Attribute: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{learned|what an attribute is |how the concept of attributes relates to the Tygron Engine|how to add or remove attributes|how to edit attributes already implemented in the 3D..." |
|||
| (149 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A number of components, such as [[neighborhood]]s, [[area]]s, [[building]]s and [[zone]]s, have adjustable attributes. These attributes are used: | |||
* to provide meaningful information | |||
* as parameters in calculations | |||
* to provide (visual) information to distinguish themselves among peers | |||
Attributes can be defined and redefined by a user. Some attributes are predefined by the {{software}} and already exist as default properties of a component. Some components can even inherit properties from other type of components, such as a [[Building]] that inherits attributes from it's referenced [[Function]]. | |||
In general the {{software}} allows users to inspect, adjust and reset existing attributes of these components and define and remove new ones. | |||
The group of components than can store attributes is called ''Attribute Items''. The current list of ''Attribute Items'' is: | |||
* [[Area]]s | |||
[[ | * [[Building]]s | ||
* [[Functions]] and their overrides | |||
* [[Indicator]]s | |||
* [[Neighborhood]]s | |||
* [[Net load]]s | |||
* [[Net line]]s | |||
* [[Net line#Net line definitions|Net function]]s | |||
* [[Overlay]]s | |||
* [[Panel]]s | |||
* [[Terrain]]s | |||
* [[Weather]]s | |||
* [[Zone]]s | |||
Note that although [[Global]]s seem to behave similarly to attributes, they are not part of any specific ''Attribute Item'' in a project. Instead they are individual components part of the project. | |||
== | ==Attribute values== | ||
An attribute always consists of a name and a value. The name of an attribute is usually written in capital letters, and uses underscores in place of spaces. The value must always be a number. It can be either a positive or a negative number. The number can also be a decimal number (I.e., the value is not necessarily a whole number). | |||
''Note that not there are some [[TQL_name|restrictions for attribute names]].'' | |||
Some components have properties which are also reflected in attributes. Properties such as the color of the component are present both as a dedicated property and as an attribute. By changing the property, the attribute is changed as well. When the attribute is changed, the property is changed as well. | |||
Each component which can have attributes has their own list of attributes. When a given area has an attribute with a specific name, another area may or may not have an attribute with the same name as well. When 2 components have an attribute with the same name, their values are also still set per component. That means that they may coincidentally have the same value, but when the value of the attribute of one component is changed, the value of the attribute of the other component is not automatically changed as well. | |||
=== | ===Attribute arrays=== | ||
{{main|Attribute array}} | |||
Attributes are most commonly a single value, but can also be an array of values. | |||
=== | ===Attribute values during a session=== | ||
[[ | Attributes can be read during a session. Primarily, it is possible to read attributes of components using [[TQL]]. By requesting the value of an attribute of a component using TQL, the value of that attribute can be used in, for example, [[Excel]] calculations. | ||
It is possible that, when requesting the value of an attribute of a component, that attribute does not exist for that component. In this case, the value of that attribute is deemed to be "0". | |||
==== | ''Note that this means that an attribute value of 0 can mean that the proper value of the attribute is 0, or that the attribute does not exist. | ||
[[ | |||
: '' | Attributes can also be changed during a session. This can be done either via [[Event]]s or via [[TQL]]. Events, such as AREA_SET_ATTRIBUTE or ZONE_SET_ATTRIBUTE, can be used in the {{software}} to change the values of attributes. Attributes can also be changed using TQL, which means that attributes can be changed as a result of an Excel calculation. | ||
===Common attribute values=== | |||
Some attributes may have a more exact spectrum of values which are valid. For example, the ACTIVE attribute is either 1 or a 0. | |||
''Note that these attributes can be given other values as well. The resulting behavior for calculations and functionality depending on these attributes is undefined. | |||
====ACTIVE==== | |||
: ''Applies to: [[Area]]s, [[Neighborhood]]s, [[Overlay]]s, [[Indicator]]s and [[Stakeholder]]s | |||
Some components may have an "active" property. When that property indicates the component is active, the "ACTIVE" attribute's value is "1". When the component is inactive, the attribute's value is "0". | |||
====COLOR==== | |||
: ''Applies to: [[Area]]s, [[Neighborhoods]], [[Zone]]s | |||
{{main|Color}} | |||
Spatial components with attributes commonly have a "COLOR" attribute, defining the color by which they are displayed.The value corresponds to the color property of that component. When that color property is changed, the attribute is changed, and vice versa. | |||
===Examples of special attribute values=== | |||
====URBANIZATION==== | |||
: ''Applies to: [[Neighborhoods]] | |||
The "URBANIZATION" attribute is an indicator for the degree of urbanization. It ranges from 1 (dense urbanization) to 5 (virtually no urbanization). | |||
====NATURE_RESERVE==== | |||
: ''Applies to: [[Area]]s | |||
The "NATURE_RESERVE" attribute indicates whether an area is a protected area of nature. This usually means the allowance for pollution and noise is lower. Areas with an "NATURE_RESERVE" attribute value of "1" are deemed protected nature. When the attribute's value is 0, the area is not necessarily deemed protected nature. | |||
{{article end | |||
| notes= | |||
* When removing attributes which are related to properties of the component, the value of the properties will be changed as well, as though the attribute was set to "0". | |||
| howtos= | |||
[[File:Attribute editing panel.jpg|thumb|right|The [[right panel]] allows you to add new attributes. The top half allows you to edit existing attributes, the bottom half allows you to add new attributes.]] | |||
* [[How to add an Attribute]] | |||
* [[How to remove an Attribute]] | |||
* [[How to edit an Attribute]] | |||
* [[How to import Attributes]] | |||
* [[How to remove Attributes from multiple Items]] | |||
* [[How to change multiple Attributes at once for Water Overlays]] | |||
| seealso= | |||
* [[Overlay Key]] | |||
* [[Global]] | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:14, 26 January 2023
A number of components, such as neighborhoods, areas, buildings and zones, have adjustable attributes. These attributes are used:
- to provide meaningful information
- as parameters in calculations
- to provide (visual) information to distinguish themselves among peers
Attributes can be defined and redefined by a user. Some attributes are predefined by the Tygron Platform and already exist as default properties of a component. Some components can even inherit properties from other type of components, such as a Building that inherits attributes from it's referenced Function.
In general the Tygron Platform allows users to inspect, adjust and reset existing attributes of these components and define and remove new ones.
The group of components than can store attributes is called Attribute Items. The current list of Attribute Items is:
- Areas
- Buildings
- Functions and their overrides
- Indicators
- Neighborhoods
- Net loads
- Net lines
- Net functions
- Overlays
- Panels
- Terrains
- Weathers
- Zones
Note that although Globals seem to behave similarly to attributes, they are not part of any specific Attribute Item in a project. Instead they are individual components part of the project.
Attribute values
An attribute always consists of a name and a value. The name of an attribute is usually written in capital letters, and uses underscores in place of spaces. The value must always be a number. It can be either a positive or a negative number. The number can also be a decimal number (I.e., the value is not necessarily a whole number).
Note that not there are some restrictions for attribute names.
Some components have properties which are also reflected in attributes. Properties such as the color of the component are present both as a dedicated property and as an attribute. By changing the property, the attribute is changed as well. When the attribute is changed, the property is changed as well.
Each component which can have attributes has their own list of attributes. When a given area has an attribute with a specific name, another area may or may not have an attribute with the same name as well. When 2 components have an attribute with the same name, their values are also still set per component. That means that they may coincidentally have the same value, but when the value of the attribute of one component is changed, the value of the attribute of the other component is not automatically changed as well.
Attribute arrays
- Main article: Attribute array
Attributes are most commonly a single value, but can also be an array of values.
Attribute values during a session
Attributes can be read during a session. Primarily, it is possible to read attributes of components using TQL. By requesting the value of an attribute of a component using TQL, the value of that attribute can be used in, for example, Excel calculations.
It is possible that, when requesting the value of an attribute of a component, that attribute does not exist for that component. In this case, the value of that attribute is deemed to be "0".
Note that this means that an attribute value of 0 can mean that the proper value of the attribute is 0, or that the attribute does not exist.
Attributes can also be changed during a session. This can be done either via Events or via TQL. Events, such as AREA_SET_ATTRIBUTE or ZONE_SET_ATTRIBUTE, can be used in the Tygron Platform to change the values of attributes. Attributes can also be changed using TQL, which means that attributes can be changed as a result of an Excel calculation.
Common attribute values
Some attributes may have a more exact spectrum of values which are valid. For example, the ACTIVE attribute is either 1 or a 0.
Note that these attributes can be given other values as well. The resulting behavior for calculations and functionality depending on these attributes is undefined.
ACTIVE
- Applies to: Areas, Neighborhoods, Overlays, Indicators and Stakeholders
Some components may have an "active" property. When that property indicates the component is active, the "ACTIVE" attribute's value is "1". When the component is inactive, the attribute's value is "0".
COLOR
- Applies to: Areas, Neighborhoods, Zones
- Main article: Color
Spatial components with attributes commonly have a "COLOR" attribute, defining the color by which they are displayed.The value corresponds to the color property of that component. When that color property is changed, the attribute is changed, and vice versa.
Examples of special attribute values
URBANIZATION
- Applies to: Neighborhoods
The "URBANIZATION" attribute is an indicator for the degree of urbanization. It ranges from 1 (dense urbanization) to 5 (virtually no urbanization).
NATURE_RESERVE
- Applies to: Areas
The "NATURE_RESERVE" attribute indicates whether an area is a protected area of nature. This usually means the allowance for pollution and noise is lower. Areas with an "NATURE_RESERVE" attribute value of "1" are deemed protected nature. When the attribute's value is 0, the area is not necessarily deemed protected nature.
Notes
- When removing attributes which are related to properties of the component, the value of the properties will be changed as well, as though the attribute was set to "0".
How-to's
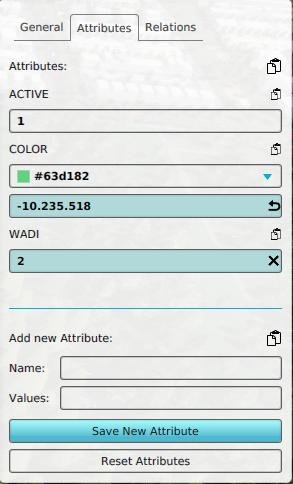
- How to add an Attribute
- How to remove an Attribute
- How to edit an Attribute
- How to import Attributes
- How to remove Attributes from multiple Items
- How to change multiple Attributes at once for Water Overlays