Bottom flow pankow benchmark (Water Module): Difference between revisions
(→Setup) |
|||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
<ref name=" | <ref name="Pankow68">J. Pankow en P.E. Rijtema, 1970. De resultaten van het waterbalansonderzoek in 1968 voor de objecten met een constant slootpeil in Hoenkoop. Nota 567. Instituut voor Cultuurtechniek en Waterhuishouding, Wageningen.</ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
{{Water Module buttons}} | {{Water Module buttons}} | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 15 December 2020
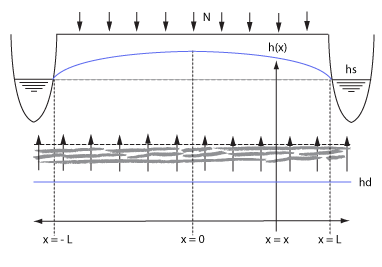
This testcase demonstrates a situation where a parcel of land is situated between two waterways with a stable water level. In combination with seepage, a characteristic curve will form over time, as shown in the image below. It is described in a water balance research in 1968 of Pankow and Rijtema [1], and also contain the accompanying formulas that describe the curve. In this case, we use the case which does not take into account the additional water flow resistance of the waterway. Secondly, rain could also be taken into account, but we set that to 0 to exclusively benchmark the seepage mechanics. The continuous rainfall case is already tested in freatic groundwater levels benchmark.
Formulas
Due to seepage and two stable water levels left and right, a specific ground water table curve will form. Part of the water seeped in will flow left and part of the it will flow right. Note that the time at which this balance occurs is dependent on the starting situation.
The following formula, taken from [1], describes the curve of ground water levels when the ground water flow to the left and right have become stable:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A = \frac{(h_1-h_2) cosh \frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c}}}{\frac{x_2^2}{2 KD} \cdot \frac{2 KD \cdot c}{x_2^2} \cdot ( cosh (\frac{x_2}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c} }) -1) - \frac{x_1^2}{2 KD} \cdot \frac{2 KD \cdot c}{x_1^2} \cdot ( cosh (\frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c} }) -1) } = \frac{(h_1-h_2) cosh \frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c}}}{c \cdot ( cosh (\frac{x_2}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c} }) -1) - c \cdot ( cosh (\frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c} }) -1) } }
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A = N + \frac{h_d-h_1}{c}}
Simplified without rain N:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_1 = h_d - \frac{(h_1-h_2) cosh \frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c}}}{( cosh (\frac{x_2}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c} }) -1) - ( cosh (\frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c}}) -1) } }
To test the correctness of the seepage, the formula can test the following condition with the accepted error margin :
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left | h_d - \frac{(h_1-h_2) cosh \frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c}}}{( cosh (\frac{x_2}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c} }) -1) - ( cosh (\frac{x_1}{\sqrt{KD \cdot c}}) -1) } - h_1 \right |< \epsilon}
where:
- : distance (m) of the point of measurement compared to the middle of the parcel.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_2} : distance (m) of the second point of measurement, which is always situated 3 meters from the edge of the waterway.
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_1} : measured ground water level (m) at Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_1}
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_2} : measured ground water level (m) at Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_2}
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_d} : seepage head
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle KD} : measured horizontal transmissivity of the ground layer (m2/day)
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N} : additional ground water due to rainfall (m/day).
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon} : accepted error margin
Setup
We setup the following situation. The grid size used is 53 by 5, with a configurable cell size of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle dx} in meters. There are two waterways, left and right, both with a stable water level of 3 meters.
One inlet is placed on the cells x = 1 and y = 1 to 3 and an other is placed on the cells x = 52 and y - 1 to 3, with the following setup to ensure a stable water level:
- UPPER_THRESHOLD set to 3 m.
- LOWER_THRESHOLD set to 3 m.
- Inlet Q set to 0, such that is unlimited.
The terrain height is set to: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin {cases} 0, & \text{if }x < 4 \text{ or } x > 48\\ 1.5, & \text{if }x = 4 \text{ or } x = 48\\ 3.5, & \text{if }x = 5 \text{ or } x = 47\\ 5, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}}
Depending on the specific test case, the seepage head Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_s} is set to:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin {cases} h_s, & \text{if }x > 5 \text{ and } x < 47\\ none, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}}
Similarly, the seepage c (in days) is set to:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin {cases} c, & \text{if }x > 5 \text{ and } x < 47\\ none, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}}
An aquifer can be added to configure the horizontal infiltration speed. An important thing to note here, is that the KD value used in the report [1] is derived from changes in water head over time, and does not mention the storage capacity of the soil. Therefor, in order to configure the Aquifer KD value in the Tygron Platform, the KD value has to be multiplied with the storage percentage.
The water level is configured to 3 m for all cells, resulting in an initial water level above and below ground of 3 meters.
The simulation time is set to n days, with rain set to 0 mm. To configure this, the rain set is set to Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [3600 \cdot 24 \cdot n,0]} .
Results
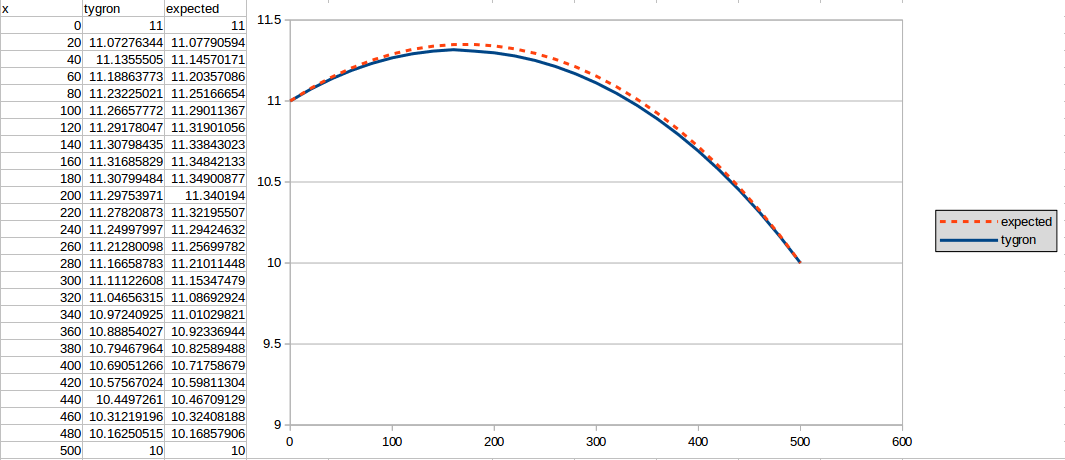
365 days
The first result is generated for n = 365:
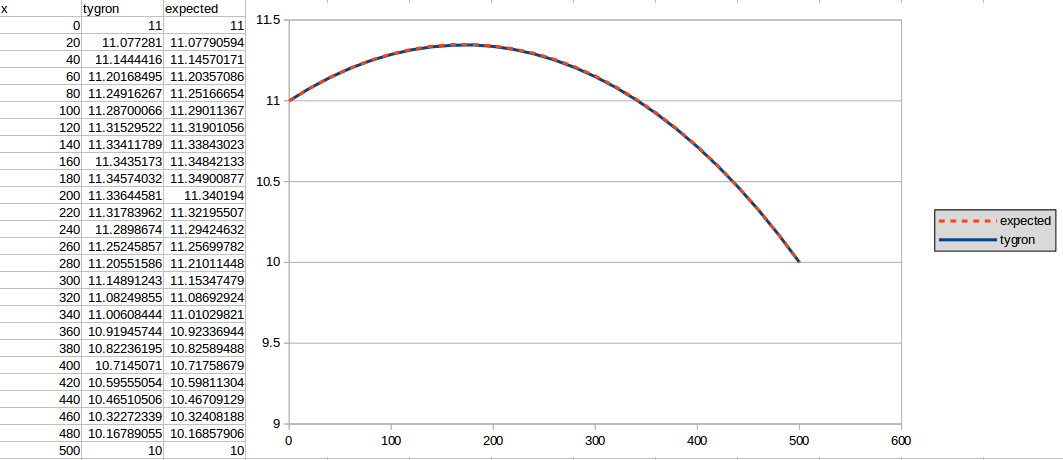
730 days
The second result is generated using n = 730:
Notes
- The amount of days it takes to reach the stable solution is highly dependent on the starting situation.
References