Pet result type (Heat Overlay): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
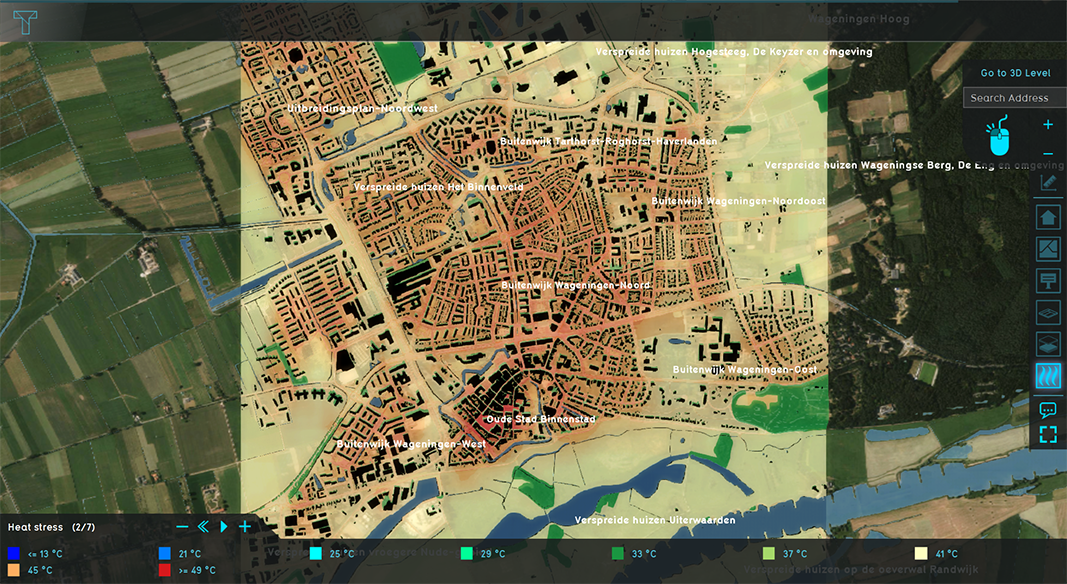
{| | [[File:DPRA Heatstress overlay.PNG|350px|thumb|right|PET (physiological equivalent temperature or heat stress) result type overlay (Wageningen)]] | ||
{{result types|<onlyinclude> | |||
{{result types|type=row|overlay=Heat | |||
|name=PET | |||
|icon=Overlay icon heat pet.png | |||
|unit=°C | |||
| | |mode=[[Result types (Heat Overlay)#Date Time type|Date-Time]] | ||
| | |description=The calculated physiological equivalent temperature. | ||
}}</onlyinclude>}} | |||
|°C | |||
|[[Result | |||
|The calculated physiological equivalent temperature. | |||
The physiological equivalent temperature is a value which expresses the effective outdoor temperature of a (complex) outdoor situation as an equivalent (simple) indoor situation. The equivalence is determined as the point where the heat balance of the human body is balanced with the surrounding environment.<ref name="pet" /> In other words, the PET of any given situation outdoors is equal to the temperature indoors at which the human body would gain or lose the same amount of heat. | The physiological equivalent temperature is a value which expresses the effective outdoor temperature of a (complex) outdoor situation as an equivalent (simple) indoor situation. The equivalence is determined as the point where the heat balance of the human body is balanced with the surrounding environment.<ref name="pet" /> In other words, the PET of any given situation outdoors is equal to the temperature indoors at which the human body would gain or lose the same amount of heat. | ||
= | {{article end | ||
|notes= | |||
|seealso= | |||
* [[Pet relative result type (Heat Overlay)]] | * [[Pet relative result type (Heat Overlay)]] | ||
|references= | |||
<references> | <references> | ||
<ref name="pet">Biometeorology education and research network. Physiological equivalent temperature. https://www.biomet-education.net/glossary/physiological-equivalent-temperature/. Last visited: 16-12-2019</ref> | <ref name="pet">Biometeorology education and research network. Physiological equivalent temperature. https://www.biomet-education.net/glossary/physiological-equivalent-temperature/. Last visited: 16-12-2019</ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
}} | |||
{{HeatOverlay result type nav}} | |||
{{ | |||
Latest revision as of 11:58, 13 September 2021
| Icon | Result type | Unit | Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
PET | °C | Date-Time | The calculated physiological equivalent temperature. |
The physiological equivalent temperature is a value which expresses the effective outdoor temperature of a (complex) outdoor situation as an equivalent (simple) indoor situation. The equivalence is determined as the point where the heat balance of the human body is balanced with the surrounding environment.[1] In other words, the PET of any given situation outdoors is equal to the temperature indoors at which the human body would gain or lose the same amount of heat.
See also
References
- ↑ Biometeorology education and research network. Physiological equivalent temperature. https://www.biomet-education.net/glossary/physiological-equivalent-temperature/. Last visited: 16-12-2019