Traffic NO2 formula (Traffic NO2 Overlay): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
The emission numbers (E) for both NOx and NO2 are computed as: | The emission numbers (E) for both NOx and NO2 are computed as: | ||
<math> | <math>E_{drive} = (1.0 - j_c) \cdot n_c \cdot E_{c,d} + (1.0 - j_v) \cdot n_v \cdot E_v + (1.0 - j_t) \cdot n_t \cdot E_t + (1.0 - j_b ) \cdot n_b \cdot E_b</math> | ||
<math>E_{jam} = (j_c) \cdot n_c \cdot E_{c,j} + j_v \cdot n_v \cdot E_{v,j} + j_t \cdot n_t \cdot E_{t,j} + j_b \cdot b_t \cdot E_{b,j}</math> | |||
<math>E = (E_{drive} + E_{jam} ) \cdot \frac{1000}{(24 \cdot 3600)}</math> | |||
where: | where: | ||
: <math>E</math> = Calculated emission of either NOx or NO2 | |||
: <math>E_{drive}</math> = Calculated emission of driving traffic of either NOx or NO2. | |||
: <math>E_{jam}</math> = Calculated emission of jammed traffic of either NOx or NO2. | |||
: <math>E_{c,d} </math> = Calculated emission of driving cars, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{v,d} </math> = Calculated emission of driving vans, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{t,d} </math> = Calculated emission of driving trucks, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{b,d} </math> = Calculated emission of driving buses, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{c,j} </math> = Calculated emission of jammed cars, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{v,j} </math> = Calculated emission of jammed vans, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{t,j} </math> = Calculated emission of jammed trucks, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>E_{b,j} </math> = Calculated emission of jammed buses, hourly or daily. | |||
: <math>n_c</math> = number of car traffic, hourly or daily value. | |||
: <math>n_v</math> = number of van traffic, hourly or daily value. | |||
: <math>n_t</math> = number of truck traffic, hourly or daily value. | |||
: <math>n_b</math> = number of bus traffic, hourly or daily value. | |||
: <math>j_c</math> = fraction of car traffic in traffic jams. | |||
: <math>j_v</math> = fraction of van traffic in traffic jams. | |||
: <math>j_t</math> = fraction of truck traffic in traffic jams. | |||
: <math>j_b</math> = fraction of bus traffic in traffic jams. | |||
* N = traffic intensity [units per day] | * N = traffic intensity [units per day] | ||
* fm = fraction vans [-] | * fm = fraction vans [-] | ||
Revision as of 09:39, 2 March 2022
The calculations follow the standard rekenmethode 1 (SRM 1).
where:
- = annual average concentration [μg/m3],
- = annual average background-concentration (default = 0 [μg/m3], can be adjusted via the overlay attributes),
- = annual average traffic contribution to NO2 concentration [μg/m3].
Contribution NO2
To compute the annual average traffic contribution to NO2, [μg/m3], the following formula from SRM1 is applied:
where:
- = annual average traffic contribution to NOx concentration [μg/m3],
- = annual average concentration ozon [μg/m3] (default = 42),
- = weighted fraction direct emitted NO2 [-],
- = parameter (default 0.6),
- = parameter for conversion NO to NO2 (default = 100 μg/m3).
Contribution NOX
To compute the annual average traffic contribution to NOX, Cb,jm[NOX] [μg/m3], the following formula from SRM1 is applied:
where:
- = calibration factor [-] (default = 0.62]
- = emission number NOx [μg/m/s]
- = dilution factor [-]
- = tree factor (default = 1)
- = 5/windspeed. Default value for windspeed is 5 m/s
The computation of the dilution factor, , is split into two situations.
For surrounding cells within a distance of 30m:
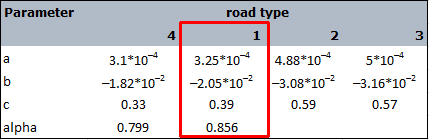
And for cells within a distance of 30-60m (for road-type 1 only):
where:
- = the calculation distance
- = configurable using model attribute: ROAD1_30M_A
- = configurable using model attribute: ROAD1_30M_B
- = configurable using model attribute: ROAD1_30M_C
- = configurable using model attribute: ROAD1_60M_ALPHA
- = configurable using model attribute: ROAD1_60M_POWER
The weighted fraction of direct emitted NO2 [-] is computed as:
where:
- = emission number NOs [μg/m/s]
Tree Factor
The tree factor is calculated as followed:
where:
- = Tree factor, value between 1 and 1.5,
- = Amount of tree cells within the search distance,
- = Search area measured in amount of cells,
- = Search distance of trees, currently set on 30 meters,
- = Grid cell area in square meters.
Emission numbers
The emission numbers (E) for both NOx and NO2 are computed as:
where:
- = Calculated emission of either NOx or NO2
- = Calculated emission of driving traffic of either NOx or NO2.
- = Calculated emission of jammed traffic of either NOx or NO2.
- = Calculated emission of driving cars, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of driving vans, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of driving trucks, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of driving buses, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of jammed cars, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of jammed vans, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of jammed trucks, hourly or daily.
- = Calculated emission of jammed buses, hourly or daily.
- = number of car traffic, hourly or daily value.
- = number of van traffic, hourly or daily value.
- = number of truck traffic, hourly or daily value.
- = number of bus traffic, hourly or daily value.
- = fraction of car traffic in traffic jams.
- = fraction of van traffic in traffic jams.
- = fraction of truck traffic in traffic jams.
- = fraction of bus traffic in traffic jams.
- N = traffic intensity [units per day]
- fm = fraction vans [-]
- fz = fraction trucks [-]
- fb = fraction buses [-]
- El = emission value cars [g/km]
- Em = emission value vans [g/km]
- Ez = emission value trucks [g/km]
- Eb = emission value buses [g/km]
- FS = fraction congested traffic [-]
- E*,d = emission factor per class (cars, vans, trucks or buses) if congested
Notes
- If the traffic amount is defined as a single value, that value is used for all defined hours. However, if the amount if an array of values, each of the 24 indexes of that array are assumed to correspond to the hour denoted by those indexes, and as such that specific value from the array is used.
- The SRM1[1] calculation method is only applicable for urban environments.
See also
References
- ↑ SRM1 ∙ Regeling beoordeling luchtkwaliteit 2007, Bijlage I ∙ Found at: http://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0022817/2013-01-01#Bijlage1 ∙ (last visited: 16-02-2022)