I3S: Difference between revisions
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
File:Feature_to_feature_class.jpg|Conversion tool | File:Feature_to_feature_class.jpg|Conversion tool | ||
File:Input_features_multipatch.jpg|Input feature | File:Input_features_multipatch.jpg|Input feature | ||
File:Output_location.jpg|Output Feature Class | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 21 November 2019
What is SLPK?
The I3S (Indexed 3D Scene Layer Specification) originates from Esri. The specification was adopted as a Community Standard by the OGC (Open Geospatial Consortium) in 2017. The I3S specification is for streaming and packaging large heterogenous 3D Geo data. An I3S dataset is also called a Scene Layer. With a Scene Layer Package (SLPK) file, one I3S layer, containing all the data can be exchanged.
How to create a SLPK?
In this documentation we will look on how to export a SLPK file with ArcGIS Pro. To learn more about ArcGIS Pro visit ESRI's ArcGis Pro Documentation. In order to export a 3D model as a SLPK, it has to be imported into ArcGIS Pro and Georeferenced to place the model on the right location. ArcGIS Pro allows for the following file formats to be imported:
- DWG (Drawing) Used in CAD software. Can be exported from most 3D animation packages.
- OBJ (Wavefront object) Used in most 3D animation packages like Autodesk 3dsmax and Maya.
- DAE (Collada) Used in most 3D animation packages like Autodesk 3dsmax and Maya.
- 3DS (3D studio) Used as an exported file from Autodesk 3dsmax.
- FLT (OpenFlight) Used in MultiGen Creator.
- WRL (Virtual Reality Modeling Language File) A VRML file format for representing 3D vector graphics.
There are differences in how a DWG file is added to your ArcGIS Pro project from other 3D file formats. Both will be explained below.
1. Creating a new ArcGIS Pro project
To add a 3D model like CAD or OBJ you should first create a new project in ArcGIS Pro. When starting a new project make sure that you select a local Scene from the Blank Templates section. You can convert a local scene to a global scene after you have imported your model(s).
2.a Adding a DWG file
If you are working with CAD data follow this procedure to import a DWG file:
- In ArcGis go to the "Map" tab and select "Add Data"
- Choose the DWG file
- Select Multipatch
2.b Importing other 3D file formats
To import other 3D files like OBJ, DAE, 3DS, FLT or WRL follow this procedure:
-
Step 1
-
Step 2
-
Step 3a
-
Step 3b
-
Step 4
-
Step 5
-
Step 6
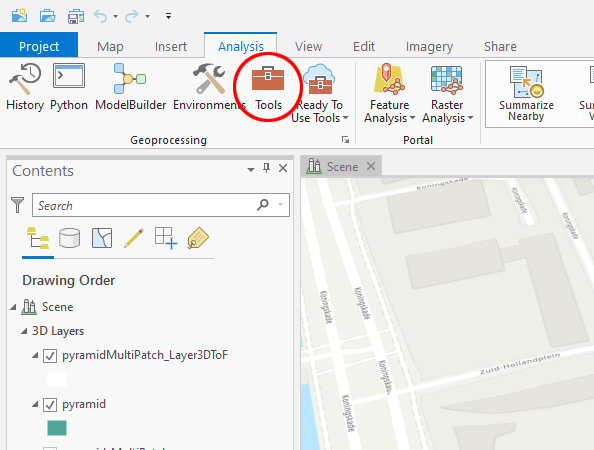
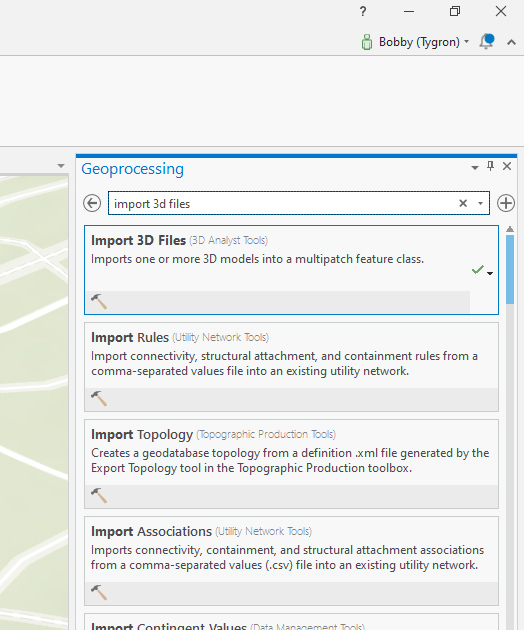
- In ArcGis go to the "Analysis" Tab and select "Tools".
- On the right pane select the "Import 3D Files" tool or type it in the search bar to find it.
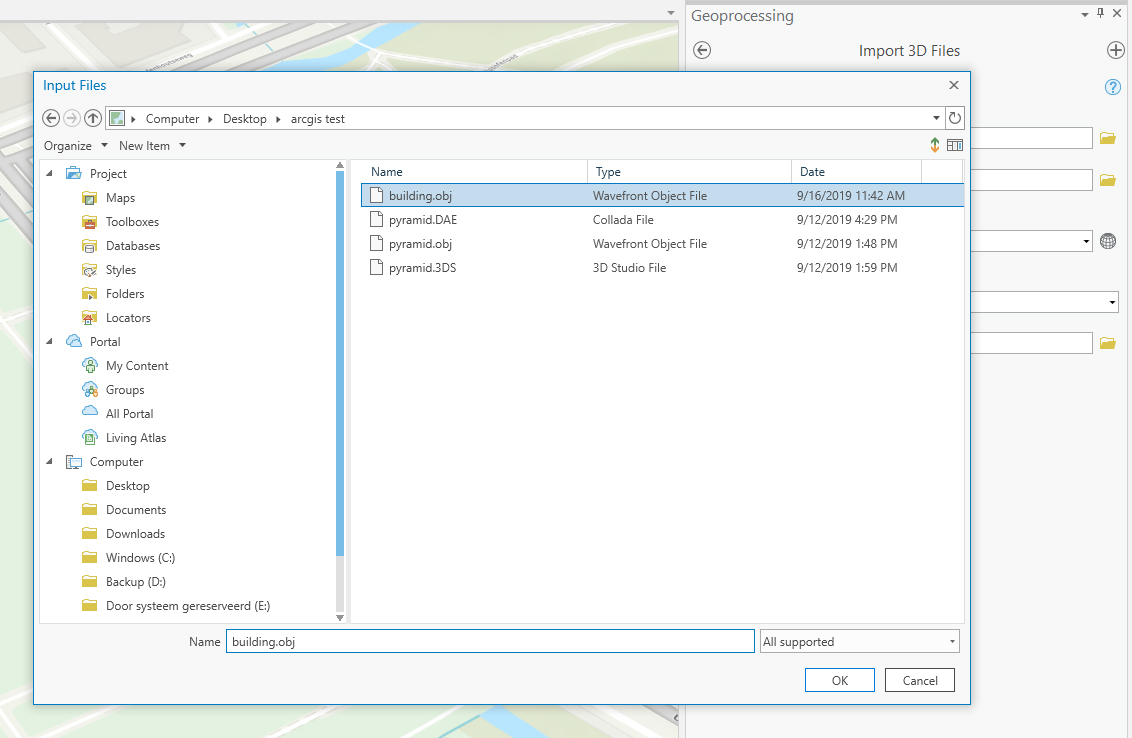
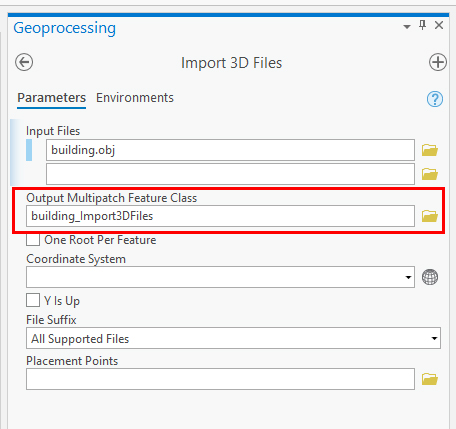
- In the "Input files" field click on the folder icon next to the field and browse to the 3D file you want to import
- A name will be automatically generated in the "Output Multipatch Feature Class" field.
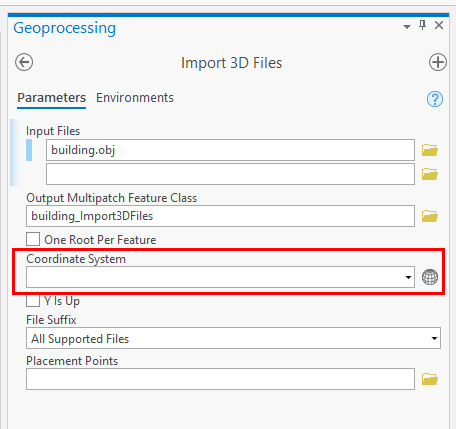
- Select a Coordinate system from the dropdown menu or select an other system by clicking on the grid sphere icon next to the field.
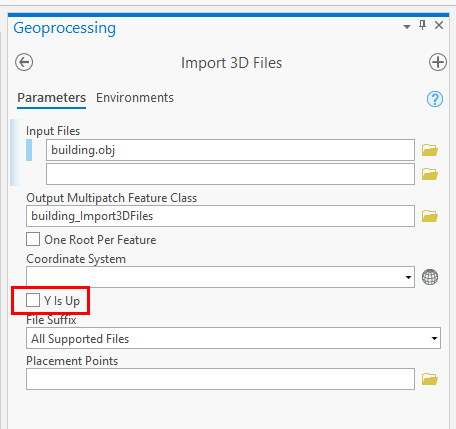
- Select "Y is Up" only if your 3d model was exported from a package wich uses Z is up.
- Click on "Run" at the lower right of the pane.
- After it is finished ArcGis will have created a Multipatch feature which can be located on the Contents Pane on the left. Note that your original 3D imported file is also present, but we will be using the multipatch for further conversion to SLPK.
3.Georeference your imported model
Imported models, if they are created in a software program without a CRS (Coordinate Reference System), are imported and probably not placed on the right location. Therefore, the model has to be moved to the right location on the map. Note that imported DWG 3d models are georeferenced in a different way than other 3d formats like obj or other 3d formats. Therefore there are 2 ways to georeference your models depending on if they are a DWG or another file format. See the steps below appropriate to your workflow.
-
Select Building
-
CAD Layer tab
-
Choose coordinate system
-
Positioning tools.
- In ArcGIS Pro, select your 3D object (Multipatch version) from the Contents pane by right-clicking on the imported multipatch feature, choosing "selection" and clicking on "select all". (If model is not visisble in the viewport choose "zoom to selection" from the same selection menu)
- Go to the "CAD Layer" Manage tab. (This tab will only appear if the imported model is a DWG file) The DWG management tools section will appear.
- Click on the "Define Projection" tool and select a coordinate system from the library (click on the globe next to the field)or choose the default one. (This can be done from the right tools pane)
- Click on "Run" in the lower right of the pane.
- Select the "Georeference" tool.
- Choose the "move", "scale" or "rotate" tool and drag, rotate and scale the 3D model along one or all of the axes to move it on the map to the desired location.
- Use the "Elevate To Ground" tool so that the model snaps to the ground (Provided that the pivot point or center of the model is at the desired groundlevel base of the model.
- Finally click on "Save To Workspace" (Next to the move, scale and rotate tools) so that the location is saved.
- Close the Georeference toolset, your model is georeferenced for use in your project and ready for export to SLPK.
-
Select Multipatch
-
Georeference 3d model
- In ArcGIS Pro, select your 3D object from the Contents pane or the Viewport.
- Go to the "Edit" tab. The tools section will appear
- Select the "Move" tool and drag the 3D model along one of the axes to move it on the map to the desired location.
- If desired, the model can be rotated and/or scaled with the "Rotate" and "Scale" tools
- Make sure that the model is at the proper height relative to the ground
4. Export the model as a SLPK file
After importing and Georeferencing your model(s) you can export them to a SLPK file by following the steps below, which are divided into three sections. Please follow them in order.
-
Conversion tool
-
Input feature
-
Output Feature Class
- In ArcGIS Pro go to the "Analysis" Tab and select "Tools".
- On the right pane navigate to the "Feature Class to Feature Class" tool or type it in the search bar to find it.
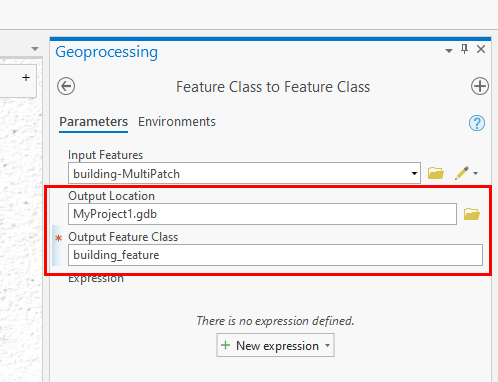
- In the "Input Features" field select the Multipatch feature of the imported object by clicking on the dropdown in the field to select it. Make sure it is the Multipatch version and not the original object
- The Output location will be a .gdb (database file) with the project as a name. Leave the default name as is or rename it if you prefer.
- In the "Output Feature Class" field type in a name.
- This will save the Multipatch to the database.
- Click on "Run" at the bottom right of the pane.
- Go to the "Analysis" Tab and select "Tools" again.
- On the right pane navigate to the "Layer 3D to Feature Class" tool or type it in the search bar to find it.
- In the "Input Feature Layer" field select the multipatch feature like before.
- An automatic name will be generated in the "Output Feature Class" field. Usually it will append a "_Layer3DToF1" tag after the Multipatch name. Leave as default or rename it if you want. Make sure that you can identify the name because we will be needing it in the final step.
- Check "Disable Color and Texture" only if you do not want these features to be converted.
- Click on "Run" at the bottom right of the pane.
- Finally go to the "Analysis" Tab and select "Tools" again.
- On the right pane navigate to the "Create 3D Object Scene Layer Package" tool or type it in the search bar to find it.
- In the "Input Dataset" field select the created Layer3d file from the previous steps.
- In the "Output Scene Layer Package" field type in the name for the SLPK file wich will be created and choose the location for the file to be saved.
- In the "Output Coordinate System" dropdown field select this projects system or select a new one by clicking on the grid sphere icon on the right of the field.
- Optimize the textures for various platform by choosing an option from the "Texture Optimization" dropdown field or leave at the default setting.
- Click on "Run" at the bottom right of the pane.
- Now a SLPK file will be created.
Importing a SLPK into the Tygron Platform
After creating a SLPK file, the data can be imported into the Tygron Platform by making use of the Geo data wizard. Read here for the steps on how to use the wizard.