How to calculate the hourly radiation: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{article end | {{article end | ||
|notes= | |notes= | ||
* The values at each hour regard the measurement over the preceding hour up to that time. To obtain the value for 10:00 UTC, the values at 10:00 UTC and 11:00 UTC must be used. | |||
|seealso= | |seealso= | ||
* [[Hourly radiation (Heat Overlay)]] | * [[Hourly radiation (Heat Overlay)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:26, 5 February 2024
According to the DPRA Heat stress report:
"De globale straling van het KNMI station is een som van het afgelopen uur. Om de hoeveelheid straling op het hele uur te schatten wordt de straling van het komende uur en afgelopen uur gemiddeld."
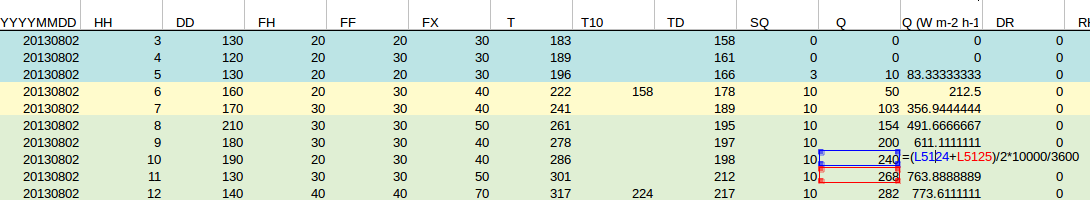
So the global radiation for the hour has to be calculated as the average of the past hour and the next hour. We use the Q column from the KNMI weather data for this. Additionally, the global radiation is in J / cm2 and has to be converted to W / m2 by multiplying:
| Column | Name | Unit | Dutch Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13/L | Q | J/cm2 | Globale straling (in J/cm2) per uurvak; |
Notes
- The values at each hour regard the measurement over the preceding hour up to that time. To obtain the value for 10:00 UTC, the values at 10:00 UTC and 11:00 UTC must be used.