How to configure the Water Overlays
Please note: This page is currently being updated.
This page describes several use cases and examples of configurations in different water overlays based on the water module.
Basics
Enhancements
Excessive water
Flooding
These use-cases can be implemented best using the Flooding Overlay.
- Levee breach with all water inside the project area (river, small lake)
- Levee breach with water from outside the project area (large lake, sea)
- Multiple sequential breaches
Rain
These use-cases can be implemented best using the Rainfall Overlay.
Water shortage
These use-cases can be implemented best using the Groundwater Overlay.
- Drought from excessive drains in the project area
- Drought from excessive evaporation in the project area
Water quality
Stationary analyses
Time-controlled flow rate in a breach area
To create a variable Outlet Q in a breach area, a CSV (comma-separated values) file can be imported. Below the steps on how to create such a breach area. For this example we create the CSV in Excel, but you can also use another program to create the CSV.
How to set-up your CSV in Excel:
- Open Excel.
- In the first column, define your time steps. This can be in seconds, minutes, hours or days.
- Add the corresponding flow rates per step in the second column.
- Save the Excel as a CSV.
How to import the CSV as the flow rate:
- Either add a breach area or have your GeoJSON file with your breach area ready. The area should have at least a breach floor attribute.
- Add a Flooding Overlay.
- Go to the Configuration Wizard of the Flooding Overlay.
- In step 2.1 either select the attribute that specifies your breach floor or import your GeoJSON file.
- Click on Next.
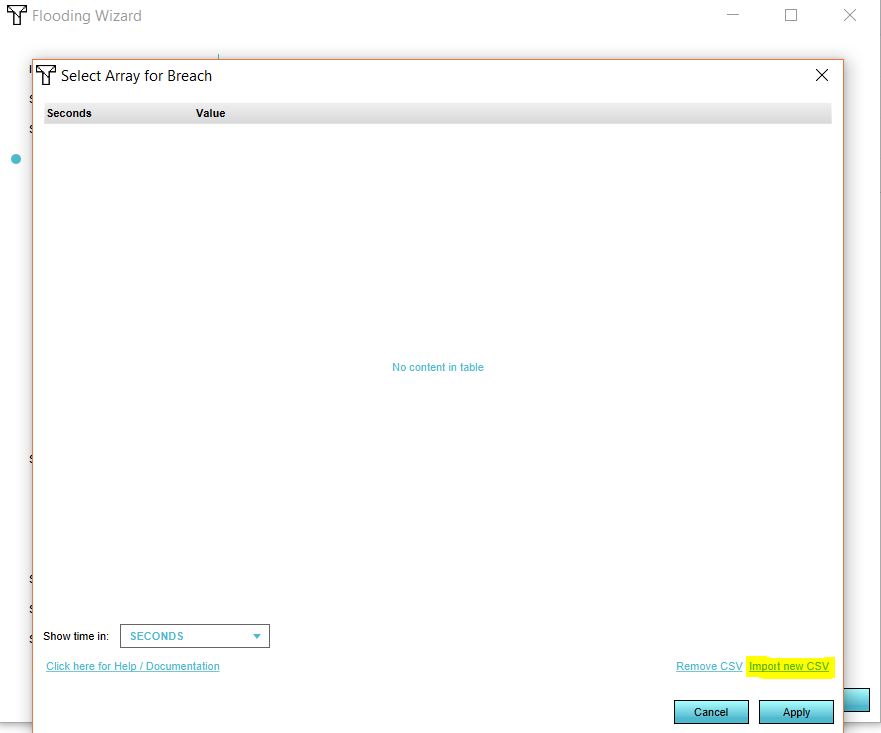
- In the dropdown menu, select your breach area. Now click on Edit.
- Import your CSV file by selecting the CSV file.
- Select the time units in your file.
- Select the seperator for your file.
- Click on Apply.