CSV (comma separated values): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==Creating a CSV file== | ==Creating a CSV file== | ||
We have a simple data set of a list of produce: 10 apples for 0,80 a piece, 5 oranges for 1,20 a piece, 1 tomato for 0,75 a piece and 3 onions for 0,50 a piece. We would like to create a table from a CSV file with columns with headers that display the name, type, | We have a simple data set of a list of produce: 10 apples for 0,80 a piece, 5 oranges for 1,20 a piece, 1 tomato for 0,75 a piece and 3 onions for 0,50 a piece. We would like to create a table from a CSV file with columns with headers that display the name, type, quantity and price of each record. | ||
We begin with the first line of column headers: | We begin with the first line of column headers: | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
apple; fruit; 10; 0,80</pre> | apple; fruit; 10; 0,80</pre> | ||
Now we add the other entries, resulting in a European CSV file, where the decimal separator is a comma and the value separator is a semicolon. This data convention is sometimes called | Now we add the other entries, resulting in a European CSV file, where the decimal separator is a comma and the value separator is a semicolon. This data convention is sometimes called SSV - Semicolon Separated Valeus: | ||
<pre>name; type; quantity; price | <pre>name; type; quantity; price | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
==CSV | ==CSV in the {{software}}== | ||
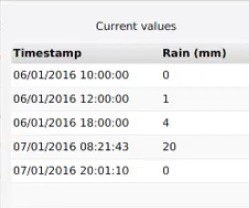
[[File:DynamicRainArray1.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Example of a dynamic rain array (timestamp/ rain in mm)]] | [[File:DynamicRainArray1.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Example of a dynamic rain array (timestamp/ rain in mm)]] | ||
CSV files can be used to | CSV files can be used to import or export data into the {{software}}. As there are many areas with this functionality in the platform, only some examples will be explained here. Below this article are links to how-to's with more information about specific situations. | ||
===Importing a CSV file in the Tygron Geodesign Platform=== | ===Importing a CSV file in the Tygron Geodesign Platform=== | ||
The CSV data structure and files are mostly used in the {{software}} as a means to import dynamic [[Attribute|attributes]]. By default, attributes of an overlay, such as rain over time, are generated as a linear event. To incorporate for example rain over time in where the amount of rain in mm varies, a custom option is available where an [[attribute array]] can be uploaded in CSV format. | |||
''It is important to note that such a CSV file containing a dynamic array, can contain up to a maximum of 10.000 records/ timestamps.'' | |||
Examples of data that can be imported as CSV: | |||
*[[Rain_model_(Water_Overlay)|Rain simulation time]] | |||
*[[Evaporation_model_(Water_Overlay)|Dynamic evaporation rates]] | |||
*[[Weir height (Water Overlay)|Weir height]] | *[[Weir height (Water Overlay)|Weir height]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Inlet_q_(Water_Overlay)|Inlet Q-t relation]] | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
===Exporting a CSV file from the Tygron Geodesign Platform=== | ===Exporting a CSV file from the Tygron Geodesign Platform=== | ||
It is also possible to export data from the Platform in CSV format | It is also possible to [[Export Geo data|export geo data]] from the Platform in CSV format. The following elements of the platform support exporting as a CSV file: | ||
*[[Buildings]] | *[[Buildings]] | ||
| Line 164: | Line 134: | ||
*[[Areas]] | *[[Areas]] | ||
*[[Measurement|Measurements]] | *[[Measurement|Measurements]] | ||
= | {{article end | ||
|seealso= | |||
[[File:YoutubeLogo1.jpg|thumb|left|link=https://youtu.be/GnTkziMUyIU| | * [[Time sequence (Water Overlay)]] | ||
*[[How to import a time sequence with a CSV]]<br> | * [[Measuring tool]] | ||
*[[How to load in dynamic rain and simulation time (Water Overlay)]]<br> | * For more information on the import and export of CSV files, see this video (Dutch only): | ||
*[[How to set dynamic breach height]]<br> | [[File:YoutubeLogo1.jpg|thumb|left|link=https://youtu.be/GnTkziMUyIU|Import and export of data with CSV files (Dutch only)]]{{clear}} | ||
*[[How to load in dynamic evaporation rate (Water Overlay)]]<br> | |howtos= | ||
* [[How to change multiple Attributes at once for Water Overlays]] | |||
*[[How to export objects | * [[How to import a time sequence with a CSV]]<br> | ||
* [[How to import a time sequence for multiple structures|How to import a time sequence for multiple hydraulic structures]]<br> | |||
* [[How to load in dynamic rain and simulation time (Water Overlay)]]<br> | |||
* [[How to set dynamic breach height]]<br> | |||
* [[How to load in dynamic evaporation rate (Water Overlay)]]<br> | |||
* [[How to export objects in a project to a CSV]] | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:Files]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:16, 30 January 2023
CSV files are used to transfer data sets between information systems that do not use the same (proprietary) data format. For example, by using the CSV format, data from a data base in a proprietary format can be transferred to a spread sheet program with another proprietary format.
Comma separated values (CSV) is a specification of this tabulated data, where the data is stored on single lines in a text based file and entries are separated with a comma or other character.
In the Anglo Saxon influence sphere, commas are in use as separators and periods as decimal separators. In the rest of the world commas are already in use as decimal separators and periods as thousand-separators. In these regions semicolons are used in stead of commas as value separator in a CSV file.
Another variation in separator characters is when copying an HTML table into memory. When pasting it in plain text, the tab character ('\t') is automatically used as separator in stead of a comma or semicolon.
A CSV file can be created and read with a simple text editor. The file consists of line entries that correspond with the rows in a spreadsheet. Each line (row) has the same number of (columns) entries, separated with a comma or other separator. The first line can be used to name column headers of the resulting table. Lines are sometimes ended with only a line feed and no carriage return, which results in the text being displayed in a text editor as one single line without separation per table row. Spreadsheets can ususally read these line feeds without problem, ordering the data in its proper rows again.
Creating a CSV file
We have a simple data set of a list of produce: 10 apples for 0,80 a piece, 5 oranges for 1,20 a piece, 1 tomato for 0,75 a piece and 3 onions for 0,50 a piece. We would like to create a table from a CSV file with columns with headers that display the name, type, quantity and price of each record.
We begin with the first line of column headers:
name; type; quantity; price
Then we add the first data record on the next line:
name; type; quantity; price apple; fruit; 10; 0,80
Now we add the other entries, resulting in a European CSV file, where the decimal separator is a comma and the value separator is a semicolon. This data convention is sometimes called SSV - Semicolon Separated Valeus:
name; type; quantity; price apple; fruit; 10; 0,80 orange; fruit; 5; 1,20 tomato; vegetable; 1; 0,75 onion; vegetable; 3; 0,50
Save the text file with ".csv" as extention, to save it as a CSV file and not as a regular text file.
This CSV file will result in a similar table as below, when importing the file in a spread sheet program:
| name | type | quantity | price |
| apple | fruit | 10 | 0,80 |
| orange | fruit | 5 | 1,20 |
| tomato | vegetable | 1 | 0,75 |
| onion | vegetable | 3 | 0,50 |
An example of the data as a USA/UK CSV file, where the decimal separator is a period and the value separator is a comma:
name, type, quantity, price apple, fruit, 10, 0.80 orange, fruit, 5, 1.20 tomato, vegetable, 1, 0.75 onion, vegetable, 3, 0.50
Which will result in the following table:
| name | type | quantity | price |
| apple | fruit | 10 | 0.80 |
| orange | fruit | 5 | 1.20 |
| tomato | vegetable | 1 | 0.75 |
| onion | vegetable | 3 | 0.50 |
Most programs that can receive CSV files, provide an option to select what to use as separator when importing the file.
CSV in the Tygron Platform
CSV files can be used to import or export data into the Tygron Platform. As there are many areas with this functionality in the platform, only some examples will be explained here. Below this article are links to how-to's with more information about specific situations.
Importing a CSV file in the Tygron Geodesign Platform
The CSV data structure and files are mostly used in the Tygron Platform as a means to import dynamic attributes. By default, attributes of an overlay, such as rain over time, are generated as a linear event. To incorporate for example rain over time in where the amount of rain in mm varies, a custom option is available where an attribute array can be uploaded in CSV format.
It is important to note that such a CSV file containing a dynamic array, can contain up to a maximum of 10.000 records/ timestamps.
Examples of data that can be imported as CSV:
Exporting a CSV file from the Tygron Geodesign Platform
It is also possible to export geo data from the Platform in CSV format. The following elements of the platform support exporting as a CSV file:
How-to's
- How to change multiple Attributes at once for Water Overlays
- How to import a time sequence with a CSV
- How to import a time sequence for multiple hydraulic structures
- How to load in dynamic rain and simulation time (Water Overlay)
- How to set dynamic breach height
- How to load in dynamic evaporation rate (Water Overlay)
- How to export objects in a project to a CSV
See also
- Time sequence (Water Overlay)
- Measuring tool
- For more information on the import and export of CSV files, see this video (Dutch only):