Evaporation model (Water Overlay): Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
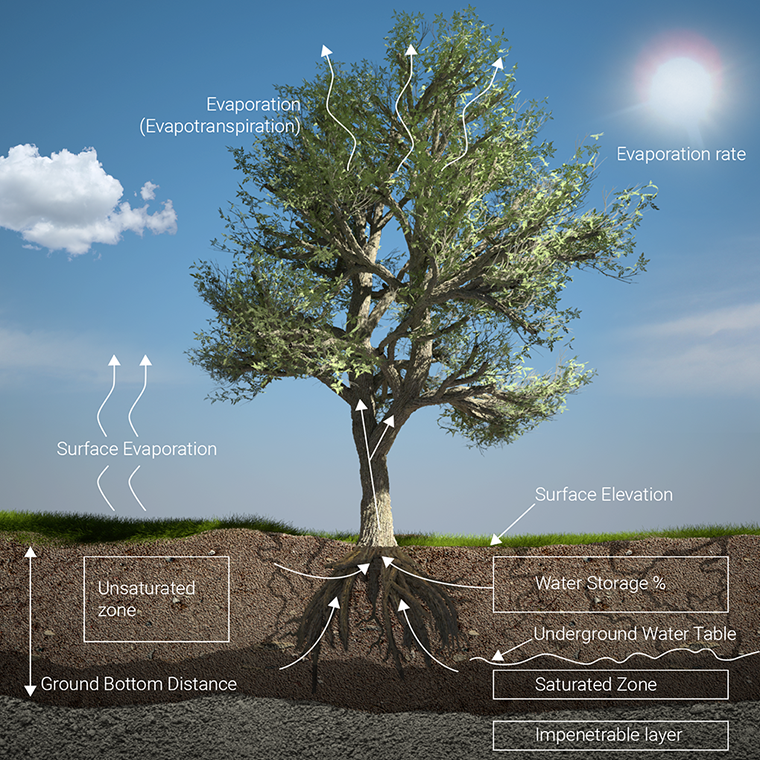
Water can evaporate from the hydrological model over time. Multiple forms of evaporation are implemented, namely surface and underground evaporation. | Water can evaporate from the hydrological model over time. Multiple forms of evaporation are implemented, namely surface and underground evaporation. | ||
Both forms of evaporation can be configured directly by setting the [[ | Both forms of evaporation can be configured directly by setting the [[weather (Water Overlay)|weather]]'s [[Evaporation m (Water Overlay)|evaporation rate]]. If the evaporation rate is set to 0, no evaporation will take place in any form. | ||
The weather's evaporation rate is defined as a period during which a certain rate of evaporation will take place, similar to [[ | The weather's evaporation rate is defined as a period during which a certain rate of evaporation will take place, similar to [[rain model (Water Overlay)|rainfall]]. Multiple periods of evaporation can be defined, and at any specific moment during the simulation an exact evaporation rate is defined by the weather. | ||
Per form of evaporation, the weather's evaporation rate is used as a base for determining the exact amount of evaporation per timestep. | Per form of evaporation, the weather's evaporation rate is used as a base for determining the exact amount of evaporation per timestep. | ||
=====Surface evaporation model===== | =====Surface evaporation model===== | ||
Water situated on the [[Surface model (Water Overlay)|surface]] is conceptually able to evaporate. The amount is based on the weather's [[ | Water situated on the [[Surface model (Water Overlay)|surface]] is conceptually able to evaporate. The amount is based on the [[weather (Water Overlay)|weather]]'s [[Evaporation m (Water Overlay)|evaporation rate]] and the overlay's [[Surface water evaporation factor model attribute (Water Overlay)|SURFACE_WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR]]. These two multiplied result in a evaporation amount per second. The water on the surface of each individual cell is then subject to the calculated rate of evaporation. | ||
=====Underground evaporation model===== | =====Underground evaporation model===== | ||
Water can evaporate from the [[Underground model (Water Overlay)|underground]] if the cell has | Water can evaporate from the [[Underground model (Water Overlay)|underground]] if the cell's surface meets either of the following criteria: | ||
* A construction on the surface | |||
** The construction has a non-zero [[Water evaporation factor (Water Overlay)|WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR]]. | |||
** The construction has a non-zero [[Root depth m (Water Overlay)|ROOT)DEPTH_M]]. | |||
* No construction on the surface | |||
** The surface terrain type has a non-zero [[terrain water evaporation factor (Water Overlay)|WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR]]. | |||
** The surface terrain type has a non-zero [[terrain root depth m (Water Overlay)|ROOT)DEPTH_M]]. | |||
In other words: if a construction is present the construction's properties are used, otherwise the terrain's properties are used. | |||
Conceptually, water can evaporate from the underground via crops and foliage. These can draw water from the unsaturated and saturated zones in the underground, if their roots reach deep enough and the terrain or construction have a positive evaporation factor. Water is drawn from the underground and evaporated into the air, effectively removing it from the hydrological model. | Conceptually, water can evaporate from the underground via crops and foliage. These can draw water from the unsaturated and saturated zones in the underground, if their roots reach deep enough and the terrain or construction have a positive evaporation factor. Water is drawn from the underground and evaporated into the air, effectively removing it from the hydrological model. | ||
Revision as of 09:43, 18 June 2019
Water can evaporate from the hydrological model over time. Multiple forms of evaporation are implemented, namely surface and underground evaporation.
Both forms of evaporation can be configured directly by setting the weather's evaporation rate. If the evaporation rate is set to 0, no evaporation will take place in any form.
The weather's evaporation rate is defined as a period during which a certain rate of evaporation will take place, similar to rainfall. Multiple periods of evaporation can be defined, and at any specific moment during the simulation an exact evaporation rate is defined by the weather.
Per form of evaporation, the weather's evaporation rate is used as a base for determining the exact amount of evaporation per timestep.
Surface evaporation model
Water situated on the surface is conceptually able to evaporate. The amount is based on the weather's evaporation rate and the overlay's SURFACE_WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR. These two multiplied result in a evaporation amount per second. The water on the surface of each individual cell is then subject to the calculated rate of evaporation.
Underground evaporation model
Water can evaporate from the underground if the cell's surface meets either of the following criteria:
- A construction on the surface
- The construction has a non-zero WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR.
- The construction has a non-zero ROOT)DEPTH_M.
- No construction on the surface
- The surface terrain type has a non-zero WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR.
- The surface terrain type has a non-zero ROOT)DEPTH_M.
In other words: if a construction is present the construction's properties are used, otherwise the terrain's properties are used.
Conceptually, water can evaporate from the underground via crops and foliage. These can draw water from the unsaturated and saturated zones in the underground, if their roots reach deep enough and the terrain or construction have a positive evaporation factor. Water is drawn from the underground and evaporated into the air, effectively removing it from the hydrological model. Water for evaporation can only be drawn from sections of the underground which are within the root depth.
Evaporation can only take place if the roots of the terrain or construction can reach underground water. The depth the roots can reach is defined by either the construction's ROOT_DEPTH_M or the surface terrain's ROOT_DEPTH_M.
The underground evaporation can be configured directly by changing the terrain type's WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR and construction 's WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR. If these attributes are set to 0, no underground evaporation will take place.
Similar to the surface evaporation, the rate of underground evaporation is also determined by the weather's evaporation rate.
Again, the amount of evaporation per timestep is WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR x WEATHER_EVAPORATION_RATE.
Underground evaporation first draws water from the saturated region and then from the unsaturated region. The sum of these two with be no larger than WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR x WEATHER_EVAPORATION_RATE.
Related formulas
Related models
Notes
- Surface evaporation only uses one factor: the overlay's SURFACE_WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR.
- Zero evaporation is allowed, but negative is not.
- Underground evaporation will not take place when the Underground model is not active.