Water Overlay: Difference between revisions
m (→Sewer overflow) |
m (→Sewer overflow) |
||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
|SEWER_OVERFLOW | |SEWER_OVERFLOW | ||
|mNAP | |mNAP | ||
|The height of the | |The height of the bottom of the sewer, relative to the average terrain height of the connected sewer. Starting from this height, the water level in the sewer must exceed the height of the terrain at the location of the overflow in order for water to flow out. | ||
|n/a | |n/a | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 8 January 2019
What are the Water Overlays
With the Water Overlays the following overlays are meant:
Each of these overlays have some common configuration steps which will be described on this page.
Tips on creating a new project when working with the Water Overlays
When creating a new project in the new project wizard, take into account the Advanced options. In this menu for example the AHN3 dataset can be selected, which, if available for your project area, provides the most recent heightdata available as Open Data. Also, the IMWA dataset is already checked, this means that if available in your project area, Water Level areas and/or Culverts are already imported.
Configuration Wizard
Each of the Water Overlays has a configuration wizard which helps the user with configuring the overlay.
The Configuration Wizard can be found in the General tab of the overlay.

For the Flooding Overlay the wizard has an extra step, the Rainfall and Groundwater Overlay wizard are basically the same.
The settings in the wizard can always be changed after finishing the wizard by opening the wizard again and changing a value and recalculating the overlay.
Step 1
In the first step the simulation time is set, based on either a rainfall or without a rainfall. Also the evaporation reference factor (over time) can be set.
Step 2
In the second step the elements of the water system can be imported. In some sub-steps the there are four options: to do nothing and proceed, to import the data with the Geo data wizard, or when you already have the data imported to select it based on an attribute of the data or to let the Tygron Platform automatically generate some data.
The following elements can be imported:
- the breach areas (only for the Flooding overlay)
- water level areas; when automatically generating data one water level area covering the whole project area is created. The water level can be adjusted afterwards.
- ground water data
- sewer areas; can also be automatically generated based on the urbanization of the project area
- inundated areas; these are areas that are already inundated at the start of the flooding
- constructions; for the constructions keep in mind that when the data is point data, it has to overlap two water level areas. Therefore make sure the point data is on the border of two water level areas
- Weirs
- Culverts
- Pumps
- Sewer overflows; if chosen to automatically generate the sewer areas, the sewer overflows can also be automatically generated
Step 3
Adjust, if needed, the hydrological coefficents used for the calculations for the surface terrain, the underground terrain and the function values (for example the amount of water storage for a certain type of building).
Step 4
The water system can be made visable with panels and a network visualization.
Step 5
In step 5 you have to choose the result types (the different results which can be exported) you want to see after the calculation is done. Some overlays require a threshold value. Read below for the different result types to choose from and the threshold values. One of the overlays can be selected as the first overlay, which then will be visible as the parent Overlay. You can always adjust the result types you want to see later and calculate the Overlay again.
Also you can set the number of timeframes in the slider. The timeframes are the intermediate results of the calculation and are not the same as the timesteps. Each timeframe contains numerous timesteps, based on the grid cell size and the speed of the flooding (see for more information the Courant number). The more timeframes you choose, the more insight you will get into the calculation. Each of the timeframe results can be exported.
Step 6
In the last step, some additional result types can be chosen to be visualized. Thes overlays contain input data that is used for the calculation, for example the manning value.
Hydrological constructions
The water system can be enhanced with a number of hydrological constructions. These are constructions which effect water flow in specific cells, according to the parameters and rules of the constructions used. Constructions can be either line-based or point-based.
Line-based constructions form a direct connection between two exact cells, allowing water to flow from one point to another. The flow is dictated by the construction's formula. The endpoints of a line-based construction, the exact cells which are connected by the construction, are computed based on the orientation and size of their polygon. Essentially, the furthest ends of the polygon are used as end-points. Because the cells are considered adjacent, flow through line-based hydrological constructions is instantaneous.
Point-based constructions add or remove water in one or more computational layers, based on their formula's. The centerpoint of a point-based construction, the exact cell where the effect takes place, is is the geometric center of the construction's polygon.
Culvert
Culverts are effectively tunnels or pipes directly connecting two bodies of water, and allow water to flow in either direction. Culverts can also be used to model tunnels on land, creating a hole which water can flow through when it is flowing over land. The throughput of a culvert is limited by its dimensions.
A culvert is a line-based construction.
| Attribute | Unit | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| CULVERT_WIDTH | m | The diameter of the culvert. For throughput calculations, the culvert is assumed to have a spherical cross-section. | 1 |
| CULVERT_HEIGHT | mNAP | The height of the culvert. (When set to a level lower than the terrain for either endpoint of it, the culvert's height is equal to the height of the (highest) terrain under either endpoint.) | 0 |
| CULVERT_N | manning value | The manning value of the culvert's material, which influences the flow speed. | 0,014 |
Weir
Weirs are effectively small dams in the water, and allow water to flow from a water body with a higher water level to a lower water level. Any water exceeding the height of the weir can flow over it, increasing the throughput as the water level increases. Strictly, water can flow over the weir in either direction.
A weir is a line-based construction.
| Attribute | Unit | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| WEIR_HEIGHT | mNAP | The height of the weir. | n/a |
| WEIR_WIDTH | m | The width of the weir. | 5 |
| WEIR_COEFFICIENT | coefficient | The flow coefficient related to the shape of the weir | 1,1 |
Pump
Pumps are constructions which can move water against its natural flow. Specifically, it moves water from the lower end of the pump to the higher end of the pump. The terrain height is used to determine the low end and the high end of the pump.
A pump is a line-based construction.
| Attribute | Unit | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUMP_SPEED | m3/s | The speed at which water is pumped from the lower water level to the higher water level. | n/a |
If a pump is placed such that both ends are at equal height, the pump will be inactive and no water will flow through it.
Sewer overflow
Sewer overflows are points where water is moved from the sewer area to the above-ground water system. A sewer overflow will allow water to flow through if the water in the sewer exceeds the SEWER_OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD, and the water in the connected sewer exceeds the height of the terrain at the location of the sewer overflow.
A sewer overflow is a point-based construction, and must intersect with a sewer area.
| Attribute | Unit | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEWER_OVERFLOW | mNAP | The height of the bottom of the sewer, relative to the average terrain height of the connected sewer. Starting from this height, the water level in the sewer must exceed the height of the terrain at the location of the overflow in order for water to flow out. | n/a |
| SEWER_OVERFLOW_SPEED | m3/s | The speed at which water is pumped from the lower water level to the higher water level. | 10 |
Result types
Each Water Overlay is a grid overlay showing results on the surface (flooding), sub-surface (groundwater), open water and sewer system. The following results are produced:
| Result type | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BASE_TYPES | nominal value | Division of gridcells in water, land, water level areas, sewer areas that are connected to the sewer, breach areas and hydrological constructions |
| CHLORIDE | Description will be added when available | |
| DIRECTION | Degrees | The direction of the flooding |
| EVAPORATED | m (mm)¹ | The amount of water that is evaporated |
| GPU OVERVIEW | nominal value | Shows which GPU cluster calculated which part of the overlay |
| IMPACTED_BUILDINGS | nominal value | Constructions impacted by flood: the value from the function value indicator is assigned to a building if the water depth at a grid-cell surrounding the building exceeds the overlay attribute value IMPACT_FLOOD_TRESHOLD_M |
| LAST SPEED | m/s | The speed of the flooding at the last calculated timestep |
| MAX SPEED | m/s | The maximum speed of the flooding of all the calculated timesteps |
| NITROGEN | Description will be added when available | |
| PHOSPHORUS | Description will be added when available | |
| SEWER_LAST_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The amount of water in the sewer storage at the last calculated timestep |
| SEWER_MAX_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The maximum amount of water in the sewer storage of all the calculated timesteps |
| SURFACE_DURATION | s (min)¹ | The amount of time the water depth in a cell exceeds the value set in the overlay attribute value SHOW_DURATION_FLOOD_LEVEL_M |
| SURFACE_FLOW | m3/m2 | Total volume of water passed a grid-cell, scaled by the cell surface (grid cell-size^2) |
| SURFACE_LAST_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The water depth at the last calculated timestep |
| SURFACE_MAX_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The maximum water depth of all the calculated timesteps |
| UNDERGROUND_FLOW | m³/m² | Total infiltration amount from the surface to groundwater |
| UNDERGROUND_LAST_STORAGE | Description will be added when available | |
| UNDERGROUND_LAST_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The amount by which the groundwater table has risen above the initial groundwater level at the last calculated timestep |
| UNDERGROUND_MAX_STORAGE | Description will be added when available | |
| UNDERGROUND_MAX_VALUE | m (mm)¹ | The maximum amount by which the groundwater table has risen above the initial groundwater of all the calculated timesteps |
| UNDERGROUND WATERTABLE | Description will be added when available | |
| WATER_STRESS | m (mm)¹ | The maximum water depth of all the calculated timesteps (almost the same as the SURFACE_MAX_VALUE, but if the terrain type is water only a water depth is shown if the depth exceeds the overlay attribute value ALLOWED_WATER_INCREASE_M) |
¹ the units between () are as displayed in the 3D client. If exported to GeoTiff the SI-convention is used: meters (m) and seconds (s).
General Tab
The General Tab can be found at the panel on the right side, when selecting a Water Overlay. In this tab several settings can be adjusted.
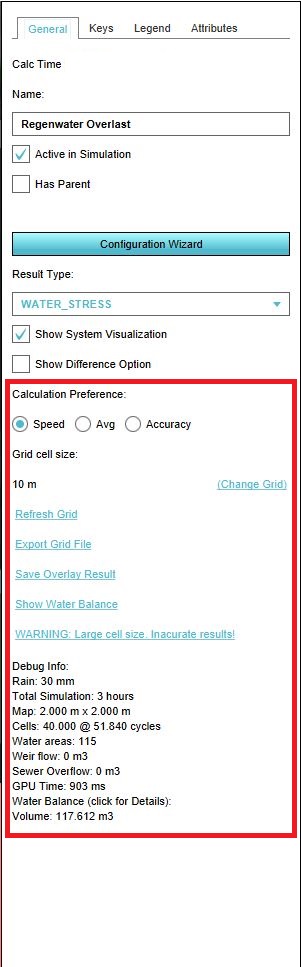
Calculation Preference
Here you can manipulate the computation time step by choosing between the option SPEED, AVERAGE and ACCURACY. The computational timesteps will be set according to the Courant criterion:
Δt = Δx /umax
where:
- Δt = computational timestep
- Δx = grid cell size
- umax = max velocity, assumed 2.5 (SPEED), 5 (AVERAGE) and 10 (ACCURACY) m3/s respectively
Grid cell size
The Tygron Platform computes flow equations over a rectangular cartesian grid, the grid cell size can be set by clicking on Change Grid. After the grid cell size is changed, the Overlay is immediately being recalculated. Note: if you choose a smaller grid cell size, both the amount of time steps (see Calculation Preference) and amount of computational cells increase.
Refresh Grid
By Refreshing the grid, the Overlay is recalculated. This may take some time, depending on the grid cell size, the size of your project and the calcualtion preference. Below some use cases when to use Refresh Grid:
- when you have changed a setting in the Configuration Wizard, but not clicked on the Finish button of the wizard.
- when you change the Result type or calculcation preference in the General tab
- when you change the legend in the Legend tab
- when you change the keys in the Keys tab
- when you change the attrbutes of the Overlay in the Attributes tab
Export Grid File
You can export the current result type as either a GeoTiff (binary file/bitmap image can be opened in a GIS or in an image viewer) or ASCII (text file, can also be opened in a GIS but is also readable in a text editor) file. Also, it is possible to export the difference result type of the current and maquette situation.
Save Overlay result
With this option you can create a duplicate inactive copy of the current overlay. This is noticeable in the Overlays panel on the left side of the screen. The duplicated overlay will have (inactive copy) behind the overlay name and is greyed out. This copy is not being recalculated when changing settings in the original duplicated overlay. When checking the checkbox: active in simulation, the copy becomes active again and can be recalculated. Also the overlay name is again in black and not grayed out anymore.
Show Water Balance
The Water Balance panel shows the in- and outflow of water in m3. The Water Balance panel is also visible when clicking on the Debug info (see below). The water balance is made up of the following components (depending on what is in the project):
- Land surface: amount of water on the land surface after simulation (m3)
- Water surface: amount of water stored on water cells after simulation (m3)
- Building storage: amount of water stored in building storage (m3)
- Sewer storage: amount of water stored in sewers after simulation (m3)
- Underground storage: amount of water stored in the sub-soil after simulation (m3)
- Evaporated: amount of water evaporated after simulation (m3)
- Outlet: amount of water extracted from the model during the simulation via outlets of water areas or sewer pumps (m3).
Warnings
When the grid cell size is too large in combination with the project size, a warning pops up. This means that calculated results are not accurate. The solution to this is to reduce the grid cell size.
Debug Info
The debug info contains the following information:
- Rain: the amount of rainfall (mm) in the duration of the rainfall event (hours)
- Total Simulation: the simulation period (hours)
- Cells: The dimensions of the simulation: the amount of computational cells and the amount of time steps (cycles)
- Water areas:
- Weir flow: the amount of water flown over weirs during simulation (m3)
- Sewer overflow: the amount of water flown over sewer overflows during simulation (m3)
- GPU time: the computation time on GPU (seconds)
- Volume: total volume of the in- and outflow of water in the model.
If you click on the Debug Info the Water Balance panel pops up.
Keys tab
The tab Keys refers to the settings for the water system (areas and constructions) that are adjusted by following the configuration wizard in the General tab. It is therefore generally not needed to change the keys in this tab, as most of the keys are adjusted via the configuration wizard. However, below an explanation of the Keys for areas and buildings.
| Attribute | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Water Level | m + datum | initial water level, relative to datum, for all water cells in a water area |
| Outlet | m3/s | water abstraction for all water cells in a water area |
| Outlet level | m + datum | initial water level, relative to datum, for all water cells in an outlet area (breach for example) |
| Outlet capacity | m3 | maximum amount of water that can be used for the outlet |
| Sewer Storage | m | available storage in sewers at the start of simulation in a sewer area |
| Sewer Pump Speed | m3/s | sewer water abstraction for all cells in a sewer area |
| Breach Floor | mNAP | Modified terrain height, to simulate a breach in a levee. |
| Inundation level | mNAP | Initial water height, to simulate water present at the start of the simulation. |
Keys referring to constructions (building attributes)
| Attribute | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Weir Height | m + datum | weir crest level |
| Weir Output | m3/s | The amount of water that flows through a weir/culvert |
| Weir Coefficient | linear weir coefficient for accounting discharge & contraction losses | |
| Culvert Speed | m3/s | the discharge capacity of a culvert |
| Pump Speed | m3/s | the capacity of a pump |
| Sewer Overflow Height | m + datum | the height of a crest of a sewer overflow |
| Sewer Overflow Speed | m3/s | the discharge capacity of a sewer overflow |
| Chloride | x/m2 | Amount* of chloride which is created per second, per m² of construction with this attribute. |
| Nitrogen | x/m2 | Amount* of nitrogen which is created per second, per m² of construction with this attribute. |
| Phosphorus | x/m2 | Amount* of phosphorus which is created per second, per m² of construction with this attribute. |
* The unit of the substances is left incomplete, as the project creator is free to set their own unit for quantities of substances.
Attributes tab
This tab shows the attributes of result types that can be adjusted. These attributes can also be adjusted in the configuration wizard in step 5 in the General tab. It is therefore generally not needed to change the attributes here. However, below an overview of the Overlay Attributes.
| Attribute | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ALLOWED_WATER_INCREASE_M | m | increment by which the water level on a water cell is allowed to increase before the depth is shown in the WATER_STRESS result type |
| AVG_SURFACE_WATER | Description wil be added | |
| DESIGN_FLOOD_ELEVATION_M | m | Constructions in the 3D world are assumed to have at most this height compared to the surface of the terrain. Greater values can create a more accurate model but will impact performance. |
| GROUND_BOTTOM_DISTANCE_M | m | Assumed distance under the terrain surface where the soil becomes impenetrable for water. The groundwater level cannot go below this depth, relative to the surface. The maximum amount of water that can be stored underground is equal to this attribute multiplied by the local terrain's WATER_STORAGE_PERCENTAGE. |
| GROUND_WATER | Description wil be added | |
| IMPACT_FLOOD_THRESHOLD_M | m | maximum waterdepth on a cell which touches the building where after the building is assumed impacted, visualized in the IMPACTED_BUILDINGS result type |
| MAX_SPEED_MS | Maximum speed at which water is allowed to flow. As the maximum speed is set higher, the time per step of the calculation is reduced, increasing total time for the calculation to complete. | |
| MIN_SLOPE | slope whereunder the pressure slope is assumed 0 | |
| SEWER_OVERFLOW_THRESHOLD | fraction of storage whereafter sewer overflows take place | |
| SHOW_DURATION_FLOOD_LEVEL_M | m | threshold value of the amount of water on a grid cell that is used for the SURFACE_DURATION result type |
| SUPERGRID | This marks an experimental feature which is currently under development and may result in unexpected behavior when activated. | |
| SURFACE_WATER_EVAPORATION_FACTOR | Description wil be added | |
| TIMEFRAMES | the number of intermediate (overlay) results you would like to see of the calculation. A timeframe is not the same as a timestep. A timeframe is an intermediate (overlay) result and can contain already a number of timesteps. The number of timesteps is based on the grid cell size and the speed of the flooding (see for more information the Courant number). |