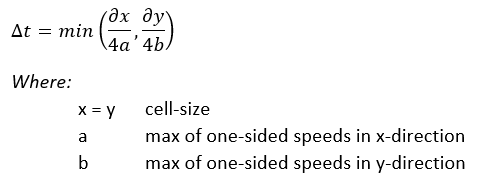Flooding Overlay
What is the Flooding overlay
The Flooding Overlay is developed for the computation of surface (water) flow in a wide range of applications. These applications include large scale inundations due to dike breaches and inundations at the bottom of hill-slopes. Therefore the commonly applied 2D Saint Venant Equations are implemented on a highly parallel applicable explicit numerical scheme suitable for Tygron GPU clusters.
Adding and removing
- Select in the editor 'Geo Data' from the ribbon
- Select 'Overlays' from the ribbon bar
- Select the Flooding Overlay from the drop down menu
- Select in the editor 'Geo Data' from the ribbon
- Select 'Overlays' from the ribbon bar
- Select the Flooding Overlay from the list of active overlays on the left panel
- Select 'remove' from the bottom of the left panel
- Confirm the removal in the pop up confirmation message
Configuring the Overlay
The Flooding Overlay has a configuration wizard which helps the user with setting up the Overlay. The Configuration wizard can be found on the right panel, when the overlay is selected. The wizard contains generic steps for the Water Overlays page, but has also a specific step for the Flooding Overlay:step 2.1: the Breach area. Below this step is explained. Please see the Water Overlays page for more information on how to go through the generic steps of the wizard.
Defining a Breach area
The breach area is the location where the inflow of water starts and results in a flooding. In the Platform this is defined as an Area where the terrain height is lower than the surrounding areas causing water to flow through this 'hole'. Basically, an hole in the DEM is made in where water starts flowing.
Attributes
The area can have/needs to have the following attributes. The name of the attribute may differ from the name stated below. In the Configuration Wizard the name of the attribute can be linked to the correct attribute.
| Attribute | Unit | Description | Optional | Example value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breach_floor | m | The ground floor height of the breach area | No | -4 |
| Outlet_level | m + datum | The water level in the breach area | Yes, if not specified the default value -100.000 is used which means this value is ignored | 2 |
| Outlet Q | m3/s | The amount of water that is flowing through the breach | Yes, if not specified,... | -4 |
| Outlet_capacity | m3/s | The maximum amount of water that can flow into the project area | Yes, if not specified, the volume of the adjacent waterbody is used | 500.000 |
It is possible to model different scenario's, using one or more of the attributes defined in the table above. For example, if you want to model what happens when there is a dike breach near a very large waterbody. You will not have to create a project in where the whole waterbody is present. If knowing or estimating for example the maximum volume of the water body, this amount can be filled in the Outlet_capacity attribute to model the correct inflow of water from the large waterbody.
The breach area can be defined in two ways: drawing an area manually or importing a breach area.
Drawing the area manually
Read the following page how to add and draw a new area. Don't forget to add the attributes to the area.
By checking or unchecking the 'Active in Simulation' checkbox, the breach area is either included or not included in the calculation.
In this way, multiple breaches can be added.
When you have added a new area, in the Configuration Wizard, choose for the option: Select Existing Breach Areas based on attributes.
Here you can link the attributes in your data that represent the attribute needed for the calculation. If some attributes are not present in the data, just leave it on the default settings.
Importing a breach area
In the Configuration Wizard, choose the option: Import Breach Areas (Start Geo Data Wizard). Read for more information about importing data the Geo data wizard page, the user is.
Result types
The Flooding Overlay is a grid overlay showing results of a dike breach/heavy rainfall on the surface (flooding), sub-surface (groundwater), open water and sewer system. For the produced results, see the result types.
Visualization
In the Configuration Wizard in step 5 and 6, several visualization methods can be chosen. In step 5 the results types (overlays) are chosen. After these are chosen the result types can be found in the left panel.
Flooding Model
2D Saint Venant equations
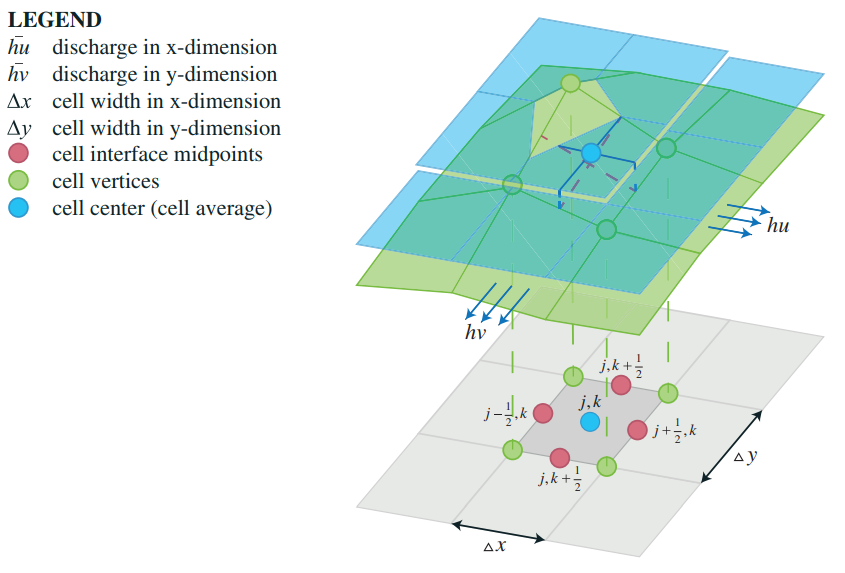
The 2D Saint Venant equations describe the conservation of mass in a gridcell and the conservation of momentum in both x and y, direction:
File:Inundation overlay 01.PNG
The Saint Venant equations describe the following processes:
- friction
- bed slope
- water pressure
- convection (changes in bathemetry over space)
- inertia (increase or decrease of velocity over time)
Numerical scheme
The explicit second-order semi-discrete central-upwind scheme for the 2D Saint Venant Equations is implemented. A reconstruction of cell bottom, water level and velocity at the interfaces between computational cells as proposed by Lax and Wendroff (Rezzolla, 2011). The Tygron Platform Inundation module relies on the scheme described in Kurganov and Petrova (2007). The reconstruction method is taken from Bolderman et all (2014) and ensures numerical stability at the wetting and drying front of a flood wave.
A clear explanation on the numerical approach can be found at Horváth et al. (2014), but in general it follows these steps:
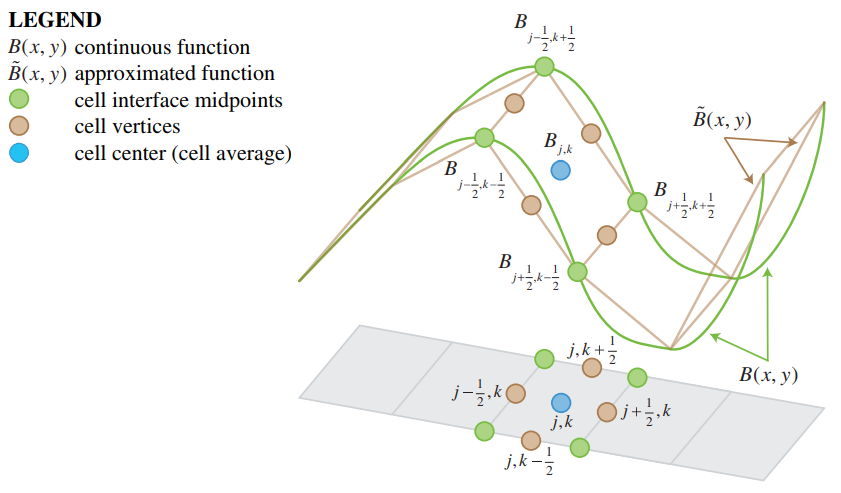
- The elevation value of the cell (B in figures below) is equal to the elevation value at the center of the cell. At the same time, it is equal to the average value of the elevation values at the cell interface midpoints
- The slopes of the conserved variables (U in figures below), continuity and momentum in x and y direction, are reconstructed
- Values of conserved variables at the cell interface midpoints are compared with the left-sided and right sided values at cell centres
- At partially dry cells, the slope is modified to both avoid negative depths and numerical instability
- (Numerical) fluxes are computed at each cell interface to determine the values of the conserved variable at the cell centres for the next time-step
Source: Horváth et al. (2014)
The numerical scheme as been tested on the benchmark of the UK Environmental Agency (EA, 2013) and the Dutch STOWA (STOWA, 2017)
Computation time step
An adaptive timestep is implemented according to Kurganov and Petrova (2007). At every timestep, the courant-number is kept smaller than 0.25 for every active computation cell:
Especially at low depths, choosing the appropriate timestep is critical to avoid numerical instability. Therefore the following principles are used to determine the right time step:
- the timestep is choosen so that all computation cells follow one of the following criteria
- if a cells waterdepth is below the flooding threshold, 5 * 10&sup-3; (m) there is no flow assumed between that cell and it neigboring cell
- if the cells waterdepth is above above the flooding threshold, the maximum timestep is assumed to be 100 * the waterdepth at the cell
- if the waterdepth increases, the timestep is assumed to be not larger than the formula above
If he numerical flux decreases, the larger timesteps are allowed than set by Kurganov and Petrova, depending on the calculation preference set in the general tab of the inundation overlay (speed, average or accuracy).
References
- Bollermann A, Chen G, Kurganov A and Noelle S (2014) ∙ A Well-Balanced Reconstruction For Wetting/Drying Fronts ∙ found at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269417532_A_Well-balanced_Reconstruction_for_Wetting_Drying_Fronts (last visited 2018-06-29)
- Environmetal Agency (2013). Benchmarking the latest generation of 2D hydraulic modelling packages ∙ report Report – SC120002 ∙ found at: https://consult.environment-agency.gov.uk/engagement/bostonbarriertwao/results/appendix-6---neelz--s.---pender--g.--2013--benchmarking-the-latest-generation-of-2d-hydraulic-modelling-packages.-bristol_environment-agency.pdf (last visited 2018-08-03)
- Kurganov A, Petrova G (2007) ∙ A Second-Order Well-Balanced Positivy Preserving Central-Upwind Scheme for the Saint-Venant System ∙ found at: http://www.math.tamu.edu/~gpetrova/KPSV.pdf (last visited 2018-06-29)
- Rezzolla L (2011) ∙ Numerical Methods for the Solution of Partial Differential Equations ∙ found at: http://www.scirp.org/(S(lz5mqp453edsnp55rrgjct55))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1886006 (last visited 2018-06-29)
- STOWA (2017) ∙ Benchmark Inundatiemodellen, Modelfunctionaliteiten en testbankberekeningen ∙ found at: https://ruimtelijkeadaptatie.nl/publish/pages/129612/benchmark_inundatiemodellen_stowa_2017.pdf (last visited 2018-08-13)
- Zsolt Horváth, Jürgen Waser, Rui A. P. Perdigão, Artem Konev and Günter Blöschl (2014) ∙ A two-dimensional numerical scheme of dry/wet fronts for the Saint-Venant system of shallow water equations ∙ found at: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.700.7977&rep=rep1&type=pdf ∙ http://visdom.at/media/pdf/publications/Poster.pdf ∙ (last visited 2018-06-29)