Geo Data
What is GEO Data
Geo data is Geographical information linking data with a location component. In this case, the information is documented in digital maps and databases. Specifically GIS-data is used because of the function to attach attributes and/or objects that are assigned to a specific location. This GIS-data contains geometric characteristics where area (not points and/or lines) information is stored in vectors. Additional information about the requirements to use Geo data in the Tygron Engine can be found on the GeoJSON page.
How does GEO Data relate to the Tygron Engine?
The Tygron Engine automatically connects relevant Geo Databases for The Netherlands to generate the 3D World. When a selection is made on the map in the wizard, the 3D World is generated based on the available GEO Data in the connected databases. For all the different environmental elements the database with the most complete and relevant Geo data is requested. All together this forms the 3D World. For this process the following general principle applies: if your 3D World lacks certain information, it is not available in the database (as all available spatial information is automatically present in the 3D World). To add missing Geo data you can either update the information in the database and regenerate the 3D world, or you can add additional Geo data manually. More information about manually adding data is provided on the GeoJSON page and the page about ArcGis.
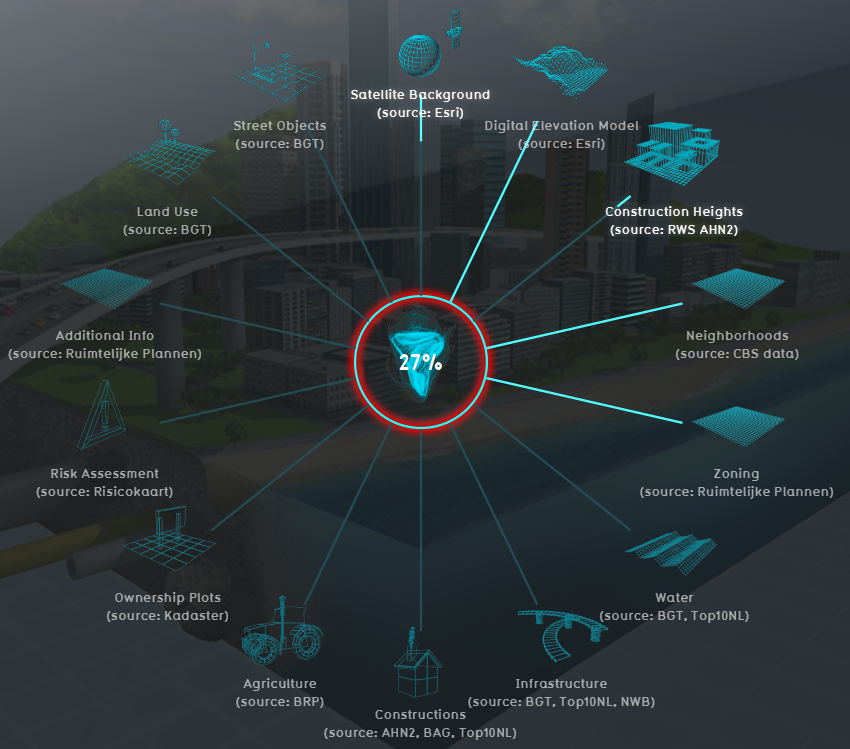
Which GEO Databases are used?
The following table contains the automatically connected data sources that are used when selecting a location in The Netherlands. When selecting a location outside The Netherlands some Geo Data has to be provided manually. Nevertheless, the overview below can give the user a good example of the type of data that can be added to a Tygron project. At the bottom of the table an integrated data source connection is mentioned. More information about his option is explained in the next topic about when to use your own Geo data.
| Name | File Type | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BGT | GML-File | PDOK | Basisregistratie Grootschalige Topografie: Contains information regarding street objects. For instance roads, parks, trees, water surfaces, etc. (specifically for the Netherlands). |
| BAG | OGC-service | PDOK | Basisregistraties Adressen en Gebouwen: Contains building information. For instance building contours, building type definitions, construction year, etc. (specifically for the Netherlands). |
| Aerial View | ESRI service | ESRI / CycloMedia | Satellite/aerial photos used to define the basic texture of landscapes and rooftop colors. |
| DEM | ESRI service | ESRI | Digital Elevation Model: the terrain height (excluding buildings). |
| AHN 2/3 | ESRI service | ESRI | Actueel Hoogte bestand Nederland: Contains detailed elevation information (specifically for the Netherlands). |
| Neighborhoods | OGC service | PDOK / CBS | Area information: Used to determine relevant communities/municipalities and neighborhoods and their specific characteristics. |
| Zoning information | GML service | Ruimtelijke Plannen | Land-use/Zoning plans: Containins information about authorized dimensions and -functions of buildings. Also contains additional feature attributes such as Monumental status. |
| Top10NL | OGC service | Tygron / PDOK | Contains geographical information from the Netherlands. Used for location where BGT information is not available. |
| NWB | OGC service | PDOK | Nationaal Wegen Bestand: Contains detailed information about the road infrastructure of the Netherlands. For instance number of lanes and road type. Also contains a road ID used in conjunction with INWEVA (see below). |
| INWEVA | Excel | Rijkswaterstaat | Inschatting Wegvakintensiteit: Contains general traffic information for all major roads in the Netherlands Information on all major roads in The Netherlands (information is based on a traffic model which is yearly updated). |
| BRP | OGC service | PDOK | Basis Registratie Percelen: Used to determine information about agricultural land use (specifically for the Netherlands). |
| Cadastral map | OGC service | PDOK | Information about land ownership (specifically for the Netherlands). |
| CycloMedia | CycloMedia | CycloMedia | Detailed building information about locations of windows, floors, wall color of buildings. |
| Risk map | GML service | Risicokaart.nl | Information on hazardous- and / or nuisance buildings (for example LPG station). Also contains additional information on vulnerable buildings (hotels, pension, etc.). |
| Natura 2000 | OGC service | PDOK | Information about areas that are designated as a Natura2000 location (an EU wide project linking nature areas to one network). |
| Build in possibility to add additional GEO Data from the Tygron Engine | |||
| ArcGIS Online maps | ESRI service | ESRI | Ability to add additional ArcGIS Online maps if desired. |
| Manual possibility to add additional GEO Data to the Tygron Engine | |||
| ArcGIS Online maps | ESRI service/ ESRI JSON | ESRI | Ability to add additional ArcGIS Online maps if desired. |
| OGC-service | GeoJSON | Open Geo Consortium | Make use of PDOK services. |
| GML-service | CityGML (simple) | i.a. Risicokaart.nl | Make use of data via web-services. |
| GML-files | CityGML (simple) | i.a. BGT | Make use of downloadable data. |
| Excel | Microsoft XLSX | personal | Use custom excel sheets to link data to geographical objects. |
| Cyclomedia | Cyclomedia service | Cyclomedia | For example information about textures of walls and rooftypes. |
When to use your own GEO Data?
When a project takes place outside The Netherlands only ESRI data is (automatically) used to configure a 3D world. Besides landtype (i.e. water of land) and elevation, this does not contain any information about constructions and/or environmental characteristics. Therefore it is advised to make use of additional GEO data to complement your 3D world instead of creating the 3D world from scratch. Adding additional data can be done in different ways. First of all you can add GeoJSON files. In use case 3 an example is given of the Geo Data needed to built up a 3D environment. It is also possible to implement your own additional Geo data by using the inter-grade function of ArcGis. For this function you need to have an ArcGis account or make use of available open data.