Shade calculation model (Heat Overlay)
Whether a cell is in the shade or not is an important factor in the Heat Overlay. Whether a cell is shaded or not determines which PET function is used, PETsun or PETshade, night. In the model described by the DPRA Heat stress report, cells can be shaded by buildings, terrain and foliage.
The shade is dependent on the location of the sun. This in turn is dependent on the date and the time of day and the world location of the project.
Since each timeframe result of a Heat Overlay is related to a particular date and time of day, each time frame will have a related sun altitude and sun azimuth angle. These angles are calculated automatically based on the world location of your project and the date of the timeframe.
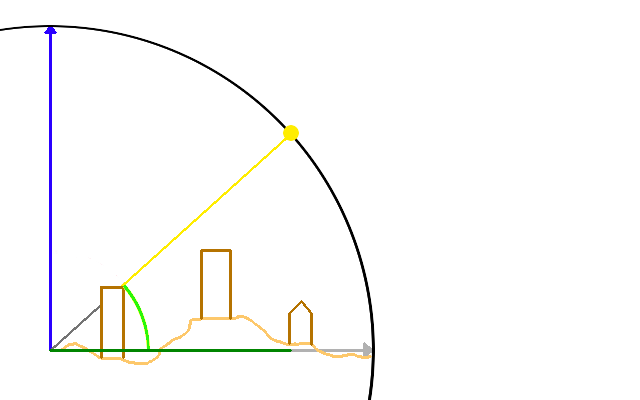
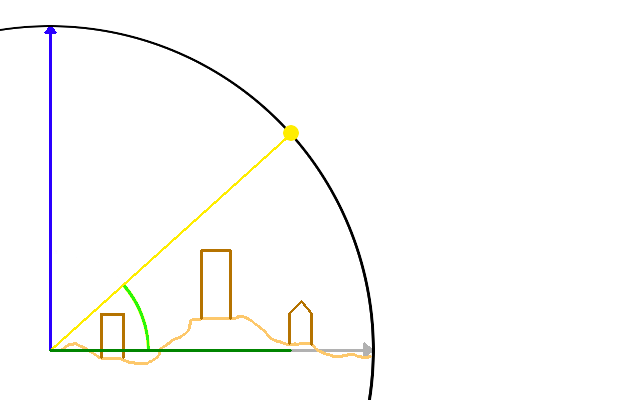
Once the sun angles and the building, terrain and foliage height are known, whether the cell is shaded or not is computed as follows for each cell:
- Travel away from the cell in the direction of the sun azimuth angle.
- For each cell traversed this way, calculate the height of the sun ray based on the altitude angle.
- Compare the sun ray altitude with the maximum height (terrain, building and foliage) at the traversed cell.
- If the surface height in the traversed cell higher, the cell is shaded and we can stop.
- If the sun ray altitude in the traversed cell is higher, the calculation is performed again for the next traversed cell.
- If all cells are traversed and the computation didn't stop in any cell, the cell can be reached by direct sunlight and the cell is not shaded.
-
Rays to the sky are blocked by a tall construction, so the cell is considered to be in the shade.
-
Rays to the sky are uninterrupted, so the cell is in direct sunlight.
Notes
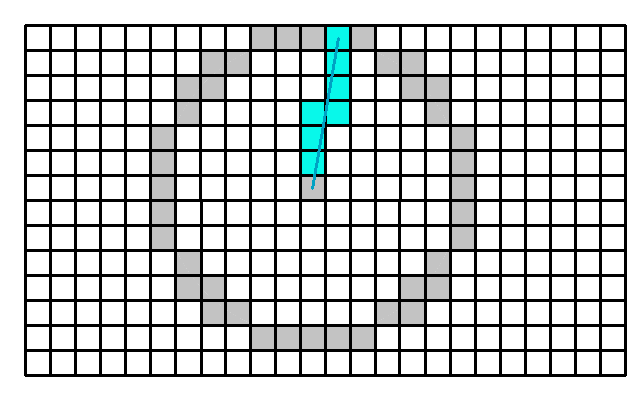
- Shade calculations are based on the 2D models of Buildings. When a Building has a 3D model applied to it, the 3D model is for visual purposes only. The Building still has a 2D polygon and height properties associated with it, forming a box-like structure based on which the shade is computed.
See also