Subsidence calculation: Difference between revisions
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
===Subsidence calculation=== | ===Subsidence calculation=== | ||
{{:Subsidence formula (Subsidence Overlay}} | {{:Subsidence formula (Subsidence Overlay}} | ||
===Indexation=== | ===Indexation=== | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 10 February 2021
The subsidence model calculates the gradual downward settling of the ground's surface where a peat layer is present. The considered subsidence takes place due to oxidation and compaction of the peat layer. The total subsidence is currently calculated as the result of oxidation and compaction over the years. Oxidation is dependent on the ground water level and the clay thickness. Compaction is dependent on the toplayer thickness, the peat fraction and raised surface terrain.
The ground water level is initialized by either raster or surface area data and optionally adjusted each year (indexation). When indexation is active, the surface water level is adjusted for the settling each year and the ground water levels will change accordingly.
The calculation model is configured by the subsidence overlay wizard and it's result are visualized with the subsidence overlay.
Calculations
During a calculation step, the following aspects are calculated in order:
- The temperature at the start of the year is calculated
- Based on that, parameter a of the oxidation formula is calculated
- The oxidation subsidence is calculated
- The compaction subsidence is calculated
- The surface water levels are lowered by the amount of subsidence times the indexation
- The ground water level is lowered based on subsidence and surface water level indexation
- The new ground water level serves as input for the next calculation step
Oxidation calculation
The amount of subsidence due to oxidation is calculated by the following formula:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_O = a_{y} \cdot d_{gw,y,c} - b \cdot d_{ct,c} - c}
where
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_O} is the subsidence due to oxidation.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{gw,y,c}} is the calculated ground water depth for year y in cell c.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_{y}} is the calculated a parameter value for the current year Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} .
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{ct,c}} is the clay thickness of the terrain in cell c, defined by CLAY_THICKNESS
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b} is the b parameter value, defined by the model attribute B
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c} is the c parameter value, defined by the model attribute C
This formula was provided by experts, who have derived this formula empirically.
Ground water depth
At the start of a simulation, the ground water depth is initialized with the ground water depth GeoTIFF (if provided) and is optionally overwritten by (managed) water areas' water level.
Furthermore, the ground water level can be managed with drainages (provided as underground buildings), either actively or passively.
Additionally the terrain height can change due to subsidence that occurred in previous years and due to actions taken that raised the terrain. Managed water areas can react to these changes when indexation is configured. For indexation, see indexation formula.
The following formulas describe how the yearly adjusted ground water depths are obtained.
Ground water level managed by drainages
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{gw,y} = \begin{cases} d_{d,active}, & \text{if }n\text{ drainage is larger than 0} \\ max(0.0, d_{a} - \Delta{d_{a,y}} + d_{d,passive}, & \text{if }n\text{ drainage is smaller than 0} \\ max(0.0, d_{gw} + \Delta{d_{a,s,y}}) & \text{ otherwise } \end{cases} }
where
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{gw,y}} is the calculated ground water depth of a grid cell at year y.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{d,active}} is the ground water depth actively maintained by a drainage
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{a}} is the ground water depth of the managed water area.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{a,y}}} is the area water level adjustment for year y.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{d, passive}} is the ground water level passively maintained by drainages.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{a,s,y}}} is the ground water level increase calculated based on the are water level adjustment due to indexation and the subsidence in the previous year.
Ground water level managed by water areas
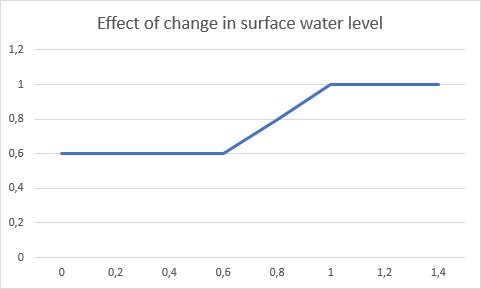
The ground water level can also be managed by water areas, which control the surface water levels. To make sure ground water levels do not rise (too much), surface water levels in the water areas can be lowered automatically with respect to the subsidence. This process is called indexation. The new ground water level can then be estimated based on the indexation on the managed water level of surface water and the calculated subsidence of the previous year. The increment in ground water level is rarely exactly the adjustment of the managed surface water level and is often less, depending on the relative depth of the surface water level. The following formulas have been developed to estimate the increase of the ground water level.
The new relative surface water level depth is calculated as:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{inc}} = - \Delta{d_{a,y-1}} - s_{y-1}}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{a,adj} = d_{a} + \Delta{d_{inc}}}
Next, based on the old and new depths, the ground water depth change is divided into three sections, each which its own rate of contribution.
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{low}} = 0.6 \cdot min(0.6, d_{a,adj})- min(0.6, d_{a})}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{high}} = 1.0 \cdot (\max(0.0, d_{a,adj}- max(0.0, d_{a})}
Finally, the ground water depth change is calculated and the new ground water depth is obtained:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{gw,y}} = \Delta{d_{low}}+\Delta{d_{mid}}+\Delta{d_{high}}}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{gw,y} = max(0.0, d_{gw,0} + \Delta{d_{gw,y}})}
where
- is the current relative water depth of water area a.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{a,adj}} is the adjusted relative water depth of water area a.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{a,y-1}}>} is the water level adjustment for indexation of current year y.
- is the subsidence that occurred up to year y.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{gw,y}} is the calculated adjusted ground water depth for year y, based on the occurred subsidence and indexation of previous years.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{gw,0}} is the initial ground water depth at the start of the simulation.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{gw,y}}} is the estimated change of the ground water level based on occurred subsidence and indexation.
Compaction calculation
The amount of subsidence due to compaction is calculated by the following formula:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{C} = \begin{cases} ( a_{peat} \cdot p_{c} + a_{tl} \cdot d{tl,c} ) \cdot log10(t_{days}) + a_h \cdot \Delta{h} + b_p \cdot p_{c} + b_{tl} \cdot d_{tl,c} & \text{if } \Delta{h} \text{ is larger than 0} \\ 0 & \text{ otherwise} \end{cases} }
where
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{C}} is the calculated subsidence due to compaction.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_{c}} is the peat fraction of the respective grid cell c.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{tl,c}} is the top layer thickness of the respective grid cell c.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{h}} The terrain height increase as a result of the actions taken during a session, such as the creation of levees.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_{days}} is the number of days in a year times the current year being calculated.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_{peat}} is the first regression constant (0.015853041) for the effect of the peat fraction and time in days.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_{tl}} is the first regression constant (0.006617643) for the top layer thickness and time in days.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_h} is a regression constant (0.200468677) for the change in surface height, for example caused by added materials.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_{peat}} is the second regression constant (0.02348519) for the effect of the peat fraction.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_{tl}} is the second regression constant (-0.010061616) for the top layer thickness.
This formula is based on provided expert data in the form of a reference table, indicating the amount of subsidence based on the parameters used in the formula above. The formula's results conform to the reference table to within an average of a tenth of the margin of error of the original table.
Subsidence calculation
Subsidence formula (Subsidence Overlay
Indexation
Indexation is the policy of managing the surface water level such that it keeps the nearby ground water levels (more or less) at the same depth.
A water area which is fully indexed (1.0 = 100%) will have its surface water level lowered by the same amount as the terrain height has lowered due to subsidence. Since it lowers just as much as the terrain itself, the ground water level(s) relative to the surface of the land will remain the same.
In a water area which is not indexed (0%) the surface water level remains at the same level. Any subsidence taking place will lower the land, and thus reduce the relative water depth. An area indexed by 50% will have the surface water level lower by half of the amount of subsidence.
To make matters a bit more complex, the change in surface water level rarely changes the ground water level with the same amount. Instead, the amount the ground water level changes is estimated using the ground water depth formula for water areas.
The indexation formula is as followed:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{a} = \frac{\sum(S_{c,y})}{n_{a}}}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{a,y}} = -S_{a} \cdot i_a}
where:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{a}} is the average subsidence for water area a.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{c,y}} is the subsidence in grid cell c for year y.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n_a} is the number of non-water grid cells within water area a.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta{d_{a,y}}} is the amount the water area is changed in meters.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i_a} is the indexation fraction for area a.
Drainage calculation
Drainage can be added to the 3D World as a construction, which affects the ground water levels. Two types of drainage exist: passive and active drainage.
Passive Drainage
When passive drainage is applied, the lowest and highest ground water levels are adjusted to match the surface water level, plus their respective PASSIVE_DRAINAGE attributes. This effect is applied once, at the start of the subsidence calculations. Afterwards, the values of the ground water level can vary due to indexation.
Active Drainage
When active drainage is applied, the ground water levels are set to a specific level relative to the surface. The exact distance between the ground water level and the surface is defined by the "drainage" Function Value of the construction placed. This effect is continuous; at the end of the calculation and for all intermediate steps the ground water level will still be at that same level.
Terrain height
The height of the terrain can be manipulated during a session by stakeholders taking a land sculpting action, creating open water, or constructing levees. These actions will result in settlement, which can be found under the Settlement result type. Creating or demolishing constructions generally do not change the height of the land, and do not result in changes in the settlement results.
Configuring overlays
The subsidence overlay has a number of ways to configure it. Both values which serve as input for the overlays directly, as references to attributes of areas which provide input for the calculations.
Keys
The subsidence overlay has a "Keys" tab in the right panel in the editor. Most keys are attributes of areas. When the overlay calculates, it will look per grid cell for the existence of these attributes.
| Icon | Key | Unit | Range | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
WATER_LEVEL | m + datum | The datum height of the water level in the Water Area. | n/a | |
| |
WATER_LEVEL_OUTPUT | m + datum | The new datum height of the water level in the Water Area as a result of indexation in response to subsidence. | n/a | |
| |
INDEXATION | m | When Indexation is non zero, the water level is automatically adjusted each simulation year, depending on the calculated subsidence. Indexation may range from 0 (0%) to 1 (100%). | 10.7 | |
| |
SUBSIDENCE | boolean | Whether or not subsidence should be calculated for a terrain or in a given area. Subsidence is calculated when the value is not equal to 0. | false | |
| |
CLAY_THICKNESS | m | The thickness of the clay layer on the peat, for the calculation of the oxidation component of subsidence. | 0.2 | |
| |
PEAT_FRACTION | The fraction of the soil composed of peat, for the calculation of the compaction component of subsidence. | 0.4 | ||
| |
TOPLAYER_THICKNESS | m | The thickness of the layer covering the peat, for the calculation of the compaction component of subsidence. | 1.2 | |
| |
DRAINAGE | m + datum | The Drainage value has several behaviors, depending on its value. See the behavior description below. | -1.0 |
Besides these attributes, 2 more model parameters can be configured.
Years
The amount of years to simulate during the calculation, in 1-year steps. It is possible to set this value anywhere between 1 to 1000. This parameter can be configured with the YEARS model attribute of the Subsidence overlay.
Ground Water Tiff
If the option to use a Ground Water Tiff is checked, a GeoTiff can be selected to use for the ground water levels. You can either use any of the provided default GeoTiffs, or upload and use your own.
Three ground water GeoTiffs covering the Netherlands are available by default. These GeoTiffs are a combination between a high resolution GeoTiff containing ground water levels for rural areas and a low resultion GeoTiff containing ground water levels for city areas, where data from the low resolution GeoTiff was only used to fill the gaps in the high resolution GeoTiff. One of the available ground water GeoTiffs, relevant for the Subsidence, is the Mean Lowest Watertable (MLW, or GLG in Dutch).
Attributes
The subsidence overlay also has model attributes. All attributes have a default value, but can be changed to configure the subsidence calculation.
Parameter b (Subsidence Overlay) Parameter c (Subsidence Overlay)
| Icon | Attribute | Unit | Range | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
A | The A parameter in the Oxidation formula. | 0.023537 | ||
| |
CLIMATE START TEMP | °C | The average temperature in the first year of the subsidence simulation. | 10.1 | |
| |
CLIMATE FINAL TEMP | °C | The average temperature in the final year of the subsidence simulation. | 10.7 | |
| |
CLIMATE_SOIL_TEMP_FACTOR | The soil temperature factor used to recalculate the climate values between 1-year calculation steps. | 0.5 | ||
| |
CLIMATE_OXIDATION | The oxidation factor used to recalculate the climate values between 1-year calculation steps. | 0.67 | ||
| |
DEFAULT_CLAY_THICKNESS | m | If no clay thickness value can be found in a particular grid cell, this value is used instead | 0.2 | |
| |
DEFAULT_PEAT_FRACTION | If no peat fraction value can be found in a particular grid cell, this value is used instead. | 0.4 | ||
| |
DEFAULT_TOP_LAYER_THICKNESS | m | If no top layer value can be found in a particular grid cell, this value is used instead. | 5.0 | |
| HI PASSIVE DRAINAGE | m | When a drainage is active, the highest ground water level (ghg) is lowered by x meters. | -0.10 | ||
| LOW PASSIVE DRAINAGE | m | When a drainage is active, the lowest ground water level (glg) is lowered by x meters . | 0.0 | ||
| |
YEARS | year | The amount of years to simulate during the calculation, in 1-year steps. | 30 |


