Radial well aquifer benchmark (Water Module): Difference between revisions
(→Setup) |
(→Setup) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
The outlet is placed on the cells x = 25 and y = 25 as an [[Inlet (Water Overlay)|inlet]] with a negative inlet. | The outlet is placed on the cells x = 25 and y = 25 as an [[Inlet (Water Overlay)|inlet]] with a negative inlet. | ||
[[Inlet q (Water Overlay)| | [[Inlet q (Water Overlay)|INLET Q]] is set to <math>\frac{-Q_0}{3600*24}</math> | ||
[[Underground (Water Overlay)|UNDERGROUND]] is set to true (1.0) | |||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Revision as of 15:52, 16 December 2020
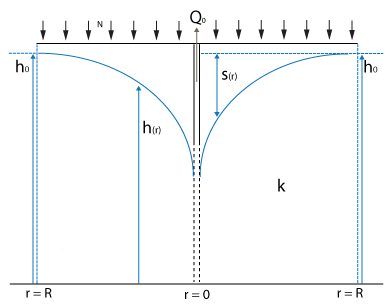
This testcase demonstrates a situation where a well is pumping up ground water. A characteristic ground water level curve will form over time.
Formulas
Stationary lowering of the ground water table in a closed water transmissive layer can be described by the following formula [1]
where:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle phi(0)} : stable water level at the considered stable water table edge
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle phi(r)} : water level between the considered stable water table edge and the well
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle phi(rw)} : water level in the well
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle kD} : transmissivity of the aquifer in m² / day
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} : distance to the well
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R} : distance of the considered stable water table edge to the well
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Q_0} : amount of water pumped out in m³ / day
Setup
We use the following setup in our tests. The grid size used is 51 by 51, with a configurable cell size of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle dx} in meters. There is one underground outlet, which pumps water away continuously with a default amount per second.
The outlet is placed on the cells x = 25 and y = 25 as an inlet with a negative inlet.
INLET Q is set to Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-Q_0}{3600*24}}
UNDERGROUND is set to true (1.0)
References
- ↑ Verruijt, A. (1970). Theory of Groundwater Flow. Macmillan, London.