Heat Reduction (Indicator): Difference between revisions
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
A number of attributes need to be added to the project. The attributes that need to be manually added are HEAT_GREEN and ROOF_GREEN. These attributes can be added in the Function Values table by writing the name of the attribute in the attribute field and selecting the ‘Add’ button. The value of the newly added attributes can be adjusted for each function separately according to the needs of the project. This can be done by choosing a function, finding the HEAT_GREEN or ROOF_GREEN attribute in the list of attributes of that function and entering a new value in the attribute field. | A number of attributes need to be added to the project. The attributes that need to be manually added are HEAT_GREEN and ROOF_GREEN. These attributes can be added in the Function Values table by writing the name of the attribute in the attribute field and selecting the ‘Add’ button. The value of the newly added attributes can be adjusted for each function separately according to the needs of the project. This can be done by choosing a function, finding the HEAT_GREEN or ROOF_GREEN attribute in the list of attributes of that function and entering a new value in the attribute field. | ||
{{Editor steps|title=| | {{Editor steps|title=| At the bottom of the function values window, enter the desired attribute name in the "Attributes" input field. Select "Add" to add the attribute to all functions.|If any function has a value for the new attribute which is not 0, set it to 0.|Set the attribute value of all functions which should affect this indicator to their desired values.}} | ||
===Add the Global=== | ===Add the Global=== | ||
Revision as of 08:25, 16 July 2019
General
What is the Heat Reduction indicator?
The Heat Reduction indicator on the Tygron platform is an indicator that computes the effect that urban green has on the heat reduction. The presence of green reduces the heat stress in the specified project area and cools down the surrounding environment. The more urban green space is present in the area, the stronger the heat reduction in that area will be. The indicator is a simplified version of a RIVM calculation model. This indicator is useful for projects where for example:
- reducing heat stress is an important goal in the project
- livability is measured in the project
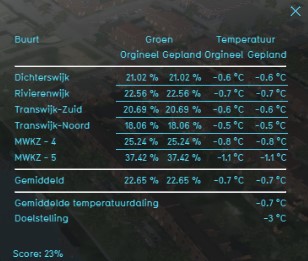
Indicator panel
The indicator panel shows per neighborhood:
- The name of the neighborhood
- The percentage of urban green space in that neighborhood in the current situation
- The percentage of urban green space in that neighborhood in the future (planned) situation
- The temperature in that neighborhood in the current situation
- The temperature in that neighborhood in the future (planned) situation
- The average heat reduction in the entire project area
- The goal temperature
Calculation
The calculations used in this indicator are based on the RIVM calculations on urban green and health effects[1].
𝑻𝒆𝒎𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒆 = 𝑨𝒗𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒈𝒆𝑻𝒆𝒎𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒆 × 𝑵𝒆𝒊𝒈𝒉𝒃𝒐𝒓𝒉𝒐𝒐𝒅𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂
𝑨𝒗𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒈𝒆𝑻𝒆𝒎𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒆 = (𝑮𝒓𝒆𝒆𝒏𝑷𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒈𝒆× 𝟏𝟎𝟎) / 𝑯𝑬𝑨𝑻_𝑹𝑬𝑫𝑼𝑪𝑻𝑰𝑶𝑵
𝑮𝒓𝒆𝒆𝒏𝑷𝒆𝒓𝒄𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒈𝒆 = 𝑮𝒓𝒆𝒆𝒏𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂 / 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂
𝑮𝒓𝒆𝒆𝒏𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂 = 𝑪𝒖𝒓𝒓𝒆𝒏𝒕𝑮𝒓𝒆𝒆𝒏𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂 × 𝑽𝒂𝒍𝒊𝒅𝑵𝒆𝒊𝒈𝒉𝒃𝒐𝒓𝒉𝒐𝒐𝒅
Where the variables are:
- Temperature: is the calculated temperature for the entire project area
- AverageTemperature: is the average temperature in the selected neighborhood
- NeighborhoodArea: is the size (m^2) of the selected neighborhood
- GreenPercentage: is the urban green percentage of a neighborhood
- HEAT_REDUCTION: is a global variable that indicates the percentage of heat reduction that urban green space has in the selected neighborhood
- GreenArea: is the green effect in the core area
- TotalArea: is the size of the entire area (m^2) specified in the project
- CurrentGreenArea: is the size of the urban green area (m^2) in the neighborhood
- ValidNeighborhood: is a value that indicates if the neighborhood is a valid neighborhood
Score
The score is based on the present urban green spaces in the specified project area. The effect that these urban green spaces have on the heat reduction is visible as the score of the indicator. For each neighborhood the percentage of urban green space in that neighborhood and the temperature in that neighborhood is determined and an average of all results is taken to calculate the final score of the indicator.
Additional configurations
Add the Attribute
A number of attributes need to be added to the project. The attributes that need to be manually added are HEAT_GREEN and ROOF_GREEN. These attributes can be added in the Function Values table by writing the name of the attribute in the attribute field and selecting the ‘Add’ button. The value of the newly added attributes can be adjusted for each function separately according to the needs of the project. This can be done by choosing a function, finding the HEAT_GREEN or ROOF_GREEN attribute in the list of attributes of that function and entering a new value in the attribute field.
- At the bottom of the function values window, enter the desired attribute name in the "Attributes" input field. Select "Add" to add the attribute to all functions.
- If any function has a value for the new attribute which is not 0, set it to 0.
- Set the attribute value of all functions which should affect this indicator to their desired values.
Add the Global
The following global variable needs to be added to the project manually:
- Global: HEAT_REDUCTION: This global variable indicates the heat reduction per urban green space percentage in a specified area. The recommended value for this variable is 0.1.
Note that this is only an example of the values that can be entered for each of the global variables. These values can be modified and changed according to the needs of the project.
- Click on the add button in the bottom left corner. A new global named VARIABLE will be added to the left panel.
- Select the global VARIABLE.
- In the right panel, change VARIABLE to the name of the new global HEAT_REDUCTION.
- Change the start value to 0.1.
- Click on the tab Indicators and the button Indicators and choose for Reset to Start values (faster) to update your project.
References
- ↑ Remme, R. (RIVM), De Nijs, T. (RIVM), & Paulin, M. (RIVM). (2017)