Demo 3-30-300 Project
The Demo 3-30-300 project is available for all users and can be found in the main menu under Edit projects. This project does not count towards your license.
This project is intended for people who are working in fields such as climate adaptation, livability, policies regarding green environments, and urban planning.
This project showcases the method for calculating the 3-30-300 policy guidelines in the Tygron Platform.
The demo is a working project in which a number of generally available Grid Overlays in the Tygron Platform are combined to perform specific policy-dictated calculations. Following the 3-30-300 guidelines as closely as possible, these methods calculate sightlines onto trees, foliage coverage, and distance to significant usable green spaces.
3-30-300
3-30-300 is a set of policy guidelines which are intended to provide consistent and testable metric for a green urban environment. The name refers to the separate guidelines which are each defined by one of the numbers. The guidelines are always combined for a complete consideration, but the individual rules and their implementations are best described separately.
Rule-3
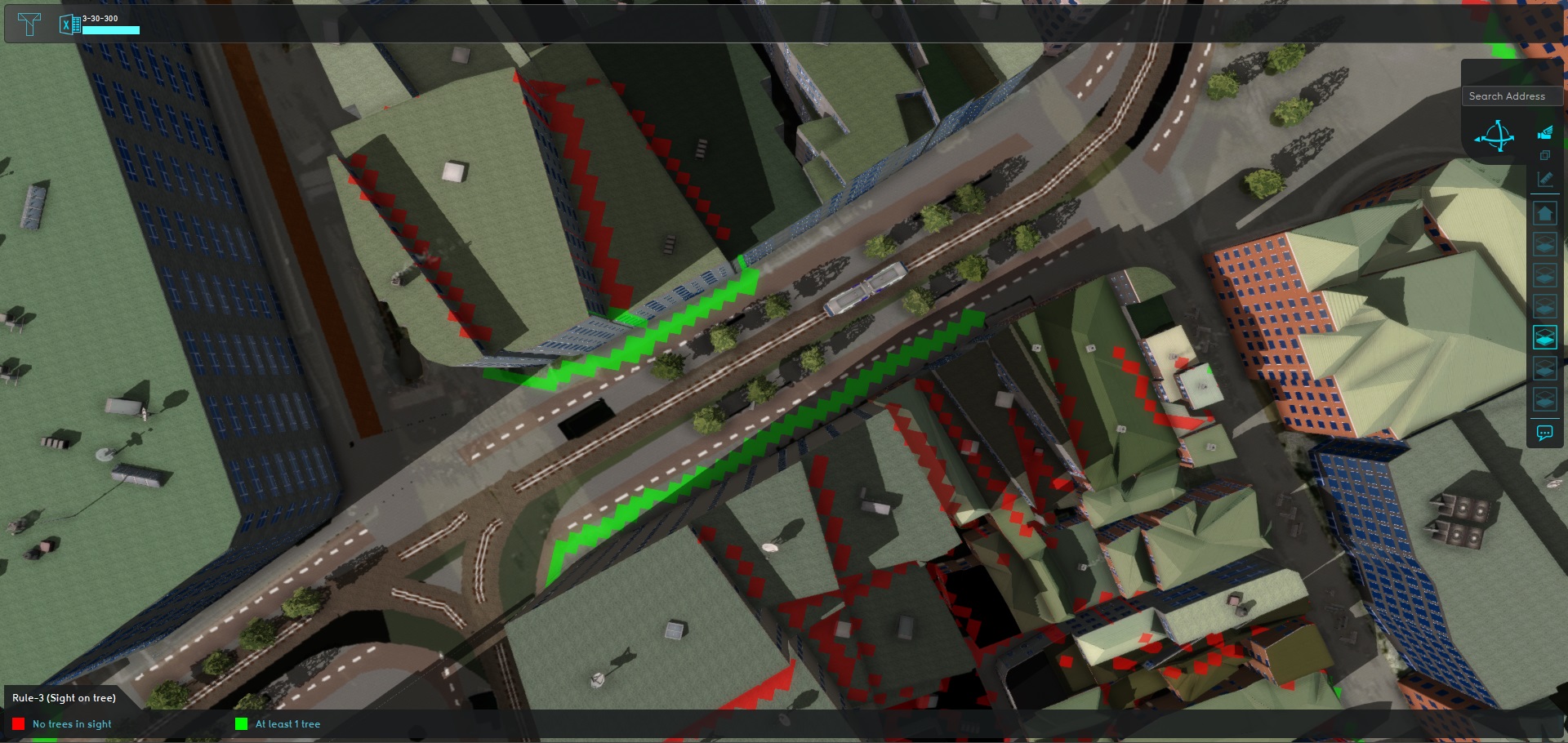
Rule 3 dictates that, from any residence, at least 3 trees should be visible. Although explicitly counting the amount of trees is currently not possible, it ís possible to draw sightlines from trees, detect outside walls of residences, and combine the two to find the walls which do or do not have sight on a tree.
- A map of Residences is created.
- A map of Walls of residences is created.
- An additional Attribute is attached to Functions of trees, indicating the distance at which they can be seen.
- A Distance Sight Overlay is used to draw sightlines to trees, by referring to that Attribute.
- A Combo Overlay combines Walls of residences and tree sightlines, to display which walls can or cannot see a tree.
Rule-30
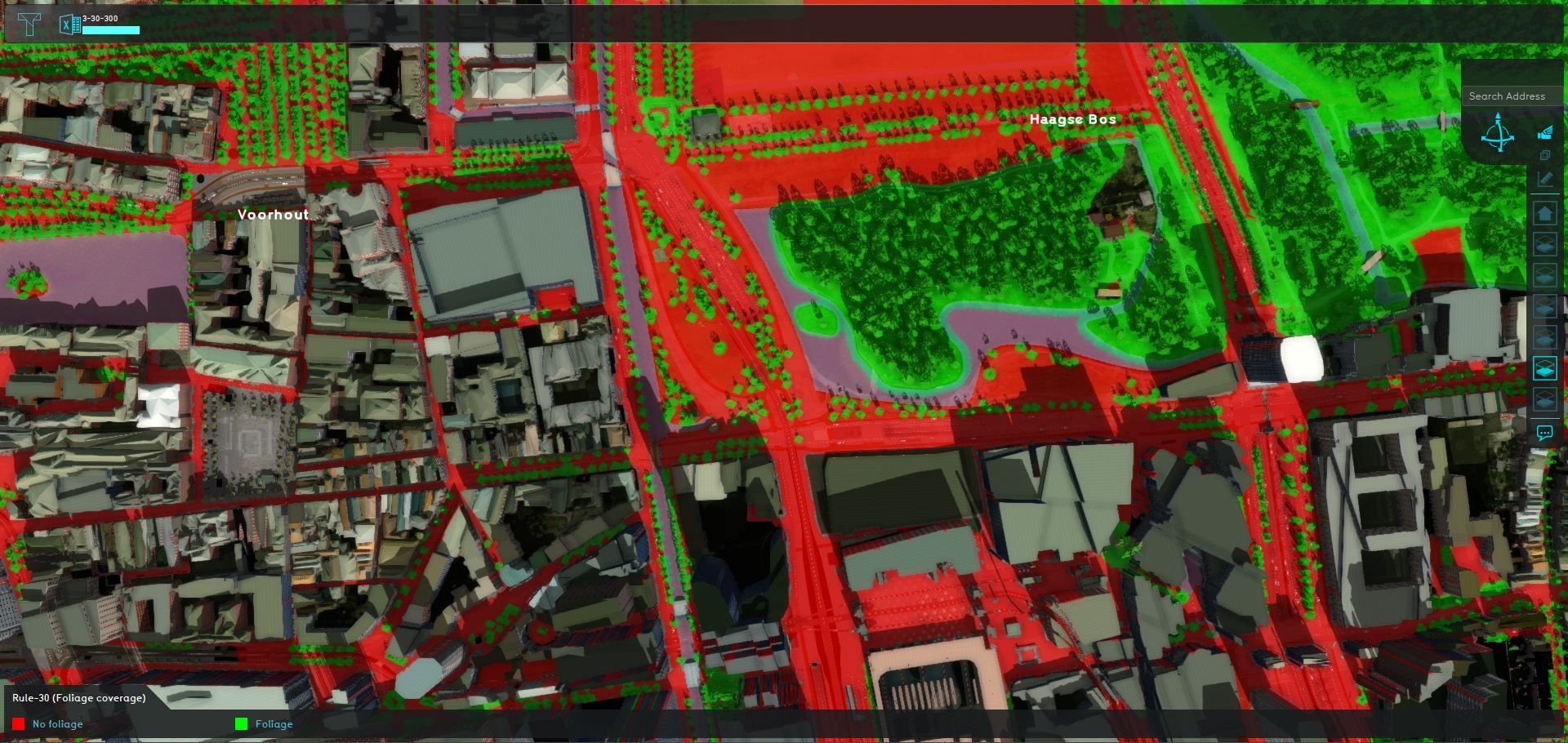
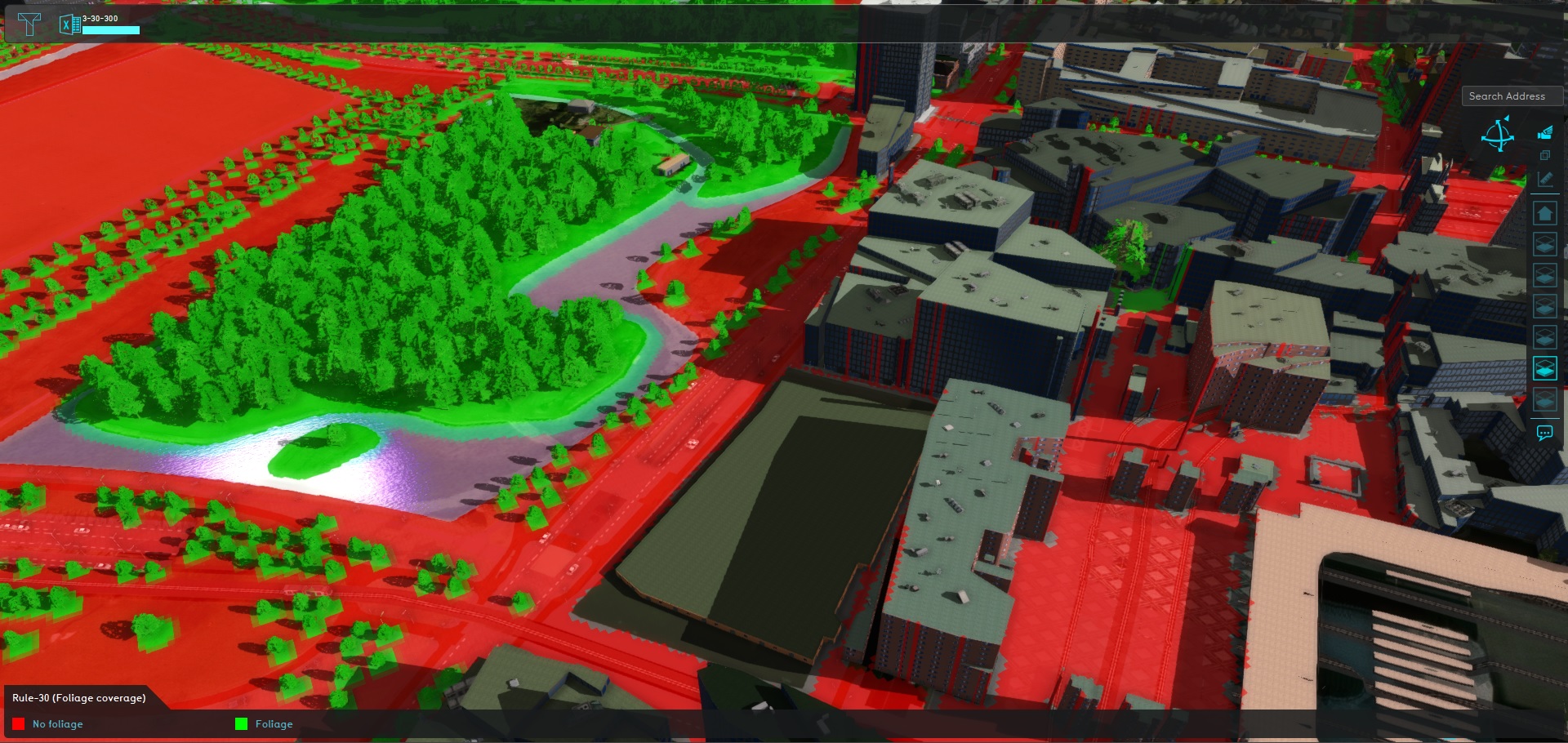
Rule 30 dictates that 30% of the public space must feature foliage. The Tygron Platform offers some options for estimating the presence of foliage. The definition of public space can be manually defined with a few simple rules.
- A map of Public space is created.
- A Heat Stress Overlay is used, set to the Foliage result type, leverages a built-in method to obtain foliage heights.
- A Combo Overlay combines Public space and Foliage, to display which public locations are also covered by foliage.
Rule-300

Rule 300 dictates that a residence must be at most 300m away from a publicly accessible and usable green area of at least 1 hectare in size (10.000 m²). This requires calculating in which locations 1 hectare of qualifying green can be found, then computing the routes which allow reaching that green in 300m.
- A map of Residences is created. Note that this can directly leverage the setup from the 3-rule as well.
- A map of Public space is created. Note that this can directly leverage the setup from the 30-rule as well.
- Function Values for bicycle paths were modified, so that they have at least one bicycle.
- Function Values for pedestrian paths were modified, so that they have at least one pedestrian.
- An Average Overlay creates a map of GREEN_M2.
- A Combo Overlay filters it, so that any remaining green is in a public space, and thus public green.
- An Average Overlay checks how much of the area within a 80 meter radius is public green. This provides a fraction of how much of such green is nearby.
- A Combo Overlay calculates from that fraction and the radius of 80 meters the amount of public green nearby, in m².
- A Combo Overlay checks whether the amount of public green nearby is sufficient to count for this rule. I.e. whether there is more than 10.000 m² (1 hectare). The result is points where there is 1 hectare nearby
- An Average Overlay draws the 80 meter radii of those points.
- A Combo Overlay checks which public green overlaps with the computed radii. This results in a map which highlights all the public green which is part of a large enough green structure.
- A Travel Distance Overlay, set to a distance of 300m, uses the green structures as destinations. It is set to allow travel routes based on bicycles and pedestrians.
- A Combo Overlay combines Walls of residences and travel distance, to display which residences are or are not in the specified distance.
Techniques
This calculation makes use of the following technique(s):
Sub-calculations
For some of the rules to be implemented correctly, some other basic information needs to be rasterized.
Residences
Residences can be rasterized as follows:
- First creating multiple Average Overlays which obtain the individual unit sizing per category of residence.
- The results can then be combined in a Combo Overlay.
Techniques
This calculation makes use of the following technique(s):
Residence walls
Determining the locations of walls requires finding the places where the DSM makes a sudden jump upward. This can be done
- Add a Heightmap Overlay set to DTM.
- Add a Heightmap Overlay set to DSM.
- Add an Average Overlay, which slightly averages out the DSM spatially.
- Add a Combo Overlay which checks that the averaged DSM is greater than the DTM as well as the DSM. This provides a map where places are highlighted where there are changes in height due to Buildings being present, and will specifically find cells just on the "outside" of the wall.
- Add an Average Overlay which slightly averages the residences, so for any residential Building a few cells around it have a non-zero value as well.
- Use a Combo Overlay to finds all the cells which are both height differences just outside walls, and just outside residences.
Techniques
This calculation makes use of the following technique(s):
Public space
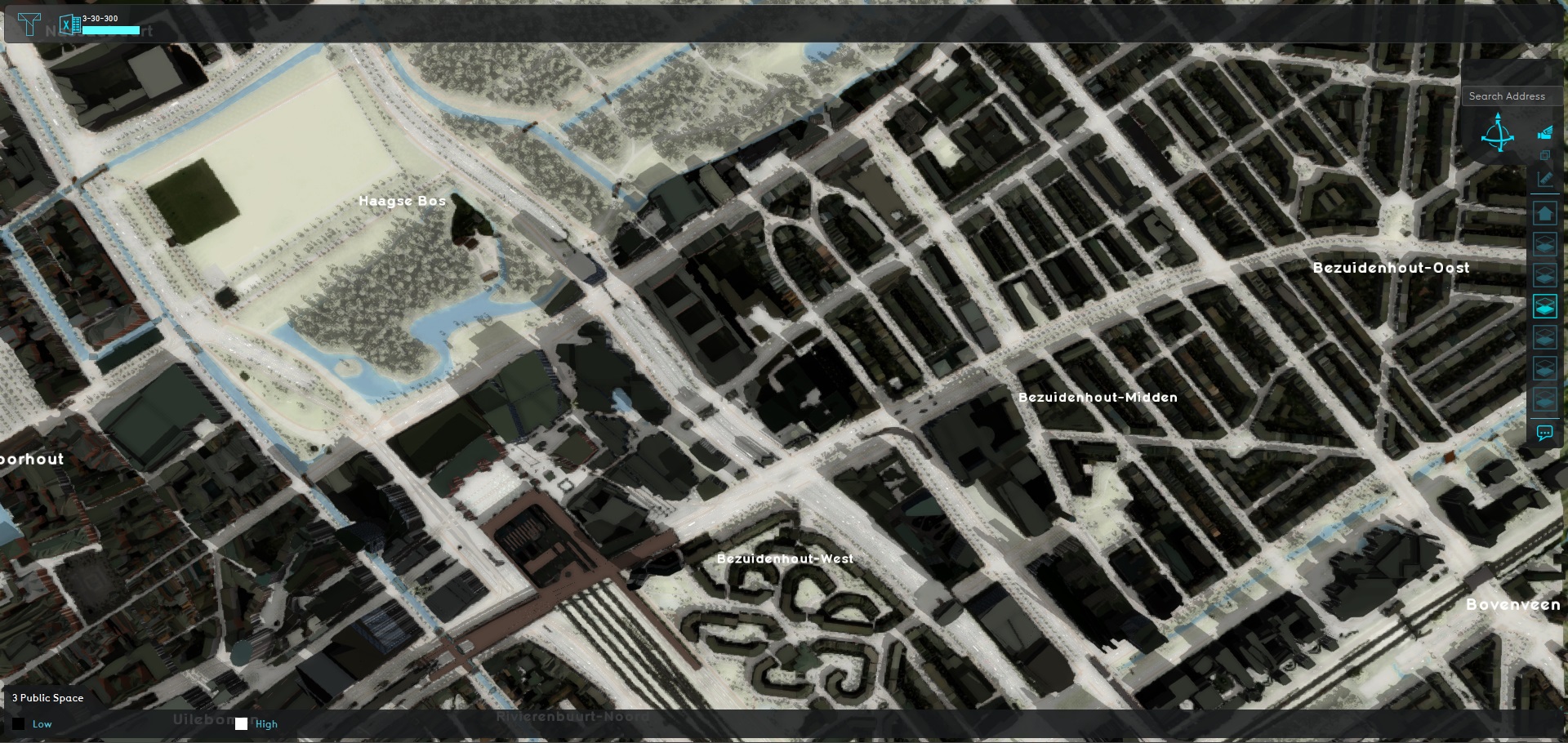

Public spaces can either be determined by testing what is, or testing what isn't public space. The approach used in this project is by testing what isn't public space.
- Add an Average Overlay set to the Attribute "PRIVATE_YARD" (to find yards)
- Add an Average Overlay set to the Attribute "SOLID" (to find structures)
- Add an Average Overlay set to the Attribute "NUM_TRAINS" (to find train tracks)
- Add a Combo Overlay to combine the results together, and flip the results. Any location in which any of the described conditions can be found is not public. Any place where not of the described conditions are found can be considered public space.
More conditions can be added in future implementations, depending on the required accuracy of the estimation, and the specific features expected to be present in any environment.
Indicator
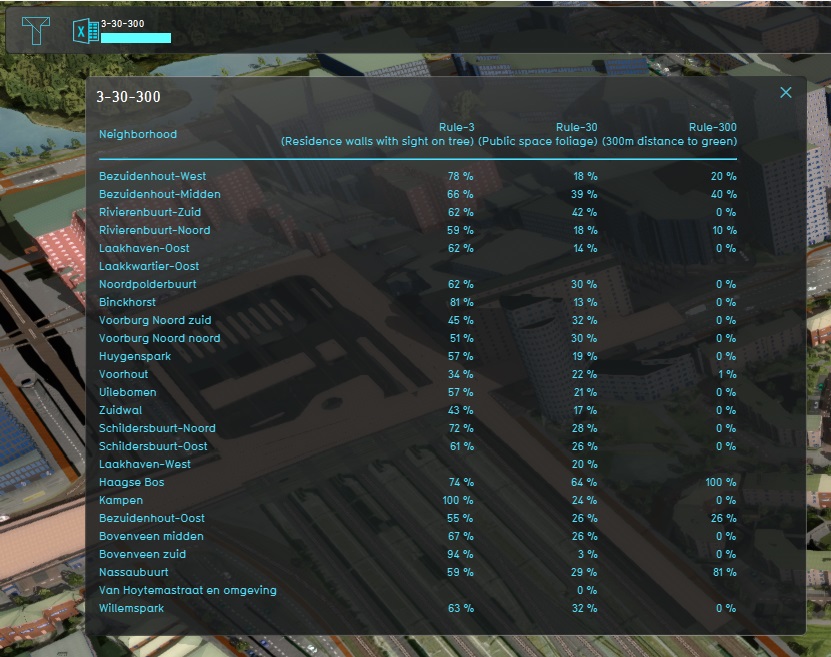
An Indicator can use queries to automatically aggregate values from Overlays and display statistical results. Because all the result Overlays produce either a NO_DATA (ignorable), 0 (does not meet requirements), or 1 (meets requirements), the following query can be permuted in 6 variants (3 overlays and 2 values) to compute a score for each of the 3 rules:
SELECT_LANDSIZE_WHERE_NIEGHBORHOOD_IS_X_AND_GRID_WITH_ATTRIBUTE_IS_[attribute]_AND_MINGRIDVALUE_IS_[value]
The Overlays for rule-3, rule-30, and rule-300 have been given the Attributes OVERLAY_RULE_3, OVERLAY_RULE_30, and OVERLAY_RULE_300 respectively.
The values are 0, or 1, for "all testable locations" and "all good locations".
Results are aggregated per Neighborhood.
