defining a foliage height value for each cell in its raster. | ||
===Further reading=== | ===Further reading=== | ||
To read more documentation about the Heat Stress Overlay go to [[Heat_DPRA_Module]] | To read more documentation about the Heat Stress Overlay go to [[Heat_DPRA_Module]] | ||
--> | |||
{{Template:Heat_Module_buttons}} | |||
[[Category: tutorials]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:45, 30 March 2023
The Heat Overlay allows users to visualize a generated Physiological Equivalent Temperature (PET) overlay, along with other intermediate overlay results. The Heat Overlay can be configured using the Wizard.
Using this tutorial you can setup a new Heat Overlay in this Heat Stress Tutorial projects by using the Heat Overlay Wizard step by step. We have selected this project so you are able to compare the outcome this project with the Demo Heat Stres project.
Getting Started
- Open the Tygron Platform, login with your username and password.
- Choose the Tutorial Heat Stress project in edit projects.
Add Heat Overlay
Hover over the button Overlays, in the Current situation tab and select Add Heat Stress.
The Heat Overlay is added to the Overlays in the left-side-panel, and in the overlay bar on the right side of the map.
Configure Wizard
- Open the Wizard by clicking on the "Configuration Wizard" button on the right panel
- Click on "Next" in the Introduction of the Wizard.
- Now you can see the steps which you will be setting up.
Step 1: Select model
In Step 1 you can choose either the new (more accurate) DPRA Model or the UNESCO Heat stress module that was used in previous releases of the Tygron Platform.
- For this tutorial select the DPRA Model.
Step 2: Choose date and time of day
In Step 2 Select Days you can select the start and end date for the PET calculation, also the specific hours. Additional paramaters can also be adjusted for the specific hours and days given.
- By default August 2nd, 2013 is selected. You can also choose to select multiple consecutive days when using the Heat Overlay Wizard.
- Select Edit and configure the hours you want to generate results for: Select every hour from 12:00 to 18:00 pm. Each day-hour combination will become a result. This result is stored as a time-frame to relate it back to the day and time. For each day, and for each time of day, the following will be automatically generated when using the wizard. It is possible to select a new start date and an end date aswell. If you do so, you need to import your own downloaded data. If you want to make use of your own data, in the Supply daily and hourly weather station data part of this page for more information on how to implement this data. For now we make use of the default settings, because of the possibility to compare the results of this tutorial to the Demo Heat Stress project.
- Select Next.
Step 2.1 Hour Values The day and time pairs, along with the project location, will be used to automatically calculate the sun altitude and sun azimuth angles for each day-time pair. If desired you can add a subsequent hour to the list by clicking Add Hour.
- If all hours are correct select Next.
Step 2.2 Day Values The sun daily motion factor is a parameter used in the atmospheric temperature formula. It will be automatically selected from the sun motion factor table, based on the date (column) and time of day (row).
- Now you see an overview of the sun angle at each time of day and other relevant factors. To find out more about the attributes and the impact they have on the overall system go to Heat Stress Overview.
- Select next.
Supply daily and hourly weather station data
By default you see an overview of the weather station data of August 2nd 2013. To learn more about how to upload weather station data go to KNMI weather data and the How to import KNMI weather data into Microsoft Excel page. Download the historical hourly weather data for your own, in the Netherlands located, project area and use the data from specific columns as input. In a nutshell, using the weather data, you have to supply both Daily and Hourly Values. Check the links below to learn how you can supply these. Per value and explanation is given so you know what kind of data you need to collect for abroad projects as well.
- How to calculate the hourly radiation
- How to calculate the hourly humidity
- How to calculate the hourly wind direction
- How to calculate the hourly wind speed
- How to calculate the daily average wind speed
- How to calculate the daily min and max temperature
- How to calculate the daily average radiation
Step 3: Foliage
In step 3 Foliage height you can define how to treat the foliage in your project. You can setup how you want the foliage height and crown factor to behave and wether or not you want to visualize foliage in the Heat Overlay. Select what source will define the foliage height, you have three options:
- Buildings with functions related to foliage. The foliage height calculation model will determine the foliage height using the height of the vegetation (as buildings) and the foliage crown factor attribute. This option is the most convenient option if you want to experiment with future design scenario's by using actions, measures and upgrades. For more information on how to adjust this option go to How to adjust the foliage height and crown factor.
- Areas with a foliage height attribute, defining the foliage height for a whole area; For more information on how to adjust this option go to How to import foliage height areas.
- GeoTIFF, defining a foliage height value for each cell in its raster. This is the most precise option to apply this data set. For more information on how to adjust this option go to How to import a foliage height GeoTIFF.
- For this tutorial, choose Use tree Function's height and foliage crown factor and click Next.
Step 3.1 Foliage Functions
In this step you can edit the Function Values of the different types of trees. By default six types of trees are present in the Platform and each have their own specific Foliage Crown Factor. If you have imported your own foliage data you can edit the Function Values in this step manually, but probably the imported data is already provided with the correct Foliage Crown factor. When you want to adjust the Function Value please select the Nature Category with the Group Filter Environment to get a overview of the different types of trees.
- For this tutorial, do nothing and select Next.
Step 3.2 Visualize Crown Factor
In this step you can select a checkbox that will provide you with insight on what kind of input values the Heat model uses. This is displayed in an Overlay of the the Foliage Crown factor.
- Select the Foliage Crown Factor checkbox and select Next.
Step 4: Overlays
In the final step you can choose which result types you want to display in the Overlay. Most users will be interested in the PET (Physiological Equivalent Temperature) but it varies from project to project. Choose all output overlays to get insight in the different components that configure the PET. For an overview of the different result types and their meanings go to Result types (Heat_Overlay).
- Choose which of these results will be shown as the parent overlay in the overlay menu bar by checking on the "First" checkbox. All other overlays which are selected by checking the checkbox in the fornt of the overlay name will be shown as a child overlay. In this case we select at least the PET (Physiological Equivalent Temperature) overlay as First.
- Select the child overlays, in this case the Foliage, Bowen Ratio, Shade, Sky view, Urban Heat Island and Wind Speed.
- Select Finish to close the Wizard. You have succesfully setup your Heat Stress Overlay.
- If no results are show in your overlays, you probably need to recalculate your outcomes in order to display it in the overlays. If that's the case, please click the recalculated button in the upper left corner as you can see in the picture below. All outcomes will be recalculated and displayed now.
Explore your results
In this part of the tutorial we will give you some suggestions on how to adjust more settings and results. Hover over the Heat Stress Overlay on the right and its different child overlays.
- You can run through the different time frame results by using the arrows in the Left corner of the viewer interface.
- Can you improve your result even further by uploading detailed Foliage data?
- Check the Shade child overlay. You can for example clearly see the impact of the high building in Buitenwijk Wageningen Oost.
- Note that you can change the grid size of your calculation by choosing (Change Grid) in the middle of the right column in your screen. Change it from 10m to 1 m and inspect the result. As a result the black gridcels of the buildings will become more accurate in your overlay and more simular to the 'HitteWageningen' project.
Further reading
To read more documentation about the Heat Overlay explore the DPRA Heat Module documentation.