Elevation model: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
#REDIRECT [[Terrain height]] | #REDIRECT [[Terrain height]] | ||
==What is an elevation model== | ==What is an elevation model== | ||
| Line 6: | Line 5: | ||
An elevation model (or DEM, Digital Elevation Model), is a model representation of terrain heights; the quantitative measurement of vertical elevation change in a landscape. On a small scale, differences in terrain height can affect shade and water distribution. On a larger scale, terrain height has an effect on weather and climate patterns.{{clear}} | An elevation model (or DEM, Digital Elevation Model), is a model representation of terrain heights; the quantitative measurement of vertical elevation change in a landscape. On a small scale, differences in terrain height can affect shade and water distribution. On a larger scale, terrain height has an effect on weather and climate patterns.{{clear}} | ||
== | ==Implementation in the {{software}}== | ||
The elevation model (also referred to as DEM) in the {{software}} is a 3-dimensional grid with values indicating the terrain height in meters relative to {{datum}}. [[Terrain]] in this context meaning the soil and the subsurface. <br> | |||
The [[3D World]] visualizes the elevation model inherently as the bottom plane upon which all other features, such as [[Construction]]s, are placed. Changes in terrain height are similarly changes in the height of that plane.<br> | |||
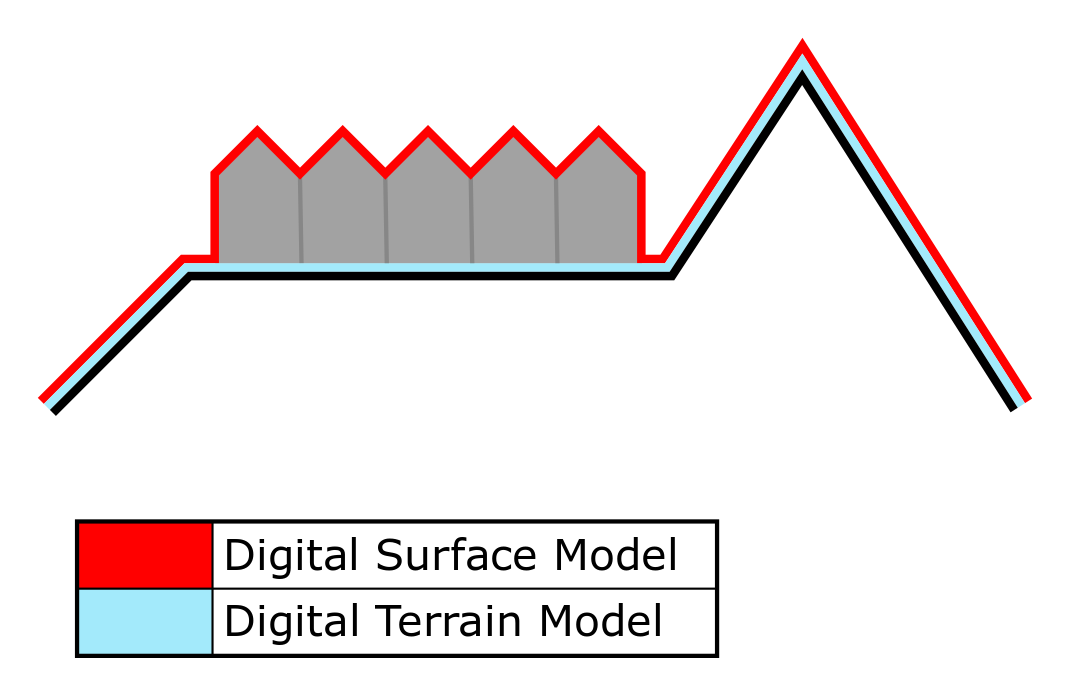
In the {{software}}, the elevation model offers terrein heights representation as both a DTM (Digital Terrain Model) and as a DSM (Digital Surface Model). A DTM represents the bare ground surface without any objects like plants and buildings. In contrast; a DSM represents the earth's surface including all objects (e.g. houses, trees, etc.) on it. Therefore features such as [[Construction]]s are explicitly not a part of the DTM, but are a part of the DSM. In locations with [[Water (Terrain Attribute)|water]], the elevation model follows the bottom of the water body for both the DTM and the DSM. | |||
The elevation model | The elevation model is generated when a [[Project]] is first created. Any changes to the elevation model are applied directly, including [[manually drawn changes]] as well as [[imported changes]]. | ||
===Heightmap Overlay=== | ===Heightmap Overlay=== | ||
{{main|Heightmap Overlay}} | {{main|Heightmap Overlay}} | ||
Revision as of 09:55, 21 August 2020
Redirect to:
What is an elevation model
An elevation model (or DEM, Digital Elevation Model), is a model representation of terrain heights; the quantitative measurement of vertical elevation change in a landscape. On a small scale, differences in terrain height can affect shade and water distribution. On a larger scale, terrain height has an effect on weather and climate patterns.
Implementation in the Tygron Platform
The elevation model (also referred to as DEM) in the Tygron Platform is a 3-dimensional grid with values indicating the terrain height in meters relative to datum. Terrain in this context meaning the soil and the subsurface.
The 3D World visualizes the elevation model inherently as the bottom plane upon which all other features, such as Constructions, are placed. Changes in terrain height are similarly changes in the height of that plane.
In the Tygron Platform, the elevation model offers terrein heights representation as both a DTM (Digital Terrain Model) and as a DSM (Digital Surface Model). A DTM represents the bare ground surface without any objects like plants and buildings. In contrast; a DSM represents the earth's surface including all objects (e.g. houses, trees, etc.) on it. Therefore features such as Constructions are explicitly not a part of the DTM, but are a part of the DSM. In locations with water, the elevation model follows the bottom of the water body for both the DTM and the DSM.
The elevation model is generated when a Project is first created. Any changes to the elevation model are applied directly, including manually drawn changes as well as imported changes.
Heightmap Overlay
- Main article: Heightmap Overlay
More insight into the elevation model can be provided by adding the Heightmap Overlay, which is a Grid Overlay showing the (average) height of the terrain per grid cell.
Elevation model generation
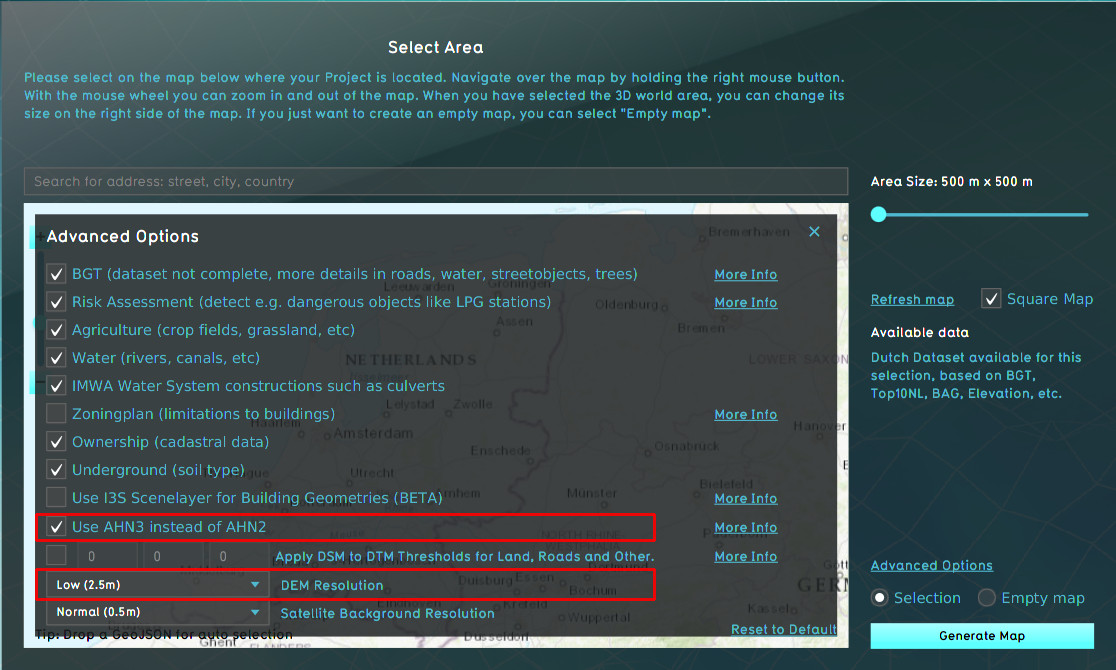
In the Netherlands, the following data sources are used to construct the elevation model:
By default the AHN3 and BGT are used. If a datasource is deactivated, the alternative is used.
DTM (Terrain height)
The DTM is determined as follows:
- The ESRI DTM is resampled to the same resolution as the AHN DTM and AHN DSM.
- The AHN DTM serves as the base data for the resulting elevation model DTM.
- In locations where the AHN DTM has NO_DATA values (such as waterbodies), the ESRI DTM is used.
- Optionally, if the option for applying thresholds is selected, the AHN DSM heights are used instead of the so far determined DTM heights, if the difference between the two does not exceed a certain threshold. The following features can have the DSM heights applied instead:
- Bare land
- Roads
- Crop fields/agriculture
DSM (Construction height)
For Constructions, the average height of the AHN DSM is determined for the Construction's footprint polygon from the features data source. That average height of the AHN DSM is then determined to be the height of the Construction.
Using image recognition techniques, the footprint polygon of the Constructions may be split up into multiple Construction sections, each with their own polygon. The AHN DSM's average height is then determined per individual section, so that the variability in the rooftops of the Construction can be taken into account.
The resulting Construction heights are not made part of DTM. Instead, they are stored as properties of the Constructions in the Project.
Water
In locations with water features, the water's depth is "carved" into the DTM as determined up to this point. The following parameters are used to do so:
- The default water depth of the determined Terrain Type of the water feature is used.
- The angle of repose of the underground Terrain Type present at or near the sides of the water feature.
Starting from the edges of the polygon of the water feature, a downward slope is created at the determined angle of repose. The downward slope continues until either it meets the slope generated from the other end, or it reaches the determined default depth relative to the DTM. This means that thin waterrways will not be as deep as their default water depth allows them to be, and that large water bodies are likely to have flat water bottoms.
The resulting terrain height changes are made part of the DTM.
Elevation model generation (outside the Netherlands)
How-to's
- How to change how the default elevation model is generated
- How to import a GeoJSON to change the elevation model
- How to import a GeoTIFF to change the elevation model
- How to import a GeoJSON of waterways
- How to import a GeoTIFF of waterway depths
- How to use the terrain height brush in selection mode
- How to use the terrain height brush in live sculpting mode
- How to export the elevation model